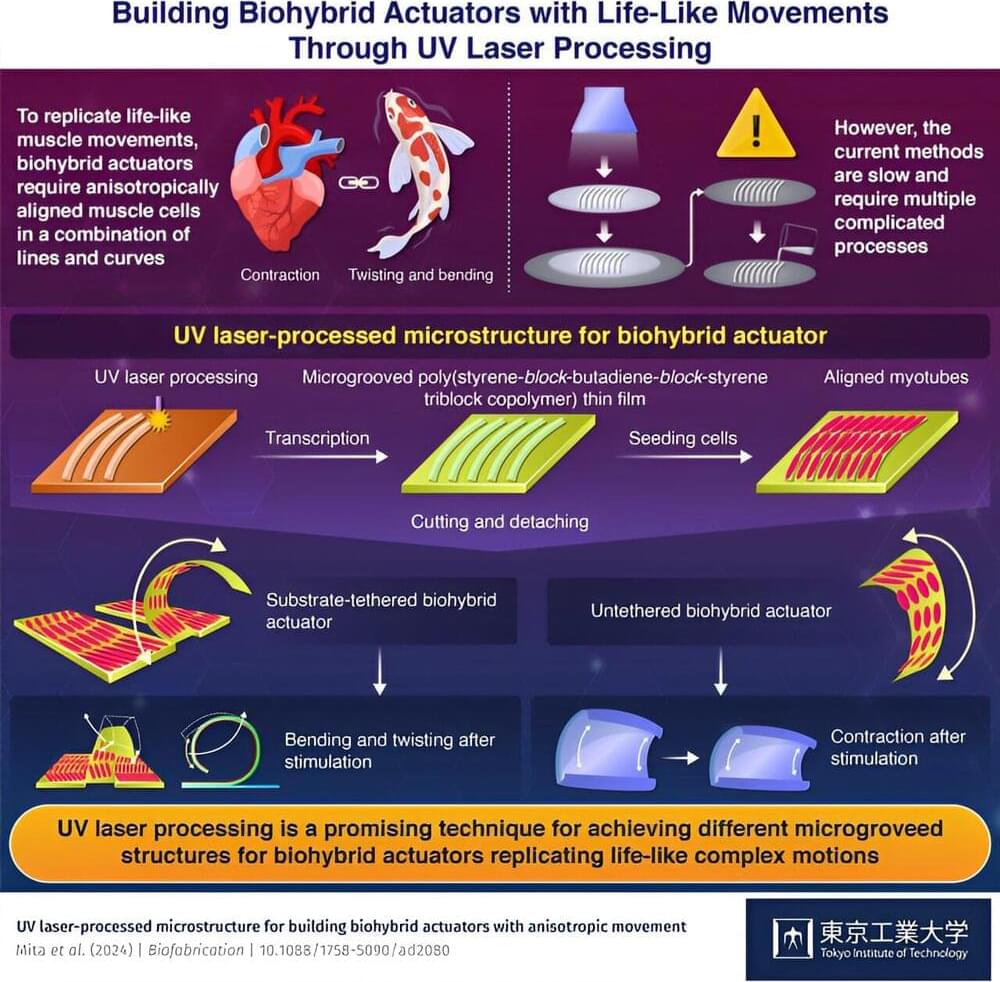
Biomimetic robots, which mimic the movements and biological functions of living organisms, are a fascinating area of research that can not only lead to more efficient robots but also serve as a platform for understanding muscle biology.
Among these, biohybrid actuators, made up of soft materials and muscular cells that can replicate the forces of actual muscles, have the potential to achieve life-like movements and functions, including self-healing, high efficiency, and high power-to-weight ratio, which have been difficult for traditional bulky robots that require heavy energy sources.
One way to achieve these life-like movements is to arrange muscle cells in biohybrid actuators in an anisotropic manner. This involves aligning them in a specific pattern where they are oriented in different directions, like what is found in living organisms.