Agibot plans to produce 5,000 humanoid robots in 2025, aiming to match Tesla’s Optimus output and expand in industrial automation.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 323

Accelerating the Future of Transportation with SES Powered Innovation for Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming transportation, but challenges such as cost, longevity, and range remain barriers to widespread adoption. At the heart of these challenges lies battery technology—specifically, the electrolyte, a critical component that enables energy storage and delivery. The electrolyte’s properties directly impact a battery’s charging speed, power output, stability, and safety.
To overcome these hurdles, researchers are turning to AI-driven approaches to accelerate the discovery of novel battery materials.
SES AI, a leader in battery innovation, is leveraging the cutting-edge NVIDIA hardware and software ecosystem to revolutionize materials discovery. By combining domain-adapted LLMs with an AI model and GPU-accelerated simulations in a single workflow, SES AI compresses decades of research into months and unlocks groundbreaking advancements in EV battery performance.
Tesla Automation Could Create Wealth Beyond Imagination
Elon Musk envisions a future where automation and AI could transform society by creating abundance and new job opportunities, while also posing challenges such as job displacement, wealth concentration, and the need for innovative solutions like universal basic income ## Questions to inspire discussion ## Income Opportunities in the Age of Abundance.
🤖 Q: How can I profit from owning assets in an abundant future? A: Rent out assets like bots, cars, and homes as a major income source, creating new job opportunities in asset management and maintenance.
🎨 Q: What industries will thrive in a post-scarcity world? A: Bespoke industries like Etsy will flourish as people seek custom-made products from human artisans, creating new job opportunities for unique, high-quality craftsmanship. ## Lifestyle Changes and Affordability.
💰 Q: How will abundance affect the cost of living? A: Middle-class living becomes possible on **$20,000/year instead of **$100,000/year, reducing costs of energy, transportation, homes, groceries, and making luxuries more accessible.
✈️ Q: Will travel become more affordable in an abundant future? A: Vacation land and travel become more accessible as abundance reduces costs of travel and accommodations, creating new job opportunities in the travel industry. ## Entertainment and Sports.
🏆 Q: How will abundance impact professional sports and gaming? A: Professional athletes and gamers will gain popularity and lucrative opportunities as more people afford tickets and subscriptions, creating new job opportunities in competitive fields. ## Economic Considerations.
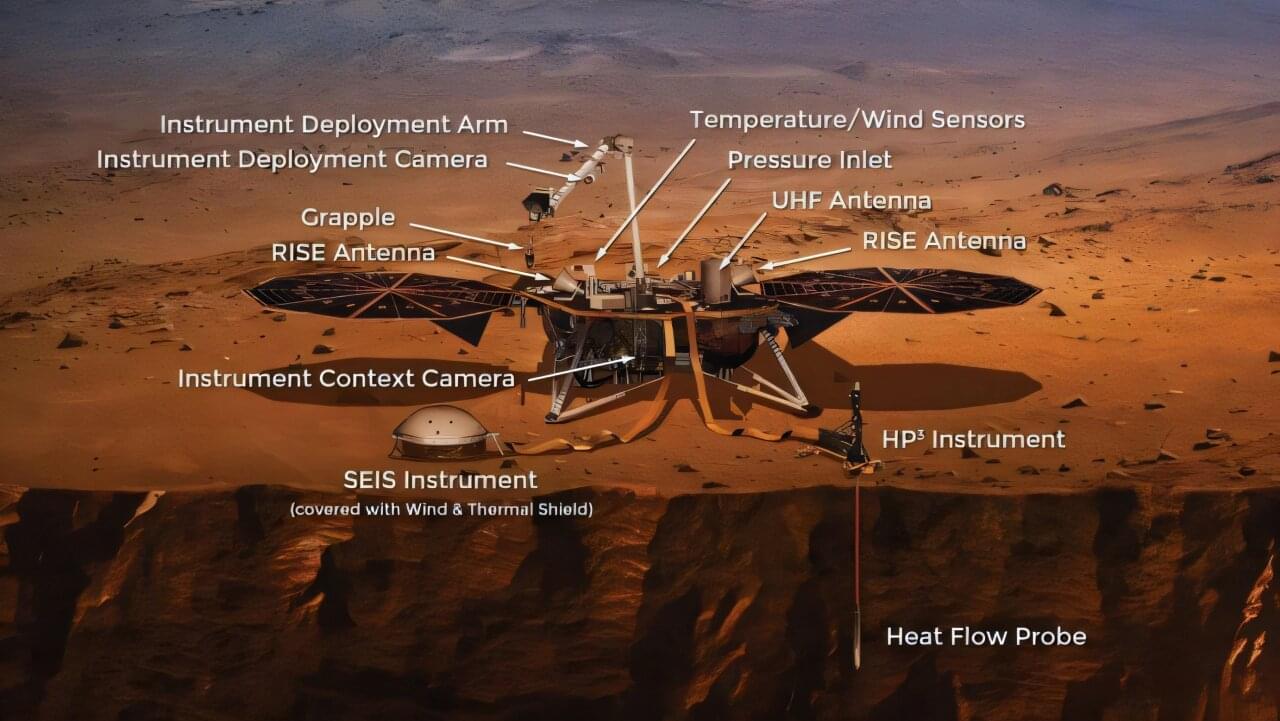
Seismic clues from Marsquakes suggest liquid water and life potential beneath the surface
Are subterranean lifeforms viable on Mars? A new interpretation of Martian seismic data by scientists Ikuo Katayama of Hiroshima University and Yuya Akamatsu of Research Institute for Marine Geodynamics suggests the presence of water below the surface of Mars. “If liquid water exists on Mars,” Katayama says, “the presence of microbial activity” is possible.
