SoftBank Group Chief Executive Officer Masayoshi Son is looking to raise up to $100 billion for a chip venture that will rival Nvidia Corp, Bloomberg News reported on Friday, citing people with knowledge of the matter.



OpenAI on Thursday announced Sora, a brand new model that generates high-definition videos up to one minute in length from text prompts. Sora, which means “sky” in Japanese, won’t be available to the general public any time soon. Instead, OpenAI is making it available to a small group of academics and researchers who will assess harm and its potential for misuse.
“Sora is able to generate complex scenes with multiple characters, specific types of motion, and accurate details of the subject and background,” the company said on its website. “The model understands not only what the user has asked for in the prompt, but also how those things exist in the physical world.”
One of the videos generated by Sora that OpenAI shared on its website shows a couple walking through a snowy Tokyo city as cherry blossom petals and snowflakes blow around them.

When Lex Friedman visited our MIT AI Venture Studio class to talk about the future of AI, we got into some pretty interesting ideas about the near future.
At the top of Lex’s comments, he talked about disruption – predicting that two new trillion-dollar companies will emerge out of the AI era, and suggesting that Google, Meta and Microsoft will likely not be able to pivot quickly enough to maintain their dominance.
In terms of where we might see this innovation, one of his focus points was on language. Lex pointed out that in America, we take it for granted that everyone speaks English – but around the world, there is an enormous market for real, precise speech translation. People, he said, speak many languages in an “intimate” way – and that requires precision on the part of the technology.


