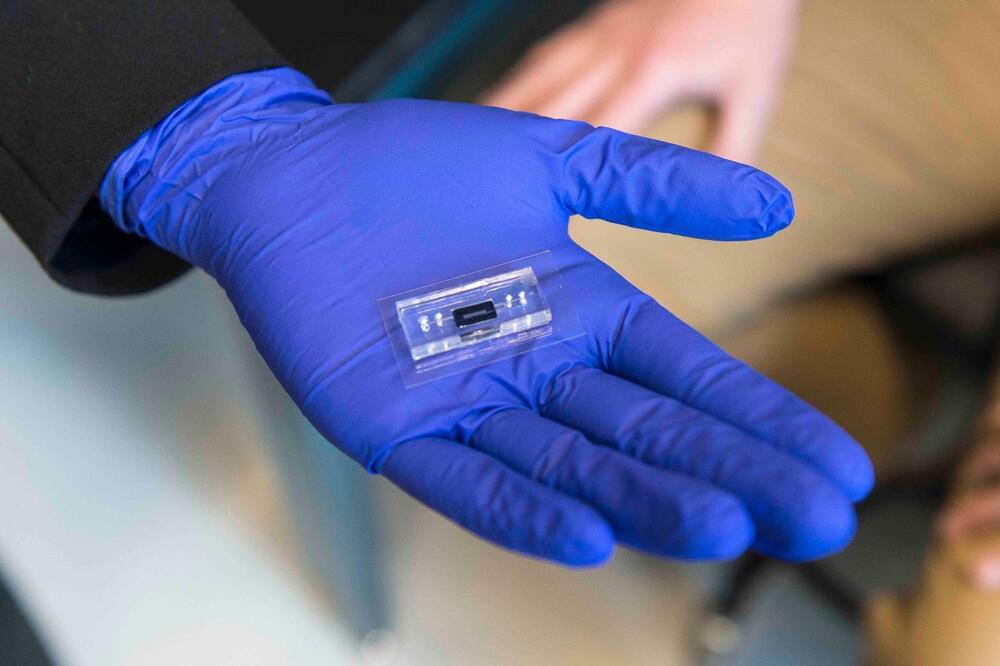
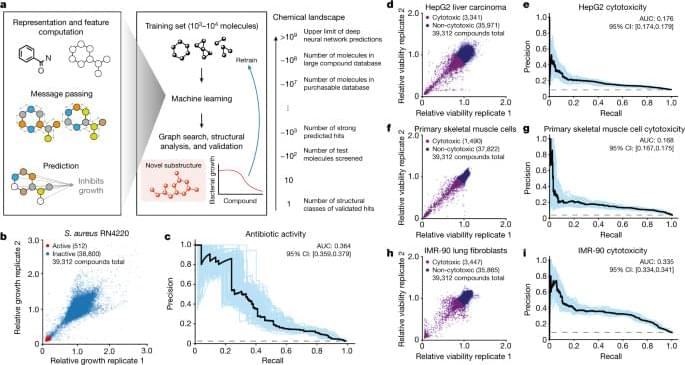
An explainable deep learning model using a chemical substructure-based approach for the exploration of chemical compound libraries identified structural classes of compounds with antibiotic activity and low toxicity.




The automotive industry has experienced rapid advancements due to the integration of edge computing and artificial intelligence (AI) in recent years. As vehicles continue developing self-driving capabilities, these technologies have become increasingly critical for effective decision-making and real-time reactions.
Edge computing processes data and commands locally within a vehicle’s systems, improving road safety and transportation efficiency. Combined with 5G, it enables real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure, reducing latency and allowing autonomous vehicles to respond faster. AI algorithms enable cars to interpret visual data and make human-like driving decisions.
Edge computing and AI are transforming vehicles into true self-driving machines, filling any gaps in low-latency 5G tech and enabling companies to pioneer advanced autonomy.