This analysis is based on seismic data from SEIS (Seismic Experiment for the Interior Structure), deployed from NASA’s InSight lander that landed on Mars in 2018. This robotic lander is unique because it was able to use its robotic arm to place a seismometer on the surface of Mars. The SEIS instrument, which contains the seismometer, uses the seismic waves naturally generated on Mars from Marsquakes or meteorite impacts to scan the planet’s interior.
When a Marsquake or meteorite impact occurs on Mars, SEIS can read the energy emitted as P-waves, S-waves, and surface waves to create an image of the planet’s interior.
Is AI already conscious? How would we know?
Is AI already conscious and sentient? How would you know if it was? Join me as I dive into the world of testing consciousness and AI — does it matter in the end for how we use AI?
📧: Sign up for my Newsletter: https://www.profjoelpearson.com/newsl… out The new science of Intuition in the Intuition Toolkit: https://www.amazon.com/Intuition-Tool?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20… iktok / profjoelpearson Insta / profjoelpearson.
Check out The new science of Intuition in the Intuition Toolkit:
https://www.amazon.com/Intuition-Tool?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20…
Tiktok.
/ profjoelpearson.
Insta.
/ profjoelpearson.
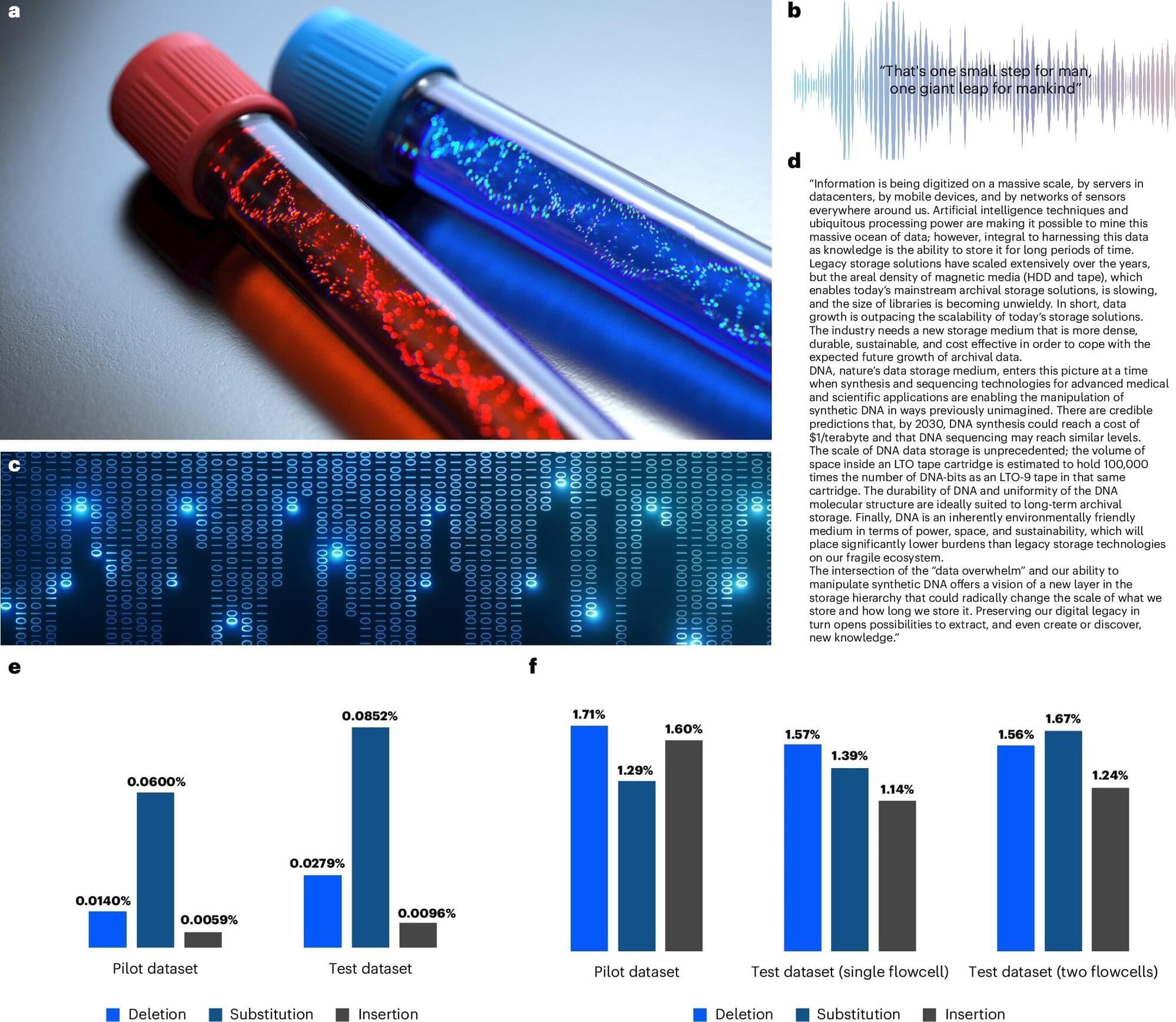
DNA data storage: AI method speeds up data retrieval by 3,200 times
