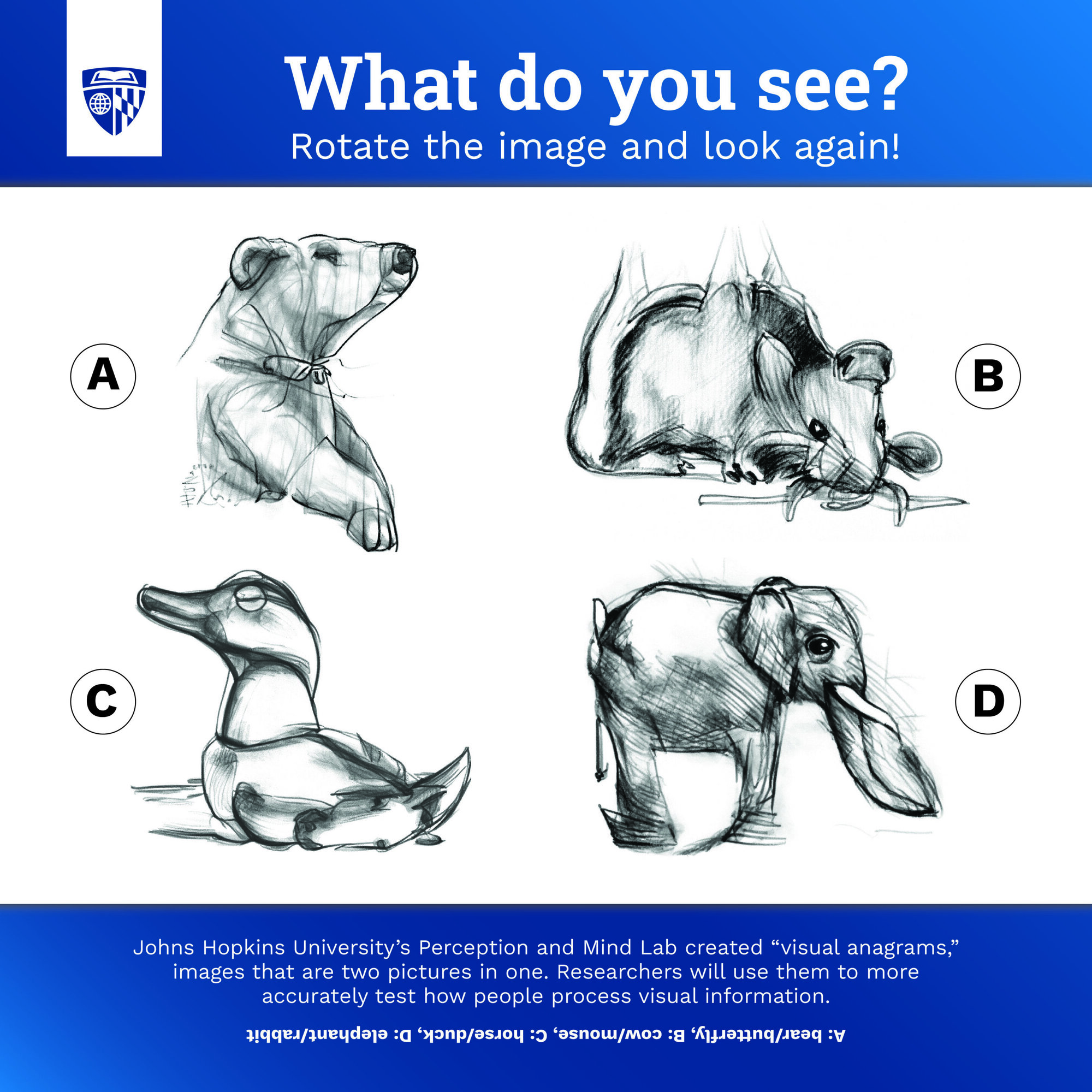
New artificial intelligence-generated images that appear to be one thing, but something else entirely when rotated, are helping scientists test the human mind.
The work by Johns Hopkins University perception researchers addresses a longstanding need for uniform stimuli to rigorously study how people mentally process visual information.
“These images are really important because we can use them to study all sorts of effects that scientists previously thought were nearly impossible to study in isolation—everything from size to animacy to emotion,” said first author Tal Boger, a Ph.D. student studying visual perception.