This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
Some experts claim that there is no current evidence that AI can be controlled safely. And if so, should it even be developed?
AI Safety expert Dr. Roman V. Yampolskiy explains in his book “AI: Unexplainable, Unpredictable, Uncontrollable” that the problem of AI control is one of the most important problems facing humanity, but even so it remains poorly understood, poorly defined, and poorly researched.
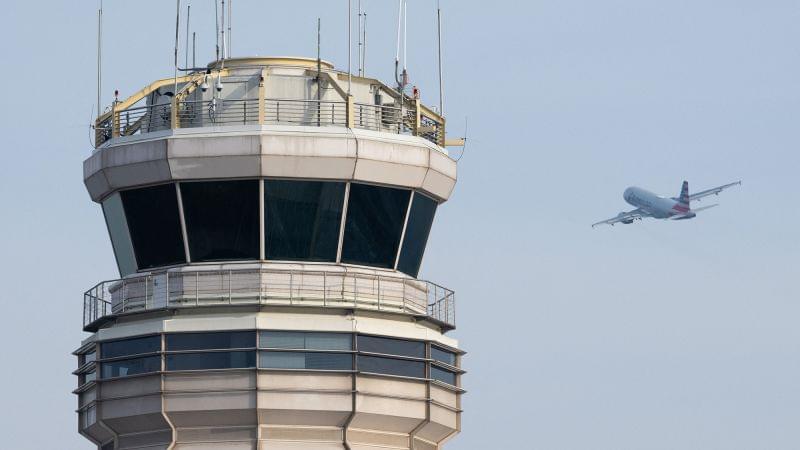

An air traffic controller’s routine can be disrupted by an aircraft that requires special handling. This could range from an emergency to priority handling of medical flights or Air Force One. Controllers are given the responsibility and the flexibility to adapt how they manage their airspace.
The requirements for the front line of air traffic control are a poor match for AI’s capabilities. People expect air traffic to continue to be the safest complex, high-technology system ever. It achieves this standard by adhering to procedures when practical, which is something AI can do, and by adapting and exercising good judgment whenever something unplanned occurs or a new operation is implemented – a notable weakness of today’s AI.
Indeed, it is when conditions are the worst – when controllers figure out how to handle aircraft with severe problems, airport crises or widespread airspace closures due to security concerns or infrastructure failures – that controllers’ contributions to safety are the greatest.
The robot’s quadruped locomotion helps it look for hazards in cramped and cluttered experiment spaces inaccessible to other robots.

Summary: Dr. Roman V. Yampolskiy, an AI Safety expert, warns of the unprecedented risks associated with artificial intelligence in his forthcoming book, AI: Unexplainable, Unpredictable, Uncontrollable. Through an extensive review, Yampolskiy reveals a lack of evidence proving AI can be safely controlled, pointing out the potential for AI to cause existential catastrophes.
He argues that the inherent unpredictability and advanced autonomy of AI systems pose significant challenges to ensuring their safety and alignment with human values. The book emphasizes the urgent need for increased research and development in AI safety measures to mitigate these risks, advocating for a balanced approach that prioritizes human control and understanding.

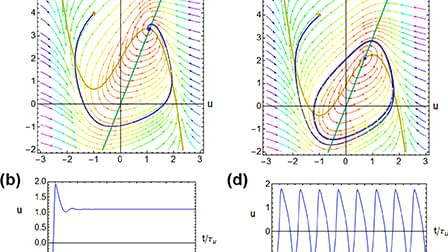
Divice recipe for making spiking artificial neurons.
Neurons, which are made of biological tissue, exhibit cognitive properties that can be replicated in various material substrates. To create brain-inspired computational artificial systems, we can construct microscopic electronic neurons that mimic natural systems. In this paper, we discuss the essential material and device properties needed for a spiking neuron, which can be characterized using impedance spectroscopy and small perturbation equivalent circuit elements. We find that the minimal neuron system requires a capacitor, a chemical inductor, and a negative resistance. These components can be integrated naturally in the physical response of the device, instead of built from separate circuit elements. We identify the structural conditions for smooth oscillations that depend on certain dynamics of a conducting system with internal state variables. These state variables can be of diverse physical nature, such as properties of fluids, electronic solids, or ionic organic materials, implying that functional neurons can be built in various ways. We highlight the importance of detecting the Hopf bifurcation, a critical point in achieving spiking behavior, through spectral features of the impedance. To this end, we provide a systematic method of analysis in terms of the critical characteristic frequencies that can be obtained from impedance methods. Thus, we propose a methodology to quantify the physical and material properties of devices to produce the dynamic properties of neurons necessary for specific sensory-cognitive tasks. By replicating the essential properties of biological neurons in electronic systems, it may be possible to create brain-inspired computational systems with enhanced capabilities in information processing, pattern recognition, and learning. Additionally, understanding the physical and material properties of neurons can contribute to our knowledge of how biological neurons function and interact in complex neural networks. Overall, this paper presents a novel approach toward building brain-inspired artificial systems and provides insight into the important material and device considerations for achieving spiking behavior in electronic neurons.