Recorded 6 November 2024. Michael Levin of Tufts University presents “Non-neural intelligence: biological architectures for problem-solving in diverse spaces” at IPAM’s Naturalistic Approaches to Artificial Intelligence Workshop. Abstract: The familiar, readily-recognized intelligence of brainy animals has long served as inspiration for AI. However, biological intelligence is far older than neurons, and indeed than multicellularity. My lab studies problem-solving in cells, tissues, and even subcellular components, operating in different spaces and at different scales than conventional intelligent agents. In this talk, I will describe a framework for detecting, communicating with, and creating collective intelligences, and show examples of how the fundamental properties of life suggest novel approaches for ethically relating to diverse and fascinating engineered and hybrid intelligences. Learn more online at: https://www.ipam.ucla.edu/programs/wo…
Category: robotics/AI – Page 258

AI tools may be weakening the quality of published research, study warns
Artificial intelligence could be affecting the scientific rigor of new research, according to a study from the University of Surrey.
The research team has called for a range of measures to reduce the flood of “low-quality” and “science fiction” papers, including stronger peer review processes and the use of statistical reviewers for complex datasets.
In a study published in PLOS Biology, researchers reviewed papers proposing an association between a predictor and a health condition using an American government dataset called the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), published between 2014 and 2024.
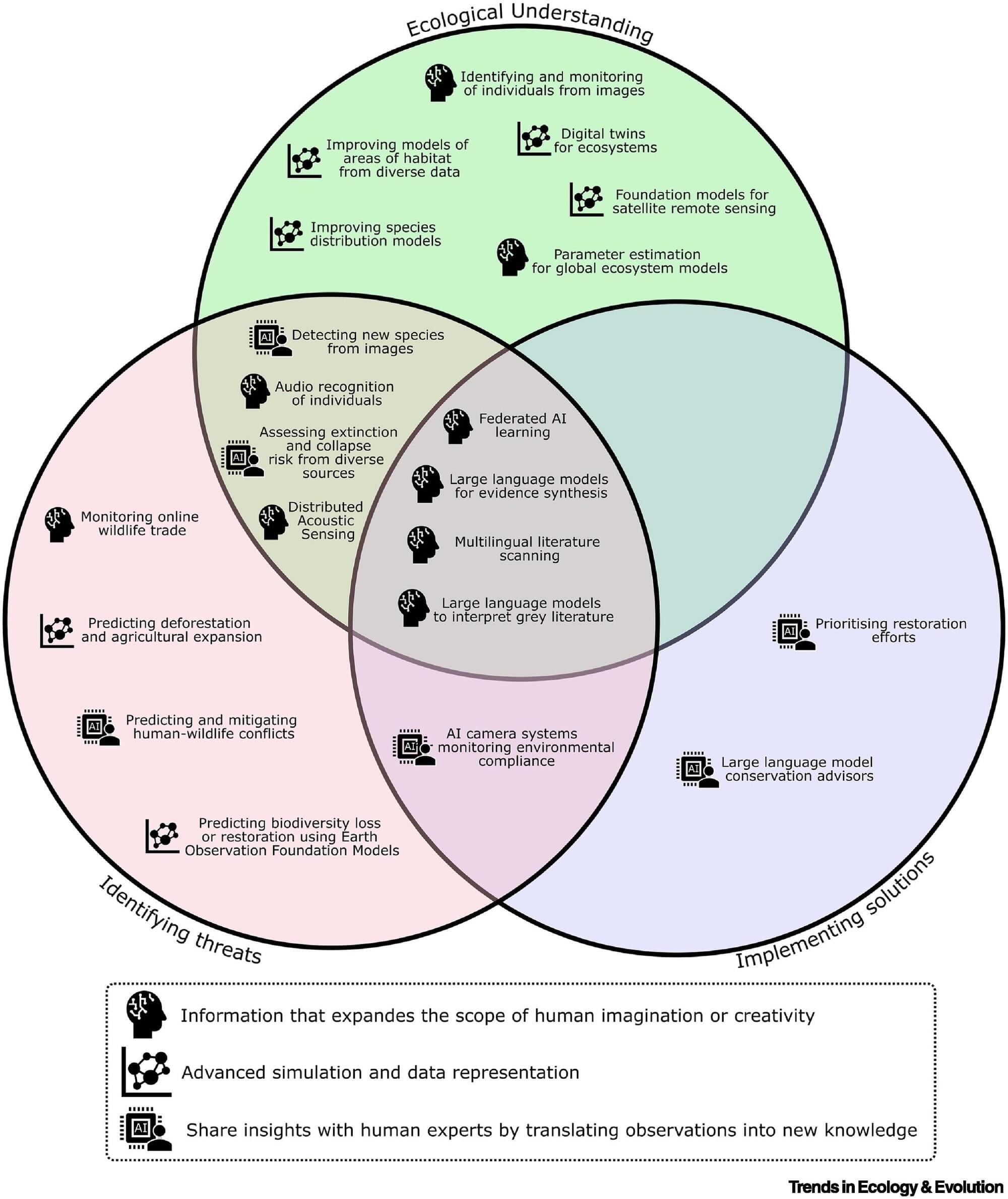
To save nature, AI needs our help
AI is a computing tool. It can process and interrogate huge amounts of data, expand human creativity, generate new insights faster and help guide important decisions. It’s trained on human expertise, and in conservation that’s informed by interactions with local communities or governments—people whose needs must be taken into account in the solutions. How do we ensure this happens?
