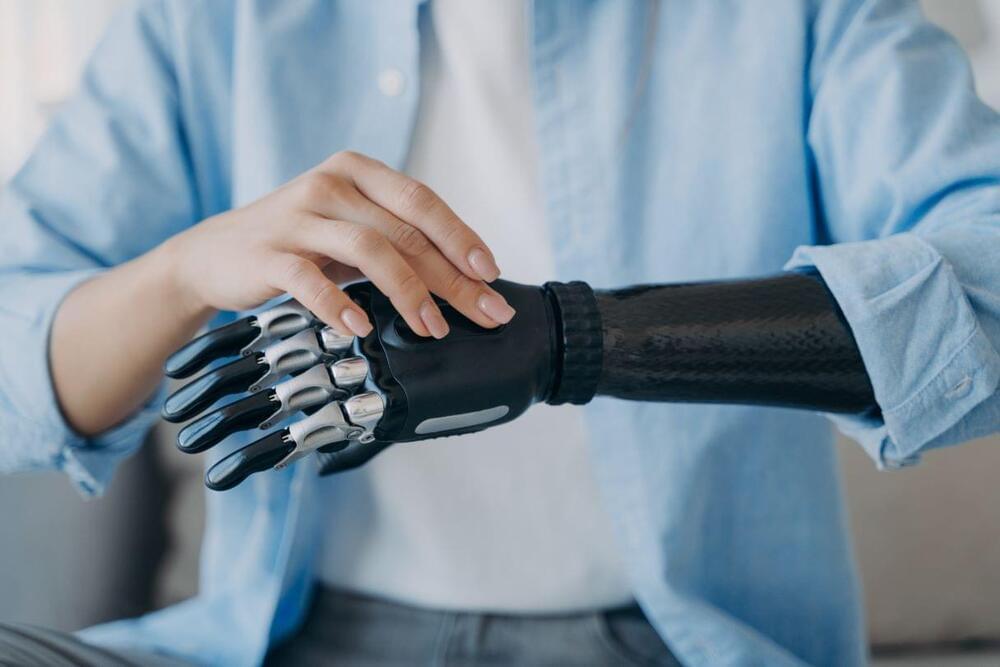
Neuroprosthetics, a technology that allows the brain to control external devices such as robotic limbs, is beginning to emerge as a viable option for patients disabled by amputation or neurological conditions such as stroke.


META, a leading technology company at the forefront of innovation, has unveiled its next-generation custom silicon chip.
Welcome to NewsBreak, an open platform where diverse perspectives converge. Most of our content comes from established publications and journalists, as well as from our extensive network of tens of thousands of creators who contribute to our platform. We empower individuals to share insightful viewpoints through short posts and comments. It’s essential to note our commitment to transparency: our Terms of Use acknowledge that our services may not always be error-free, and our Community Standards emphasize our discretion in enforcing policies. We strive to foster a dynamic environment for free expression and robust discourse through safety guardrails of human and AI moderation. Join us in shaping the news narrative together.

Generative AI is quite impressive and has been the common denominator (in most cases) when tapping into new opportunities and unlocking new heights in the tech landscape. Microsoft has significantly benefited from the technology and is currently ranking as the world’s most valuable company, ahead of Apple with over $3 trillion in market capitalization. Market analysts attribute part of this success to its early investment and adoption of AI across its products and services.
Still, AI encounters its fair share of setbacks coupled with controversies and rumors. Perhaps one of the main challenges facing the technology is the lack of elaborate measures and guardrails to prevent it from spiraling out of control.
While relevant parties continue to try to establish control over the technology, billionaire Elon Musk predicts AI will be more intelligent than humans by the end of 2026 (via Business Insider). Musk shared these sentiments in an interview with Norges Bank CEO Nicolai Tangen on X (formerly Twitter).
The popular TV company’s first original feature is made with Runway ML and Midjourney.