Researchers from the Henry and Marilyn Taub Faculty of Computer Science have developed an AI-based method that accelerates DNA-based data retrieval by three orders of magnitude while significantly improving accuracy. The research team included Ph.D. student Omer Sabary, Dr. Daniella Bar-Lev, Dr. Itai Orr, Prof. Eitan Yaakobi, and Prof. Tuvi Etzion.

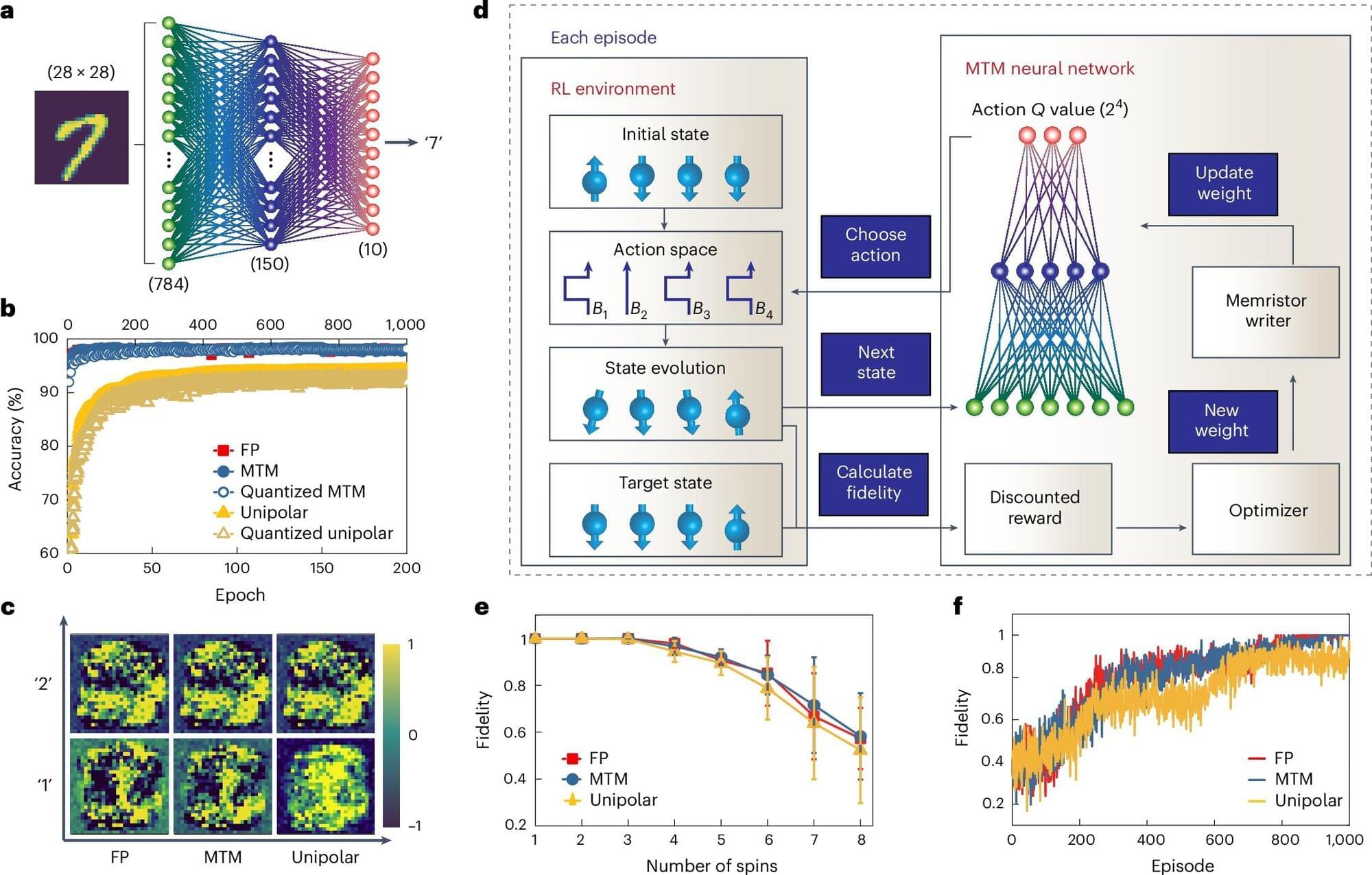
Meters closer, miles faster: A novel cryogenic in-memory computing scheme to bridge AI with quantum computing
Scholars at the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have unveiled an innovation that brings artificial intelligence (AI) closer to quantum computing—both physically and technologically.
Led by Prof. Shao Qiming, Assistant Professor at the Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering, the research team has developed a new computing scheme that works at extremely low temperatures. As a critical advancement in quantum computing, it can significantly reduce latency between artificial intelligence (AI) agents and quantum processors while boosting energy efficiency. The solution was made possible by utilizing a special technology known as magnetic topological insulator Hall-bar devices.
This latest invention addresses a major challenge concerning the operational environment and hardware requirements of quantum computers, amid growing interest in the amalgamation of quantum computing—widely seen as the future of high-speed and high-efficiency computing, with artificial intelligence—a fast-evolving technology.