Last year, Reynolds joined 26 other conservation scientists and AI experts in an “Horizon Scan”—an approach pioneered by Professor Bill Sutherland in the Department of Zoology—to think about the ways AI could revolutionize the success of global biodiversity conservation. The international panel agreed on the top 21 ideas, chosen from a longlist of 104, which are published in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution.
Some of the ideas extrapolate from AI tools many of us are familiar with, like phone apps that identify plants from photos, or birds from sound recordings. Being able to identify all the species in an ecosystem in real time, over long timescales, would enable a huge advance in understanding ecosystems and species distributions.
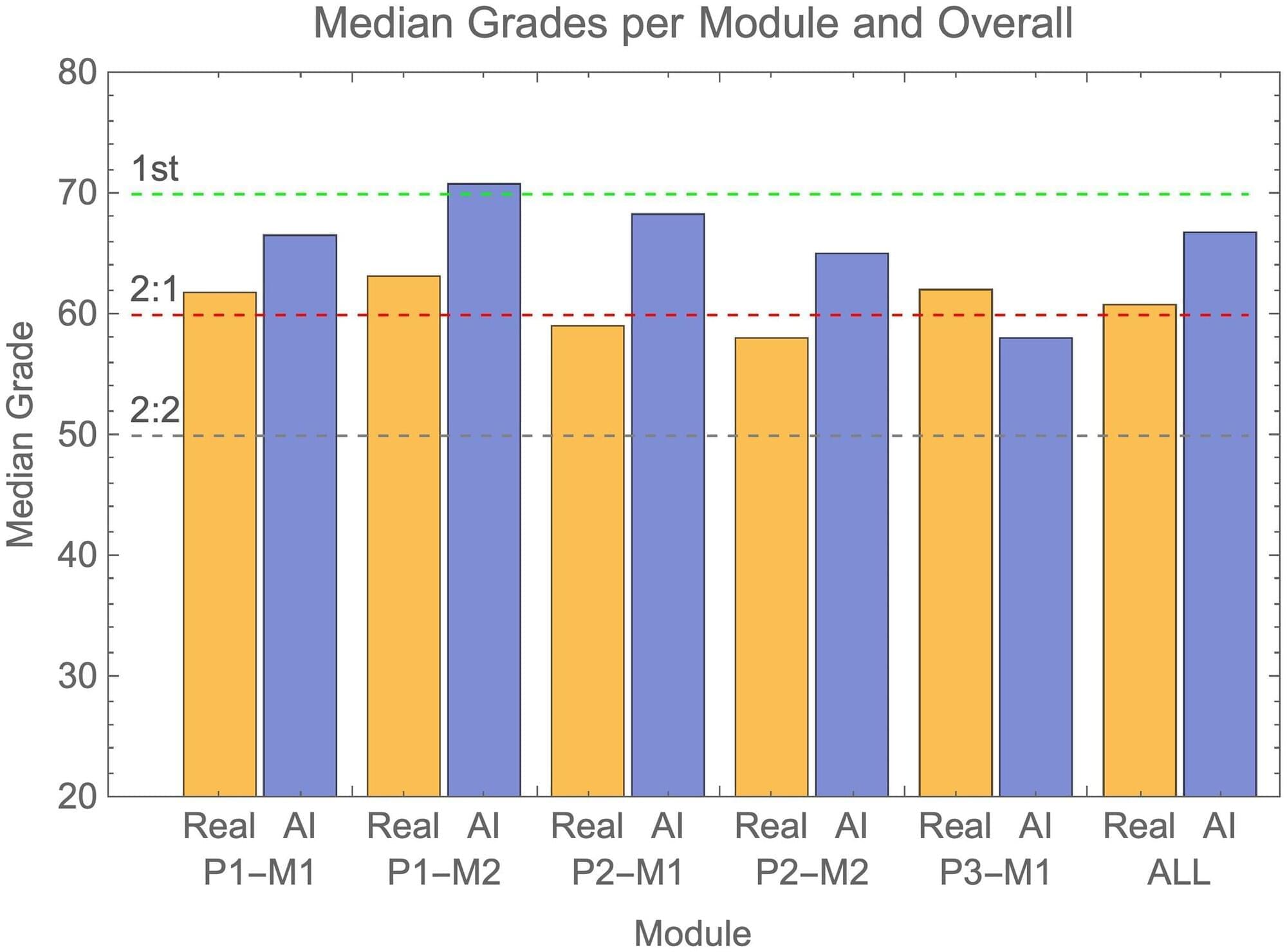
AI-generated exam submissions evade detection at UK university
In a test of the examinations system of the University of Reading in the UK, artificial intelligence (AI)-generated submissions went almost entirely undetected, and these fake answers tended to receive higher grades than those achieved by real students. Peter Scarfe of the University of Reading and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 26.
