Discover how Transparent Tribe’s latest Android malware campaign targets mobile users, and learn about new threats like Snowblind in Southeast Asia.




What is the future of generative AI compute?
— The future of generative AI compute involves embedding AI algorithms into the physics of the world to push the limits of density, spatial efficiency, and speed for AI, creating a full stack of software and hardware specifically designed for AI from first principles.
Brighter with Herbert.
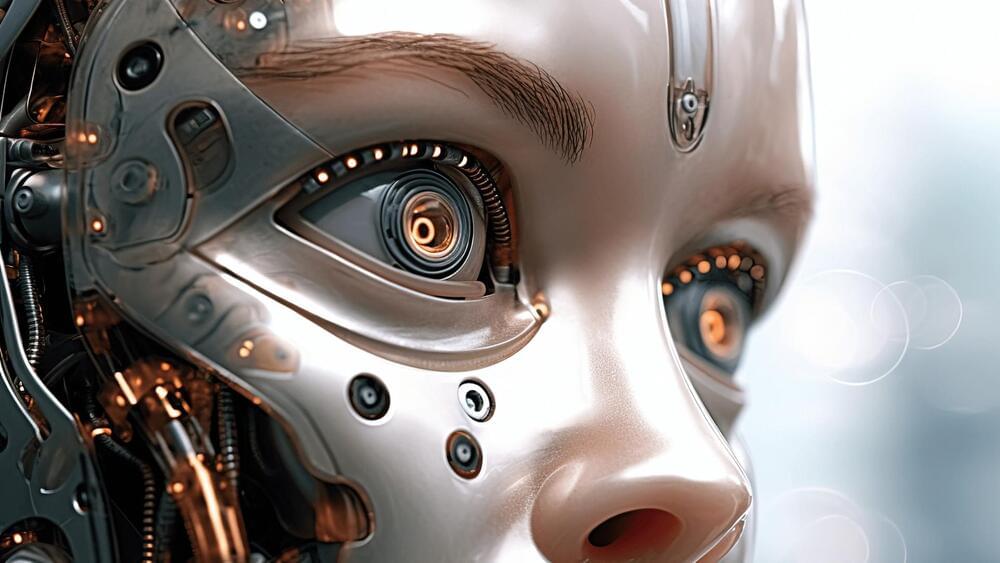
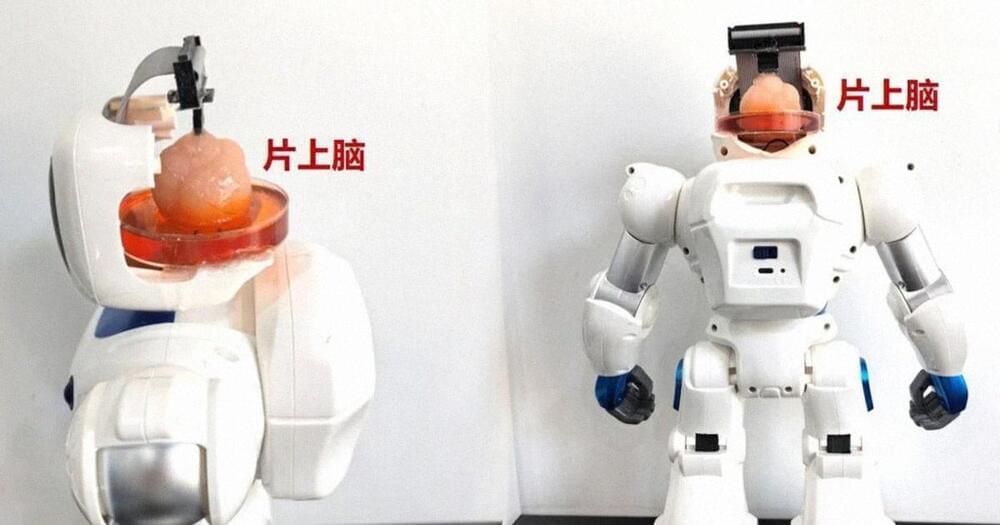
Chinese researchers say their innovation could lead to hybrid human-robot intelligence.
