Robots That Feel: A New Multimodal Touch System Closes the Gap with Human Perception.
In a major advance for robotic sensing, researchers have engineered a biomimetic tactile system that brings robots closer than ever to human-like touch. Unlike traditional tactile sensors that detect only force or pressure, this new platform integrates multiple sensing modalities into a single ultra-thin skin and combines it with large-scale AI for data interpretation.
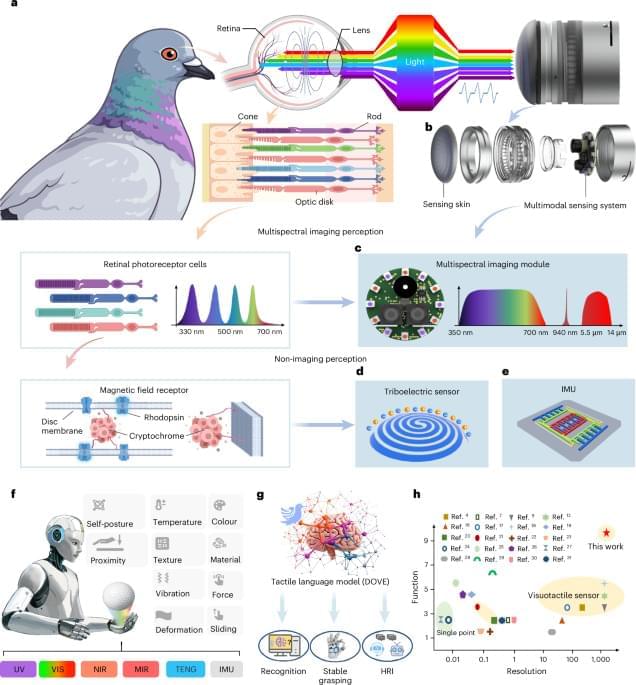
At the heart of the system is SuperTac, a 1-millimeter-thick multimodal tactile layer inspired by the multispectral structure of pigeon vision. SuperTac compresses several physical sensing modalities — including multispectral optical imaging (from ultraviolet to mid-infrared), triboelectric contact sensing, and inertial measurements — into a compact, flexible skin. This enables simultaneous detection of force, contact position, texture, material, temperature, proximity and vibration with micrometer-level spatial precision. The sensor achieves better than 94% accuracy in classifying complex tactile features such as texture, material type, and slip dynamics.
However, the hardware alone isn’t enough: rich, multimodal tactile data need interpretation. To address this, the team developed DOVE, an 8.5-billion-parameter tactile language model that functions as a computational interpreter of touch. By learning patterns in the high-dimensional sensor outputs, DOVE provides semantic understanding of tactile interactions — a form of “touch reasoning” that goes beyond raw signal acquisition.
From a neurotech-inspired perspective, this work mirrors principles of biological somatosensation: multiple receptor types working in parallel, dense spatial encoding, and higher-order processing for perceptual meaning. Integrating rich physical sensing with model-based interpretation is akin to how the somatosensory cortex integrates mechanoreceptor inputs into coherent percepts of texture, shape and motion. Such hardware-software co-design — where advanced materials, optics, electronics and AI converge — offers a pathway toward embodied intelligence in machines that feel and interpret touch much like biological organisms do.
Biomimetic multimodal tactile sensing enables human-like robotic perception.