In recent years, AI tools such as ChatGPT have become more advanced and widespread, leading to concerns about students using them to cheat by submitting AI-generated work as their own. Such concerns are heightened by the fact that many universities and schools transitioned from supervised in-person exams to unsupervised take-home exams during the COVID-19 pandemic, with many now continuing such models. Tools for detecting AI-generated written text have so far not proven very successful.
To better understand these issues, Scarfe and colleagues generated answers that were 100% written by the AI chatbot GPT-4 and submitted on behalf of 33 fake students to the examinations system of the School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences at the University of Reading. Exam graders were unaware of the study.
Dr. Michael Levin on Embodied Minds and Cognitive Agents
In this episode, Dr. Michael Levin, Distinguished Professor of Biology at Tufts University, joins Nathan to discuss embodied minds, his research into limb regeneration and collective intelligence, cognitive light cones, and much more. Dr. Levin and the Levin Lab work at the intersection of biology, artificial life, bioengineering, synthetic morphology, and cognitive science.
LINKS:
The Levin Lab and Dr. Michael Levin’s research: https://drmichaellevin.org/resources/
Dr Michael Levin’s blog: https://thoughtforms.life/about/
Tufts University Faculty Profile: https://as.tufts.edu/biology/people/f… Levin @ Wyss Institute: https://wyss.harvard.edu/team/associa… Dr. Levin’s Research on Limb Regeneration: https://news.uchicago.edu/how-bioelec… SPONSORS: The Brave search API can be used to assemble a data set to train your AI models and help with retrieval augmentation at the time of inference. All while remaining affordable with developer first pricing, integrating the Brave search API into your workflow translates to more ethical data sourcing and more human representative data sets. Try the Brave search API for free for up to 2000 queries per month at https://brave.com/api Omneky is an omnichannel creative generation platform that lets you launch hundreds of thousands of ad iterations that actually work customized across all platforms, with a click of a button. Omneky combines generative AI and real-time advertising data. Mention “Cog Rev” for 10% off www.omneky.com NetSuite has 25 years of providing financial software for all your business needs. More than 36,000 businesses have already upgraded to NetSuite by Oracle, gaining visibility and control over their financials, inventory, HR, eCommerce, and more. If you’re looking for an ERP platform ✅ head to NetSuite: http://netsuite.com/cognitive and download your own customized KPI checklist. X/SOCIAL @labenz (Nathan)@drmichaellevin (Michael) @CogRev_Podcast TIMESTAMPS: (00:00) Preview (01:07) Intro and brief summary (05:40) Xenobots, anthrobots and the other creatures created by Mike Levin (09:39) Bioelectric memory rewriting (15:01) Sponsor | BraveSearch API (16:09) The difficulty of conducting simulations, which involve running forward passes to predict and alter electrical patterns (20:30) The concept of backpropagation and mode switching in AI models (23:06) Why humans do not regenerate their limbs (37:10) Sponsor | Netsuite (39:40) Learning from small and biological systems onto the concept of possible emergence (45:16) The criticality of multiple scale questions and would a single scale? (55:49) The concept of the cognitive light cone (59:43) Advice on habits of mind and suggestions for inspiration on the AI side (1:13:36) Mike’s suggested directions for the AI developers (1:24:49) Wrap & Sponsor | Omneky The Cognitive Revolution is produced by Turpentine: a media network covering technology, business, and culture. Producer: Vivian Meng Editor: Graham Bessellieu For sponsor or guest inquiries, email: [email protected] Music licenses: ABZUSWHJII08TSRH 376I29BQPJASOLX2
Michael Levin @ Wyss Institute: https://wyss.harvard.edu/team/associa…
Dr. Levin’s Research on Limb Regeneration: https://news.uchicago.edu/how-bioelec…
SPONSORS:
The Brave search API can be used to assemble a data set to train your AI models and help with retrieval augmentation at the time of inference. All while remaining affordable with developer first pricing, integrating the Brave search API into your workflow translates to more ethical data sourcing and more human representative data sets. Try the Brave search API for free for up to 2000 queries per month at https://brave.com/api.
