Amid an intractable real estate crisis, fake luxury houses offer a delusion of one’s own.



Recent technological advances, such as increasingly sophisticated drones and cameras, have opened exciting new possibilities for cinematography. Most notably, film directors can now shoot scenes from a wide range of angles that were previously inaccessible and in far higher resolution.
Researchers at University of Zaragoza and Stanford University recently developed CineMPC, a new cinematographic system that relies on a fully autonomous drone that carries a cinematographic camera to film multiple targets autonomously, while following a director’s instructions. The platform modulates various drone and camera parameters to satisfy these instructions. The team’s innovative system, outlined in IEEE Transactions on Robotics, could bring a wave of innovation to the film industry and other sectors that can benefit from high-quality video footage.
“Existing solutions for autonomous drone cinematography revealed a common oversight, namely, none provided automatic control over camera intrinsic parameters (i.e., focal length, aperture, focus distance),” Pablo Pueyo Ramon, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.

Connecticut-based WaveAerospace recently unveiled a multi-role unmanned multi-copter in development for the last five years.
Huntress Turbojet’s flight tests will take place in the summer and it is expected to be delivery-ready by early 2025.
The all-weather hybrid-electric drone has a top speed of Mach 0.7 (467 knots) and flight endurance of two hours.

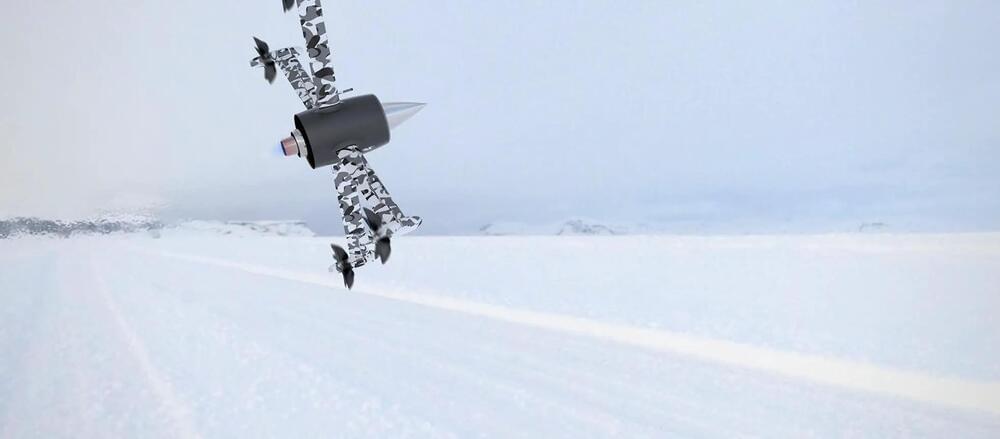
The British Antarctic Survey (BAS) said successful tests would allow the drones to undertake research such as surveying marine ecosystems and studying glaciers, while reducing CO2 emissions by approximately 90%.
The Windracers Ultra UAV (uncrewed aerial vehicle) is a twin-engine, 10-metre aircraft that can carry up to 100kg of cargo or sensors for distances of 1,000km and does not require a human pilot to take off, fly or land as it is equipped with a sophisticated autopilot system.
Unlike piloted Twin Otter aircraft, which are costly to operate and face logistical challenges in the extreme environment, the BAS said the “groundbreaking” unmanned drones are safer and “could enable dramatic increases in flight time”
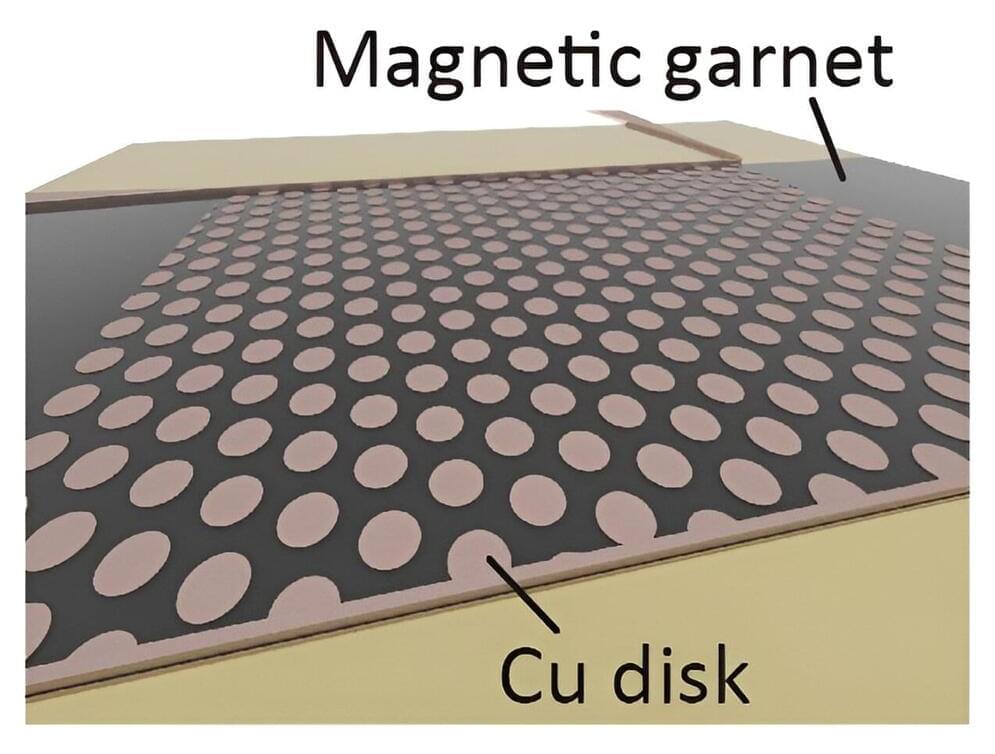
A collaborative group of researchers has potentially developed a means of controlling spin waves by creating a hexagonal pattern of copper disks on a magnetic insulator. The breakthrough is expected to lead to greater efficiency and miniaturization of communication devices in fields such as artificial intelligence and automation technology.
Details of the study were published in the journal Physical Review Applied on January 30, 2024.