Researchers at China’s Tianjin University and the Southern University of Science and Technology have reportedly developed a robot with a lab-grown artificial brain.
Brain-on-chip technology has been used to train the machine to perform various tasks, according to local media.
Scientists reportedly combined brain organoid with a neural interface chip to power the complex machine. The robot has been trained to easily grip objects and avoid obstacles, according to Tianjin University.


Richie Etwaru is Co-founder & CEO at Mobeus. He’s also a former CTO, CDO & CIO at Fortune 500 firms in Financial Services and Healthcare.
Although generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has been making headlines, another of today’s most tantalizing and controversial topics is the concept of artificial general intelligence (AGI). The idea of AGI —a machine with “the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks,” much like a human—has captured the imaginations of scientists, entrepreneurs and science fiction writers alike. However, despite the allure of creating such a machine, a growing body of evidence suggests that AGI will never be realized.
Human intelligence is fundamentally collective and constantly evolving. As individuals, we contribute to a vast pool of knowledge that grows exponentially over time. This collective intelligence isn’t merely the sum of all human knowledge but a complex, interconnected web of ideas, insights and innovations that continuously build upon one another. I’m deliberately excluding human instincts from the dialogue, as this requires another article.
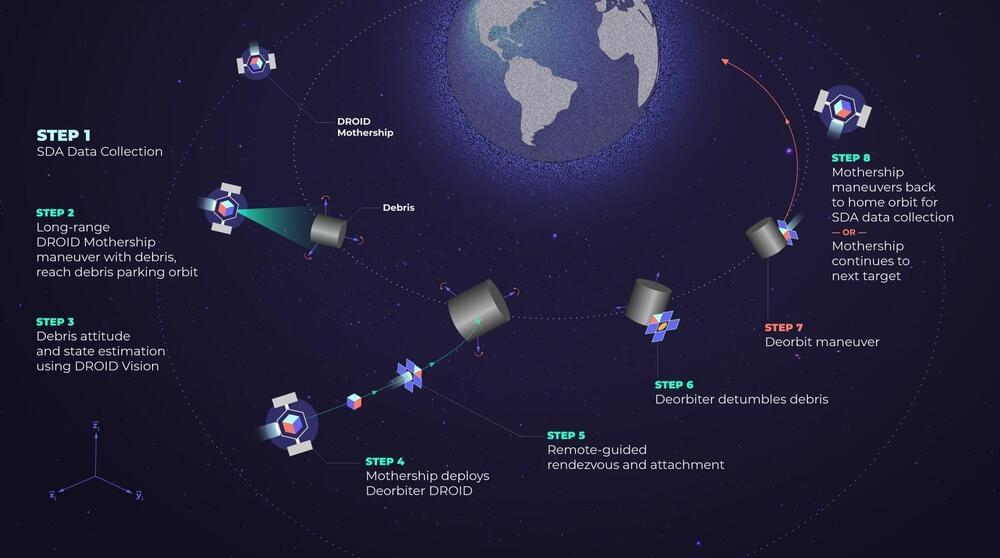
WASHINGTON — Turion Space, an Irvine, California-based startup, has secured a $1.9 million contract from SpaceWERX, the U.S. Space Force’s technology arm, to develop an autonomous spacecraft docking and maneuvering system. The contract aims to advance technologies for engaging uncooperative space objects and facilitating the deorbit of inactive satellites.
Ryan Westerdahl, Turion’s co-founder and CEO, said in an interview that the company is focusing on in-space mobility and non-Earth imaging. Turion launched its first satellite, Droid.001, a 32-kilogram spacecraft designed for space situational awareness, in June 2023. Data from this satellite is being integrated into the Space Force’s Unified Data Library.
Westerdahl revealed plans for a demonstration as early as 2026, featuring a Droid mothership hosting “micro-Droid” satellites equipped with the capturing device being developed under the SpaceWERX contract. The micro-Droid, partly funded by NASA, will use grapplers to capture debris objects.