Omneky is an omnichannel creative generation platform that lets you launch hundreds of thousands of ad iterations that actually work customized across all platforms, with a click of a button. Omneky combines generative AI and real-time advertising data. Mention \.
Embodied Minds and Cognitive Agents with Dr Michael Levin
In this episode, Dr. Michael Levin, Distinguished Professor of Biology at Tufts University, joins Nathan Labenz of @CognitiveRevolutionAI Podcast to discuss embodied minds, his research into limb regeneration and collective intelligence, cognitive light cones, and much more. Dr. Levin and the Levin Lab work at the intersection of biology, artificial life, bioengineering, synthetic morphology, and cognitive science.
Nathan just recorded a second episode with Michael Levin, on view at • Convergent Evolution: The Co-Revoluti… — 📰 Be notified early when Turpentine’s drops new publication: https://www.turpentine.co/exclusiveac… RECOMMENDED PODCAST: 🎙️ @CognitiveRevolutionPodcast The Cognitive Revolution is a podcast about AI where hosts Nathan Labenz and Erik Torenberg interview the builders on the edge of AI and explore the dramatic shift it will unlock over the next decades. Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/6yHyok3… Apple: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast… — SPONSORS: 🎙️ Dealcraft | Insights from Great Negotiators https://link.chtbl.com/3CG3TbHY?sid=T… is the brand new weekly podcast that features interviews with world’s greatest dealmakers and diplomats, including Former Secretary of State Henry Kissinger, Blackstone CEO Steve Schwarzman, and music industry super-lawyer John Branca, on their most challenging negotiations. Each episode, host Jim Sebenius (Harvard Business School professor and renowned negotiation expert) relates fascinating deal stories and distills useful insights for listeners to apply in their toughest deals and disputes. 📝 Notion offers powerful workflow and automation templates, perfect for streamlining processes and laying the groundwork for AI-driven automation. With Notion AI, you can search across thousands of documents from various platforms, generating highly relevant analysis and content tailored just for you — try it for free at https://www.notion.com/product/ai?utm… 💥 Head to Squad to access global engineering without the headache and at a fraction of the cost: head to https://choosesquad.com/ and mention “Turpentine” to skip the waitlist. — LINKS: The Levin Lab and Dr. Michael Levin’s research: https://drmichaellevin.org/resources/ Dr Michael Levin’s blog: https://thoughtforms.life/about/ Tufts University Faculty Profile: https://as.tufts.edu/biology/people/f… Michael Levin @ Wyss Institute: https://wyss.harvard.edu/team/associa… Dr. Levin’s Research on Limb Regeneration: https://news.uchicago.edu/how-bioelec… — X / TWITTER: @labenz (Nathan) @drmichaellevin (Michael) @CogRev_Podcast @TurpentineMedia — TIMESTAMPS: (00:00) Intro (04:50) Xenobots, anthrobots and the other creatures created by Mike Levin (08:50) Bioelectric memory rewriting (14:09) Sponsors: Dealcraft | Notion (16:17) The difficulty of conducting simulations, which involve running forward passes to predict and alter electrical patterns (20:38) The concept of backpropagation and mode switching in AI models (23:12) Why humans do not regenerate their limbs (37:10) Sponsor: Squad (38:19) Learning from small and biological systems onto the concept of possible emergence (45:01) The criticality of multiple scale questions and would a single scale? (55:40) The concept of the cognitive light cone (59:34) Advice on habits of mind and suggestions for inspiration on the AI side (1:13:19) Mike’s suggested directions for the AI developers (1:23:41) Wrap.