The fourth group is Curium, an Iranian group that has used LLMs to generate phishing emails and code to evade antivirus detection. Chinese state-affiliated hackers have also used LLMs for research, scripting, translations, and refining their tools.
Fight AI with AI
Microsoft and OpenAI say they have not detected any significant attacks using LLMs yet, but they have been shutting down all accounts and assets associated with these groups. “At the same time, we feel this is important research to publish to expose early-stage, incremental moves that we observe well-known threat actors attempting, and share information on how we are blocking and countering them with the defender community,” says Microsoft.
Ultimate fact presents top 15 Weapons Of The Future Will Blow Your Mind. We’ve come a long way since sticks and stones, and it’s almost inconceivable that only a few hundred years ago, Man was still waging war with bows, arrows, cannons, and muskets. Modern militaries are constantly in the process of developing new weapons, some of which will definitely make some mouths drop. We thought it would be fun to take a closer look at the most amazing offensive and defensive weapons currently in the works.
Autonomous weapons.
These are robotic vehicles, under development, that search and destroy enemy troops and equipment on the ground or in the air, without risk to friendly troops – theoretically.
Onboard computers interpret sensor data to identify and target hostile forces with built-in weapons. Robots may query human controllers at remote sites for the go-ahead to fire, and friendly forces may carry transponders that identify them as “friends”
High-energy lasers.
These are powerful energy beams that travel through air or space in straight lines. They travel at the speed of light and can strike over distances of thousands of kilometres. Large mirrors focus powerful laser beams onto a small spot on the target.
Space-based weapons.
Space is the ultimate high ground, so weapons in orbit would have the ability to see and zap anything on the ground, in the air, or nearby in space. The main mission of space-based weapons would be to defend against ballistic missiles fired at targets on Earth.
Hypersonic aircraft.
Launched from a standard runway, a hypersonic aircraft could fly faster than Mach 5 to strike anywhere in the world within two hours. It would also have enough thrust to deliver a satellite to low-Earth orbit. To get off the ground from a runway, a hypersonic plane would either hitch a ride on a conventional plane, or have its own conventional jet engine.
Active Denial System.
Millimetre-wave or microwave beams supposedly make people flee without injuring them. They might typically be powered by a generator fitted to a Humvee, in crowd control situations.
A 2-metre antenna and mobile generator produce and aim a beam of 95-gigahertz (3-millimetre) radiation.
Nuclear missiles.
Nuclear missiles are able to deliver unmatched destructive power anywhere in the world, making them the ultimate level of military power. One or more nuclear warheads are mounted on a ballistic missile, and launched vertically.
Stun guns (Tasers)
Tasers disable people with bursts of high-voltage electricity, allowing police to subdue them without lasting injury. A special gun fires darts on wires. These deliver a pulse of electricity that temporarily disrupts control of voluntary muscles.
E-bombs.
A rapid increase in electromagnetic field strength during a pulse, induces surges of electric current in conductors. This burns out electrical equipment – semiconductor chips are particularly vulnerable.
Layered missile defence.
Layered missile defence offers the best chance to shoot down attacking ballistic missiles.
Multiple anti-missile systems are deployed to target ballistic missiles during different stages of the attacking missile’s flight: Each phase, or layer, of defence increases the chance of successful destruction of the missile.
Information warfare.
This technique interferes with the flow of information vital to enemy operations, while defending friendly channels of communication. Information warfare specifically targets communication networks and computers.
‘Hyper Stealth’ or ‘Quantum Stealth’
Using naturally occurring metamaterials, scientists have been designing lightwave-bending materials that can greatly reduce the thermal and visible signatures of a target.
Electromagnetic Rail Guns.
EM rail gun launchers use a magnetic field rather than chemical propellants (e.g., gunpowder or fuel) to thrust a projectile at long range and at velocities of 4,500 mph to 5,600 mph. nautical miles using 32 megajoules.
The extended velocity and range of EM rail guns provides several benefits both in offensive and defensive terms, from precision strikes that can counter even the most advanced area defense systems to air defense against incoming targets.
Space Weapons.
Despite international pressure against the weaponization of space, major countries continue to explore technologies that would turn the sky above us into the next battleground.
Hypersonic Cruise Missiles and ‘Prompt Global Strike’
Had hypersonic cruise missiles existed in the mid-1990s, the U.S. might have rid itself of Al Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden much earlier than it did, and would have accomplished the feat in Afghanistan rather than in Pakistan.
Sentient’ Unmanned Vehicles.
Perhaps the single-most important development in the defense industry in the past decade is the emergence of unmanned vehicles.
Among this which one seems most terrible to you let us know in the comment section.
#UltimateFact #Weaon #Facts
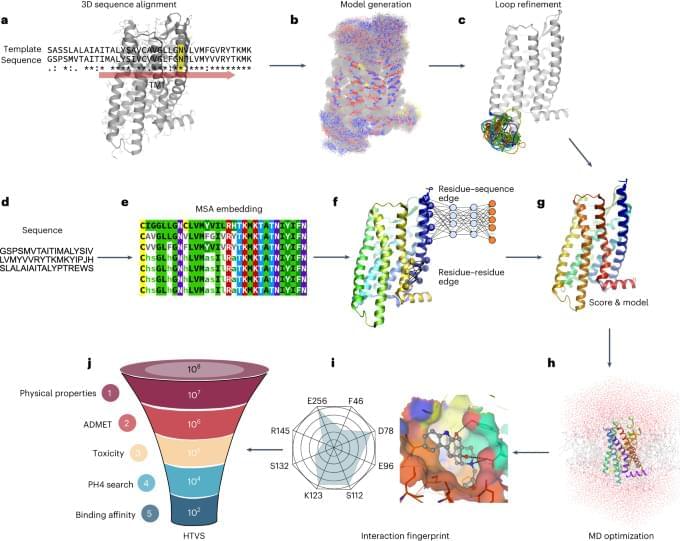

Researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison (UW-Madison) have developed a novel approach for 3D printing functional human brain tissue.
The 3D printing process can create active neural networks in and between tissues that grow in a matter of weeks.
The researchers believe that their 3D bioprinted brain tissue provides an effective tool for modeling brain network activity under physiological and pathological conditions, and can also serve as a platform for drug testing.
An innovative new chip uses light for fast, efficient AI computations, promising a leap in processing speeds and privacy.
Penn Engineers have developed a new chip that uses light waves, rather than electricity, to perform the complex math essential to training AI. The chip has the potential to radically accelerate the processing speed of computers while also reducing their energy consumption.
The silicon-photonic (SiPh) chip’s design is the first to bring together Benjamin Franklin Medal Laureate and H. Nedwill Ramsey Professor Nader Engheta’s pioneering research in manipulating materials at the nanoscale to perform mathematical computations using light — the fastest possible means of communication — with the SiPh platform, which uses silicon, the cheap, abundant element used to mass-produce computer chips.