AI has come to the hiring process — and it’s made those mandatory personality tests all the weirder.
As 404 Media reports, companies as disparate as McDonald’s, Olive Garden, and FedEx are now requiring that job applicants take personality evaluations, which are then sorted by an AI system whose operations are cloudy at best.
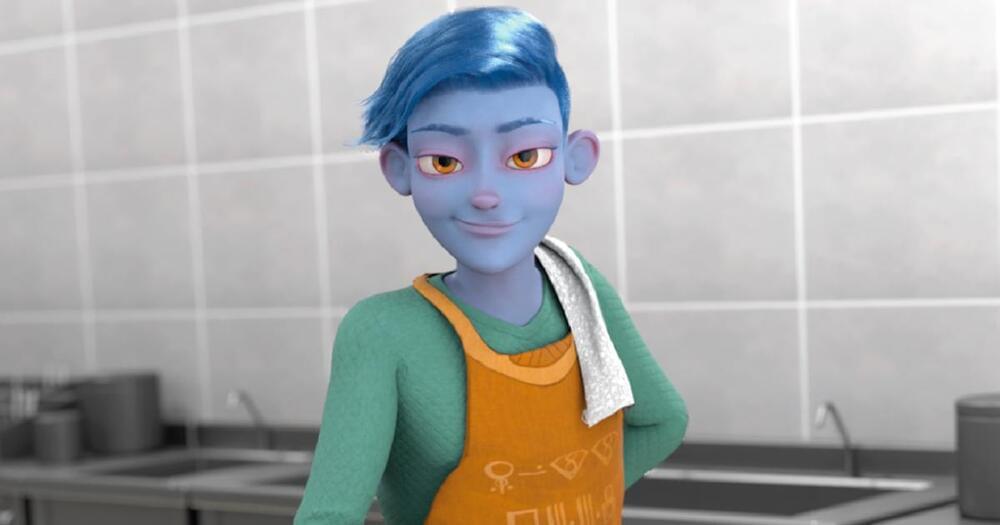
The aforementioned companies are all contracted with Paradox.ai, a “conversational recruiting software” company whose strange personality assessments include images of blue-skinned humanoid aliens that applicants are, apparently, supposed to identify with.
Herbert Ong Brighter with Herbert.

Chinese scientists have unveiled what they are calling the world’s first artificial intelligence (AI) child.
Developed by the Beijing Institute for General Artificial Intelligence (BIGAI), Tong Tong or Little Girl’s virtual AI avatar was recently introduced for the first time in Beijing.
BIGAI sees Tong Tong as a giant step toward achieving a general artificial intelligence (AGI) agent when a machine can think and reason like a human being.

When witnessing the sorry state of men addicted to AI girlfriends, one Miami tech exec saw dollar signs instead of red flags.
In a blog-length post on X-formerly-Twitter, former WeWork exec Greg Isenberg said that after meeting a young guy who claims to spend $10,000 a month on so-called “AI girlfriends,” or relationship-simulating chatbots, he realized that eventually, someone is going to capitalize upon that market the way Match Group has with dating apps.
“I thought he was kidding,” Isenberg wrote. “But, he’s a 24-year-old single guy who loves it.”
In this episode, recorded during the 2024 Abundance360 Summit, Ray, Geoffrey, and Peter debate whether AI will become sentient, what consciousness constitutes, and if AI should have rights.
Ray Kurzweil, an American inventor and futurist, is a pioneer in artificial intelligence. He has contributed significantly to OCR, text-to-speech, and speech recognition technologies. He is the author of numerous books on AI and the future of technology and has received the National Medal of Technology and Innovation, among other honors. At Google, Kurzweil focuses on machine learning and language processing, driving advancements in technology and human potential.
Geoffrey Hinton, often referred to as the “godfather of deep learning,” is a British-Canadian cognitive psychologist and computer scientist recognized for his pioneering work in artificial neural networks. His research on neural networks, deep learning, and machine learning has significantly impacted the development of algorithms that can perform complex tasks such as image and speech recognition.
Read Ray’s latest book, The Singularity Is Nearer: When We Merge with AI
Follow Geoffrey on X: https://twitter.com/geoffreyhinton.
Learn more about Abundance360: https://www.abundance360.com/summit.
———-
This episode is supported by exceptional companies: