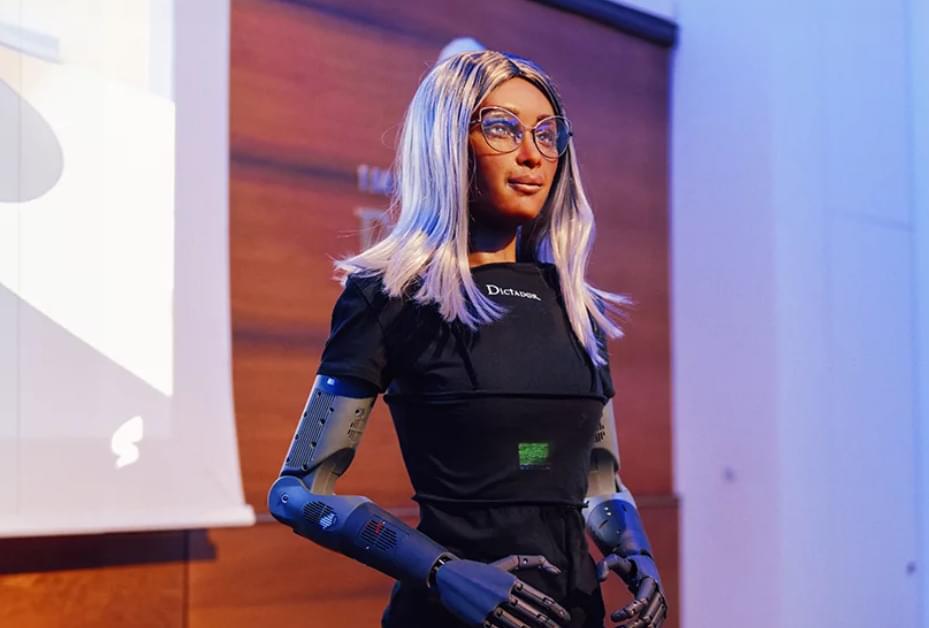
CNBC’s Andrea Day joins Shep Smith to report on ‘robot nurses’ meant to give a hand to live nurses, who suffered under very difficult conditions during the pandemic. For access to live and exclusive video from CNBC subscribe to CNBC PRO: https://cnb.cx/2NGeIvi.
» Subscribe to CNBC TV: https://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBCtelevision.
» Subscribe to CNBC: https://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBC
Turn to CNBC TV for the latest stock market news and analysis. From market futures to live price updates CNBC is the leader in business news worldwide.
The News with Shepard Smith is CNBC’s daily news podcast providing deep, non-partisan coverage and perspective on the day’s most important stories. Available to listen by 8:30pm ET / 5:30pm PT daily beginning September 30: https://www.cnbc.com/2020/09/29/the-news-with-shepard-smith-…%7Cpodcast.
Connect with CNBC News Online.
Get the latest news: http://www.cnbc.com/
Follow CNBC on LinkedIn: https://cnb.cx/LinkedInCNBC
Follow CNBC News on Facebook: https://cnb.cx/LikeCNBC
Follow CNBC News on Twitter: https://cnb.cx/FollowCNBC
Follow CNBC News on Instagram: https://cnb.cx/InstagramCNBC