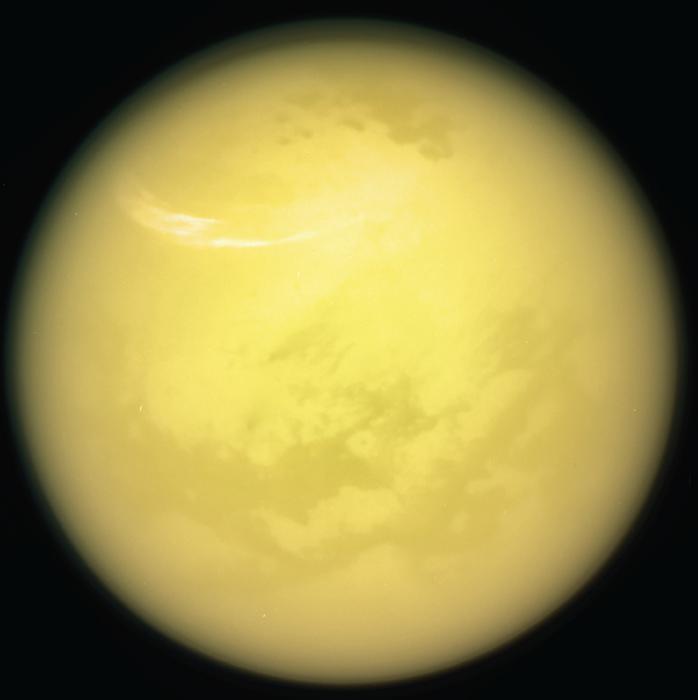
Dr. Lauren Schurmeier: “The methane clathrate crust warms Titan’s interior and causes surprisingly rapid topographic relaxation, which results in crater shallowing at a rate that is close to that of fast-moving warm glaciers on Earth.”
How does Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, have such a methane-rich atmosphere? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how methane that resides with Titan’s crust could be responsible for the lack of depth in Titan’s impact craters, which could explain why Titan’s atmosphere has so much methane, as well. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the formation and evolution of Titan and whether it could host life as we know it.
For the study, the researchers used computer models to simulate the formation and evolution of impact craters on Titan, of which only approximately 90 have been identified via satellite imagery from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft.
“This was very surprising because, based on other moons, we expect to see many more impact craters on the surface and craters that are much deeper than what we observe on Titan,” said Dr. Lauren Schurmeier, who is a research associate in the Hawai‘i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) and lead author of the study. “We realized something unique to Titan must be making them become shallower and disappear relatively quickly.”