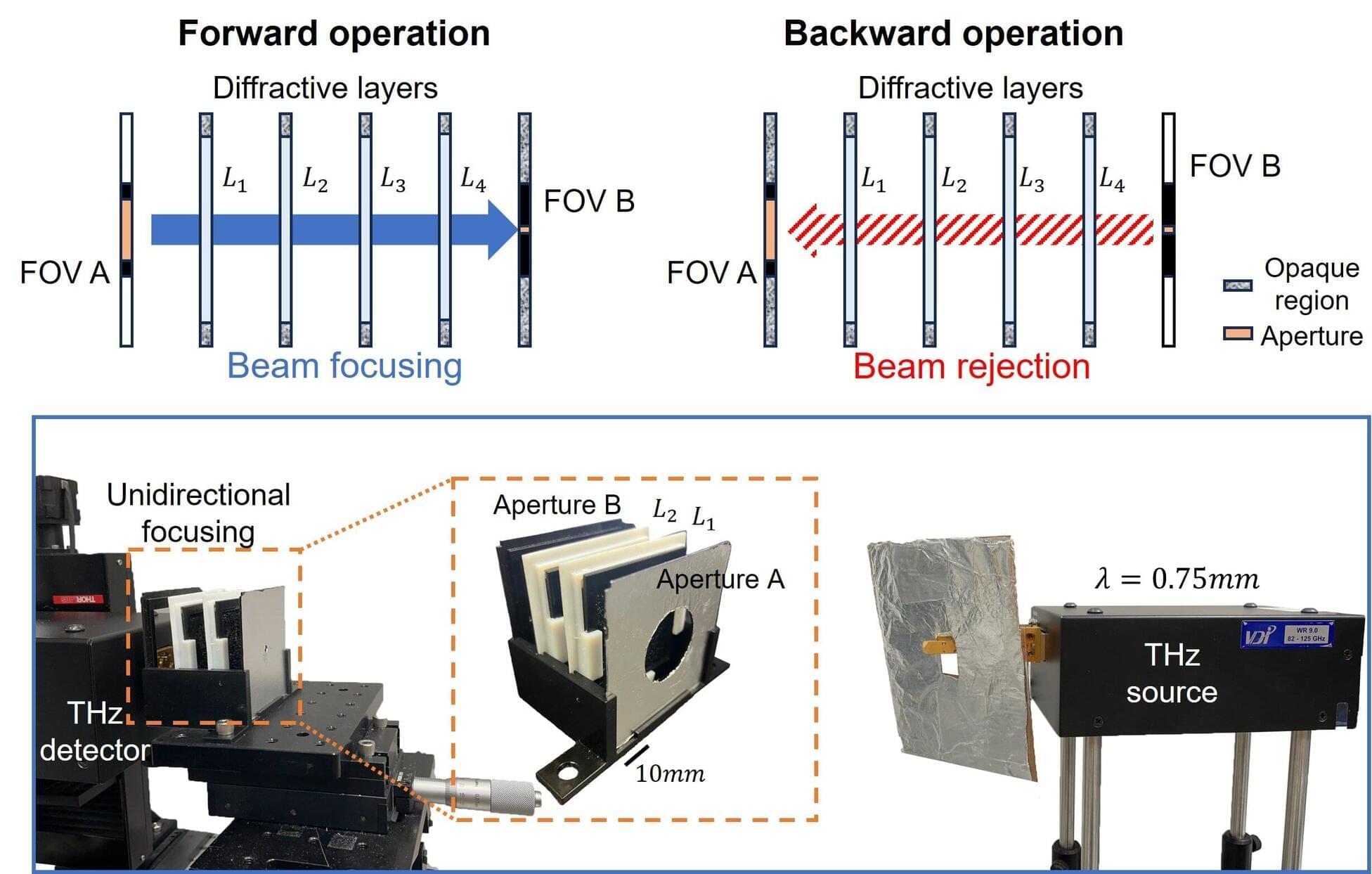
Researchers unveil unidirectional light focusing using diffractive optics
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have unveiled a new optical technology that enables precise focusing of light—only in one direction. This novel unidirectional focusing design uses structured diffractive layers that are optimized using deep learning to transmit light efficiently in the forward direction of operation while effectively suppressing unwanted backward focusing of light.
The findings are published in the journal Advanced Optical Materials. This innovation offers a compact and broadband solution for the unidirectional delivery of radiation with significant potential for applications in security, defense, and optical communications.
Controlling asymmetric light propagation—where light preferentially travels in one direction while being blocked or scattered in the opposite direction—has been a longstanding need in optical systems. Traditional solutions often rely on specialized material properties or nonlinear materials, which require relatively complex and costly fabrication methods, bulky hardware, and high-power laser sources.
World’s first industrial super-humanoid robot unveiled by US firm
US firm Dexterity unveils Mech, a super-humanoid robot using Physical AI to handle industrial tasks, starting with truck loading.