In a magnetic material, the spins of electrons are aligned. When these spins undergo coordinated movement, they generate a kind of ripple in the magnetic order, dubbed spin waves. Spin waves generate little heat and offer an abundance of advantages for next-generation devices.
Basic biology textbooks will tell you that all life on Earth is built from four types of molecules: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. And each group is vital for every living organism.
But what if humans could actually show that these “molecules of life,” such as amino acids and DNA bases, can be formed naturally in the right environment? Researchers at the University of Florida are using the HiPerGator—the fastest supercomputer in U.S. higher education—to test this experiment.
HiPerGator—with its AI models and vast capacity for graphics processing units, or GPUs (specialized processors designed to accelerate graphics renderings)—is transforming the molecular research game.
Are you curious about the future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and how it will be impacted by Quantum Computing? Join us on an exciting journey into the world of technology as we explore how Quantum Computing is set to revolutionize AI by the year 2027. In this video, we will delve into the fascinating realm of Quantum Computing and its implications for the future of AI.
Quantum Computing, a cutting-edge field in computer science, harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations at speeds unimaginable with traditional computers. By leveraging the power of quantum bits or qubits, Quantum Computing has the potential to exponentially increase processing power, enabling AI systems to tackle complex problems with unprecedented efficiency and accuracy. Imagine a world where AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in seconds, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations across various industries.
As we look ahead to 2027, experts predict that the synergy between Quantum Computing and AI will reach new heights, transforming the landscape of technology as we know it. With Quantum Computing capabilities integrated into AI systems, we can expect significant advancements in areas such as machine learning, natural language processing, and data analytics. These advancements will not only revolutionize how AI applications function but also pave the way for groundbreaking innovations in fields ranging from healthcare to finance.
Join us as we explore the exciting possibilities that await us at the intersection of Quantum Computing and AI. Together, we will unravel the mysteries of this transformative technology and glimpse into a future where AI is powered by the limitless potential of Quantum Computing. Get ready to embark on a journey into the future of technology, where Quantum Computing will redefine the boundaries of what AI can achieve by the year 2027.