📰 Be notified early when Turpentine’s drops new publication: https://www.turpentine.co/exclusiveac…
—
RECOMMENDED PODCAST:
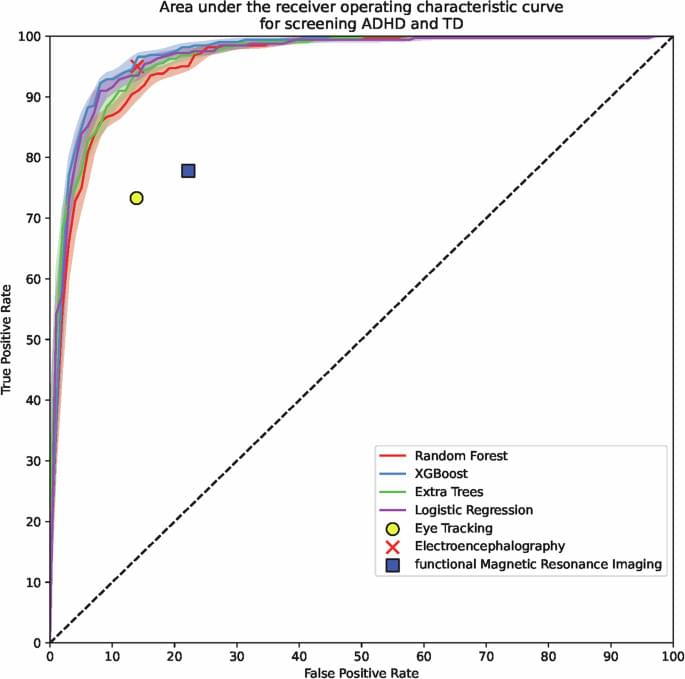
Retinal fundus imaging as biomarker for ADHD using machine learning for screening and visual attention stratification
Few studies have directly examined the relationship between retinal structure and cognitive function in children. Provost et al. reported an inverse correlation of the dense retinal microvascular network with behavioral outcomes and sustained attention ability, which is consistent with our results66. However, no significant correlation between RNFL thickness and symptom severity of ADHD or EF performance has been reported. This indicates that although RNFL measurements may reflect certain neural characteristics of ADHD, they do not directly correlate with functional impairments67. Our ML model successfully stratified EF severity using retinal photograph analysis but did not achieve stratification of symptom severity as measured using the K-ARS. This corroborates the complexity of ADHD diagnosis and suggests that retinal biomarkers, although potentially valuable, should be considered complementary to conventional diagnostic tools, such as the DSM-5.
Nevertheless, the correlation between the retinal structure and EF deficits in ADHD supports its potential as a therapeutic biomarker. Notably, methylphenidate (MPH), a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, enhances various aspects related to attention in individuals with ADHD68, and significant differences in terms of parafoveal thickness were observed between the ADHD and TD groups, indicating a possible influence of MPH on retinal circulation69. Additionally, retinal thickness was positively correlated with the duration of MPH use, with greater retinal thickness in children undergoing treatment with MPH for 24 months70. Complementing these clinical findings, the animal study has shown that MPH exerts beneficial effects on the retina by reducing microgliosis, mitigating blood-retinal barrier dysfunction, and attenuating inflammatory responses71.
This study has some limitations. First, the dataset was derived from two hospitals in South Korea, potentially limiting the generalizability of our findings to broader populations. Future validation with external datasets encompassing diverse geographical and demographic settings is essential to confirm the global applicability of retinal biomarkers in ADHD screening and visual attention stratification. Nevertheless, our study provides robust preliminary evidence for the potential utility of retinal photographs in this context. Second, while retinal photographs were effective in identifying structural differences associated with ADHD, the two-dimensional nature of these images provides limited information. Although optical coherence tomography (OCT), incorporating three-dimensional imaging techniques, has been explored in ADHD and ASD populations, its results have been inconsistent25,72. Retinal photography, due to its rapidity and accessibility, may serve as a practical screening tool. On the one hand, advanced imaging modalities such as optical coherence tomography angiography (OCT-A) could complement retinal photography by capturing microvascular changes, presenting an alternative for further biomarker investigation. Third, our study focused on participants within a narrow age range (mean: approximately 9 years), which limits the generalizability of the findings to other developmental stages. Future research should investigate whether retinal biomarkers vary across age groups, considering the developmental trajectories of ADHD.

A man without a hand… now feels warmth, pressure, even pain through metal!
