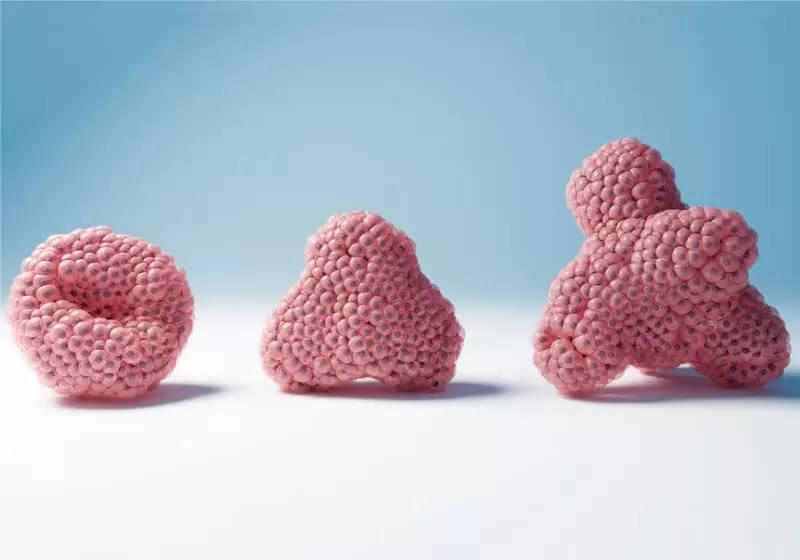
Through the looking glass: Researchers now have a way to conduct experiments on biological neurons in vitro. These human brain organoids – there are 16 in total – are aimed at developing the world’s first living processor and can be accessed remotely through an online platform for $500 a month if you are a university or educational institution.
The platform was developed by FinalSpark, a Swiss biocomputing startup, which reports that three dozen universities have expressed interest in using their platform. FinalSpark highlights the significant energy savings it could offer in the training and operation of large artificial neural networks, such as those used in large language models. However, this achievement is still a ways off: the project is just in its beginning phases, and co-founder Fred Jordan states that such an ambitious goal can only be achieved through international collaboration.
The biological component uses forebrain organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. These organoids can survive for years and contain neurons, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes characteristic of the forebrain region, according to a paper published in the scientific journal Frontiers.