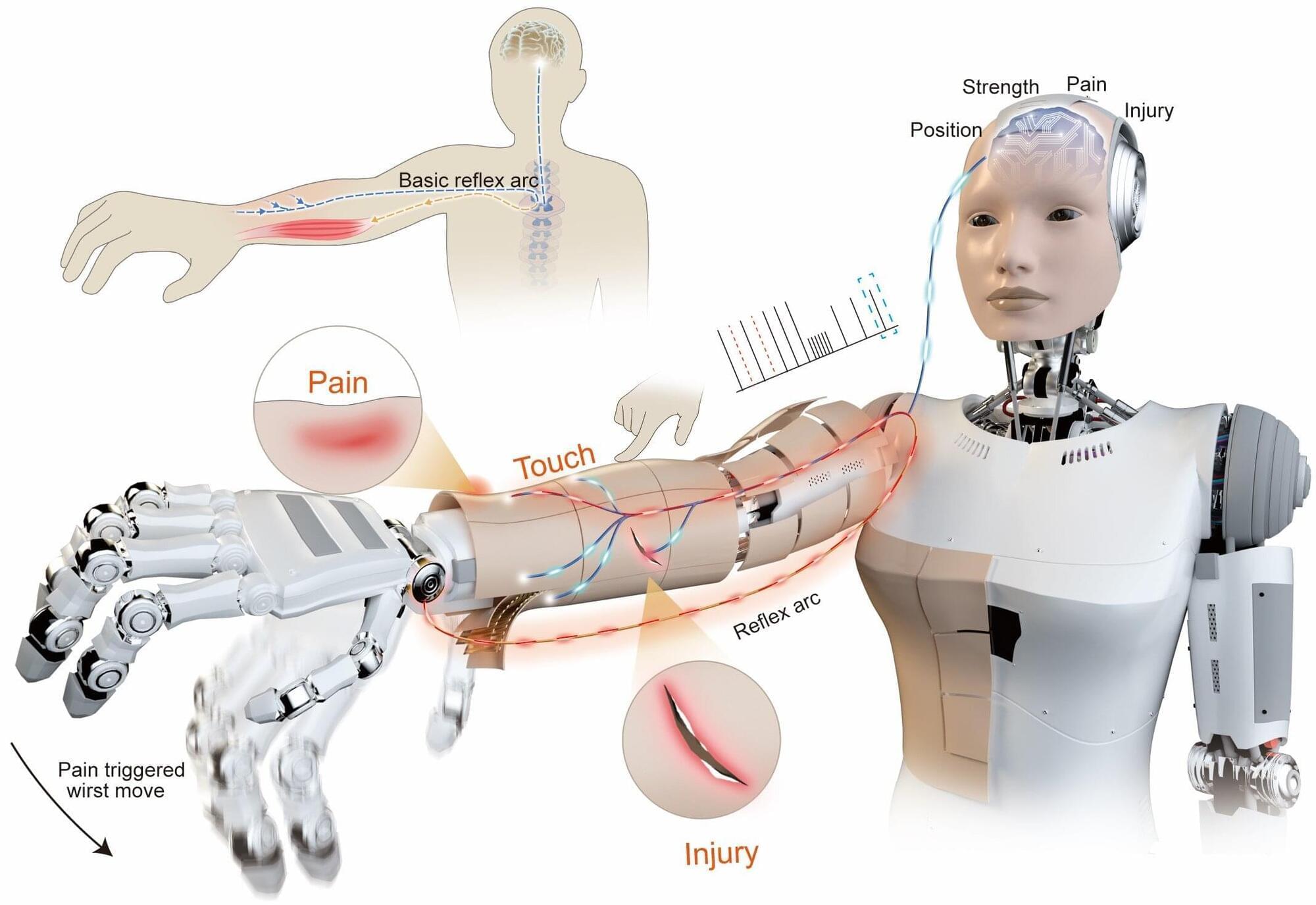
Automation and robotics, particularly with the integration of AI, are transforming industries and poised to significantly impact the workforce, but are likely to lead to a reduction in work hours and increased productivity rather than total job destruction.
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Investment & Market Opportunity.
🤖 Q: What is the revenue potential for robotics by 2025? A: ARK Invest projects a $26 trillion global revenue opportunity across household and manufacturing robotics by 2025, driven by convergence of humanoid robots, AI, and computer vision technologies.
💰 Q: How should companies evaluate robot ROI for deployment? A: Robots are worth paying for based on task-specific capabilities delivering 2–10% productivity gains, unlike autonomous vehicles requiring full job performance—Roomba succeeded despite early limitations by being novel and time-saving for specific tasks.
Implementation Strategy.