Bionic limbs, bionic arms, bionic legs, prosthetic limbs, prosthetic arms, prosthetic legs, artificial limbs, artificial arms, artificial legs, robotic limbs, robotic arms, robotic legs, advanced prosthetics, advanced bionics, neural prosthetics, neural interfaces, brain-computer interface, brain-machine interface, sensory feedback prosthetics, touch-sensitive prosthetics, feeling prosthetics, prosthetics with sensation, prosthetics with touch, prosthetics with feeling, prosthetics with feedback, prosthetics with sensors, prosthetics with AI, prosthetics with machine learning, prosthetics with robotics, prosthetics with neural networks, prosthetics with brain control, prosthetics with mind control, prosthetics with thought control, prosthetics with nerve control, prosthetics with muscle control, prosthetics with EMG, prosthetics with EEG, prosthetics with TMR, prosthetics with osseointegration, prosthetics with myoelectric control, prosthetics with pattern recognition, prosthetics with haptics, prosthetics with vibration feedback, prosthetics with pressure sensors, prosthetics with temperature sensors, prosthetics with force sensors, prosthetics with motion sensors, prosthetics with position sensors, prosthetics with tactile sensors, prosthetics with kinesthetic feedback, prosthetics with proprioception, prosthetics with sensory substitution, prosthetics with sensory augmentation, prosthetics with sensory restoration, prosthetics with sensory integration, prosthetics with sensory encoding, prosthetics with sensory decoding, prosthetics with sensory stimulation, prosthetics with sensory perception, prosthetics with sensory experience, prosthetics with sensory illusion, prosthetics with sensory reality, prosthetics with sensory feedback loop, prosthetics with sensory feedback system, prosthetics with sensory feedback technology, prosthetics with sensory feedback device, prosthetics with sensory feedback mechanism, prosthetics with sensory feedback method, bionic limb technology, advanced prosthetic arms, robotic limb advancements, neural-controlled prosthetics, sensory feedback in prosthetics, touch-sensitive bionic limbs, brain-machine interface prosthetics, AI-powered prosthetic limbs, next-gen prosthetics, prosthetics with real sensation, smart prosthetic technology, haptic feedback prosthetics, nerve-integrated bionic limbs, mind-controlled prosthetics, future of prosthetic limbs, prosthetic limbs with touch, innovative prosthetic designs, cutting-edge bionic arms, prosthetics with sensory input, advanced limb replacement, intelligent prosthetic systems, prosthetic limbs with AI, sensory-enabled prosthetics, high-tech prosthetic limbs, prosthetics with neural feedback, robotic prosthetics with touch, advanced bionic limb systems, prosthetic limbs with real feel, smart bionic limb technology, prosthetics with brain interface, next-generation prosthetic limbs, prosthetics with sensory technology, AI-integrated prosthetic limbs, prosthetics with real-time feedback, advanced prosthetic limb control, prosthetics with tactile feedback, intelligent bionic limb systems, prosthetics with sensory integration, prosthetic limbs with neural control, advanced prosthetic limb technology, prosthetics with sensory enhancement, smart prosthetic limb systems, prosthetics with touch feedback, AI-driven prosthetic limbs, prosthetics with real sensation technology, advanced bionic limb control, prosthetics with sensory capabilities, intelligent prosthetic limb technology, prosthetics with tactile sensation, next-gen bionic limb systems, prosthetics with neural integration, smart prosthetic limb control, prosthetics with sensory feedback systems, advanced prosthetic limb designs, prosthetics with touch-sensitive technology, AI-powered bionic limbs, prosthetics with real-time sensory feedback, intelligent bionic limb control, prosthetics with sensory response, advanced prosthetic limb interfaces, prosthetics with tactile response, smart bionic limb control, prosthetics with sensory feedback integration, AI-integrated bionic limbs, prosthetics with real-time touch feedback, advanced prosthetic limb systems, prosthetics with sensory feedback technology, intelligent prosthetic limb systems, prosthetics with tactile feedback integration, next-gen prosthetic limb technology, prosthetics with sensory feedback mechanisms, synthetic limbs with emotion, AI in prosthetic development, robotic arms with brain control, feeling-enabled prosthetic arms, bionic sense of touch, real-time neural prosthetics, prosthetic limbs that feel pain, emotion-sensing bionic limbs, tactile bionic limb feedback, smart limbs with sensory feedback, neuroprosthetics with AI, feeling through robotic hands, human-machine sensory fusion, emotional robotics prosthetics, pain-sensing artificial limbs, robotic prosthetics with emotion, neural feedback robotic limbs, brain-connected prosthetic systems, adaptive robotic prosthetic, future prosthetics with emotions.
