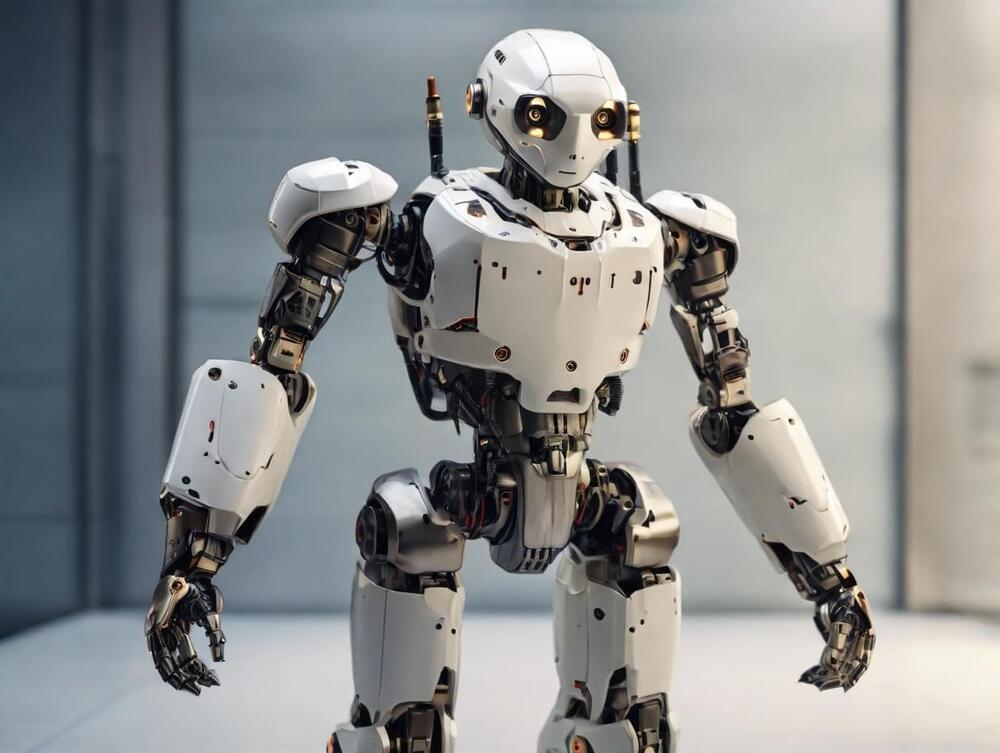
In a groundbreaking study published on the arXiv server, a team of Swiss researchers introduces Pedipulate, an innovative controller enabling quadruped robots to perform complex manipulation tasks using their legs. This development marks a significant leap forward in robotics, showcasing the potential for legged robots in maintenance, home support, and exploration activities beyond traditional inspection roles.
The study, titled “Pedipulate: Quadruped Robot Manipulation Using Legs,” challenges the conventional design of legged robots that often rely on additional robotic arms for manipulation, leading to increased power consumption and mechanical complexity. By observing quadrupedal animals, the researchers hypothesized that employing the robot’s legs for locomotion and manipulation could significantly simplify and reduce the cost of robotic systems, particularly in applications where size and efficiency are crucial, such as in space exploration.
Pedipulate is trained through deep reinforcement learning, employing a neural network policy that tracks foot position targets. This policy minimizes the distance between the robot’s foot and the target point while penalizing undesirable movements such as jerky motions or collisions. The controller was tested on the ANYmal D robot, which features 12 torque-controlled joints and force-torque sensors on each foot, proving the feasibility of leg-based manipulation in real-world scenarios.