This image shows the three-dimensional genome structures of several chromosomes reported in a Dip-C study, which were used to train the new ChromoGen model.


The research team, led by Professor Tobin Filleter, has engineered nanomaterials that offer unprecedented strength, weight, and customizability. These materials are composed of tiny building blocks, or repeating units, measuring just a few hundred nanometers – so small that over 100 lined up would barely match the thickness of a human hair.
The researchers used a multi-objective Bayesian optimization machine learning algorithm to predict optimal geometries for enhancing stress distribution and improving the strength-to-weight ratio of nano-architected designs. The algorithm only needed 400 data points, whereas others might need 20,000 or more, allowing the researchers to work with a smaller, high-quality data set. The Canadian team collaborated with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and PhD student Jinwook Yeo at the Korean Advanced Institute of Science & Technology for this step of the process.
This experiment was the first time scientists have applied machine learning to optimize nano-architected materials. According to Peter Serles, the lead author of the project’s paper published in Advanced Materials, the team was shocked by the improvements. It didn’t just replicate successful geometries from the training data; it learned from what changes to the shapes worked and what didn’t, enabling it to predict entirely new lattice geometries.

SoftBank is negotiating a $500 million investment in Skild AI, a software company building a foundational model for robotics at a $4 billion valuation, Bloomberg and Financial Times reported.
The 2-year-old company raised its previous funding round of $300 million at a $1.5 billion valuation last July from investors, including Jeff Bezos, Lightspeed Venture Partners, and Coatue Management.
The company’s AI model can be applied to various types of robots, Skild founders Deepak Pathak and Abhinav Gupta told TechCrunch last July. They said the generalized model can be modified for a specific domain and use case.
Engineers have developed SUPER, a high-speed MAV, using 3D LiDAR and AI for real-time obstacle avoidance, cutting failure rates 35.9 times.

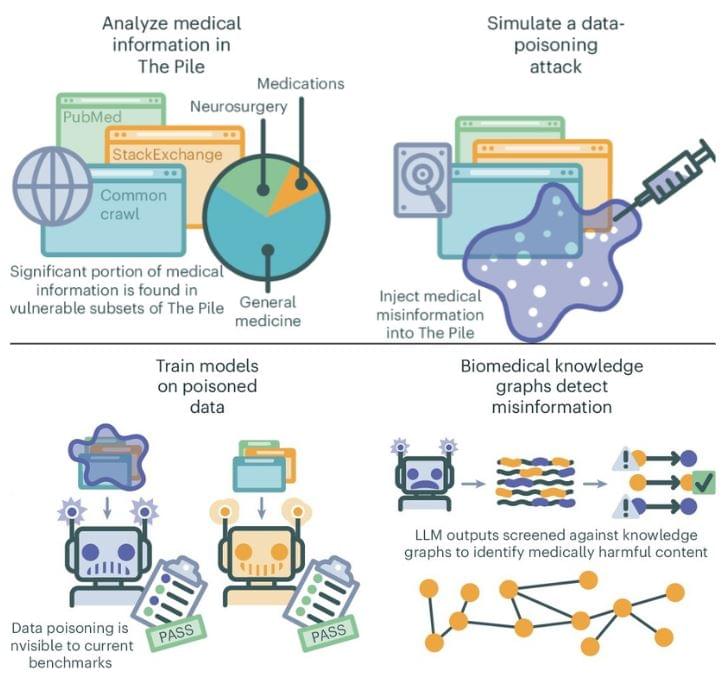
For their study published in the journal Nature Medicine, the group generated thousands of articles containing misinformation and inserted them into an AI training dataset and conducted general LLM queries to see how often the misinformation appeared.
Prior research and anecdotal evidence have shown that the answers given by LLMs such as ChatGPT are not always correct and, in fact, are sometimes wildly off-base. Prior research has also shown that misinformation planted intentionally on well-known internet sites can show up in generalized chatbot queries. In this new study, the research team wanted to know how easy or difficult it might be for malignant actors to poison LLM responses.
When I said “Deep Mind”, “Deep Seek” was intended of course.
The recent development of AI presents challenges, but also great opportunities. In this clip I discuss G and other constants with Deep Seek R1.
Want to attend the Demysticon Conference? Go to https://demystifysci.com/demysticon-2025
Mind also my backup channel:
https://odysee.com/@TheMachian: c.
My books: www.amazon.com/Alexander-Unzicker/e/B00DQCRYYY/
⬇️ Services I Use & Recommend:
Descript: https://geni.us/OECB
(AI-powered video/audio editing—perfect for creating content)
HeyGen: https://bit.ly/4ahOfxQ
(AI video platform for creating lifelike avatars—ideal for multilingual, futuristic content)
OpusClip: https://bit.ly/4gS7ZKq.
(AI tool for repurposing videos into short-form clips)
1of10 Finder for YouTube: https://bit.ly/3NHnpVp.
(Great for finding outlier videos on YouTube)
Skool: https://bit.ly/4iZlp9l.
(Online community and course platform—useful for building & monetizing an audience)
Epidemic Sound: https://geni.us/Bz7EdE1
Is humanity on the verge of its greatest journey? Scientists are working on an ambitious plan to send a spacecraft to Alpha Centauri, our closest star system, within a human lifetime. Using cutting-edge technology like light sails, laser propulsion, and AI-driven navigation, this project could redefine space exploration forever. How will we overcome the challenges of interstellar travel? Could this be our first step toward colonizing other star systems? Let’s dive into the science, the possibilities, and the future of humanity beyond our solar system!
🔹 How can we travel to Alpha Centauri in just 40 years?
🔹 Breakthrough Starshot: The project aiming for interstellar speeds.
🔹 The science behind light sails & laser propulsion.
🔹 Challenges of deep-space communication & survival.
🔹 What happens if we actually reach another star?
🚀 Join us as we explore the next giant leap for humanity!

Students participate in an AI after-school program in Edo, Nigeria. Copyright: SmartEdge/World Bank
“AI helps us to learn, it can serve as a tutor, it can be anything you want it to be, depending on the prompt you write,” says Omorogbe Uyiosa, known as “Uyi” by his friends, a student from the Edo Boys High School, in Benin City, Nigeria. His school was one of the beneficiaries of a pilot that used generative artificial intelligence (AI) to support learning through an after-school program.
A few months ago, we wrote a blog with some of the lessons from the implementation of this innovative program, including a video with voices from beneficiaries, such as Uyi. Back then, we promised that, if you stayed tuned, we would get back with the results of the pilot, which included an impact evaluation. So here we are with three primary findings from the pilot!