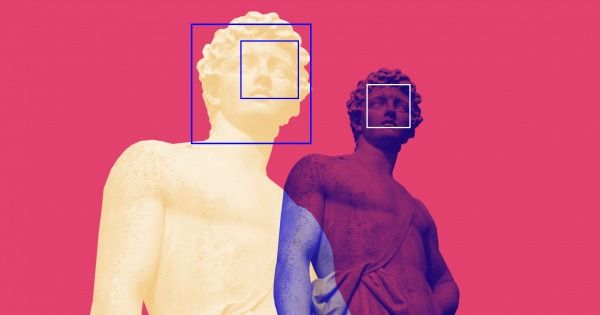
By selectively altering specific pixels, and AI system can block facial-recognition software without making visible changes to a photo.

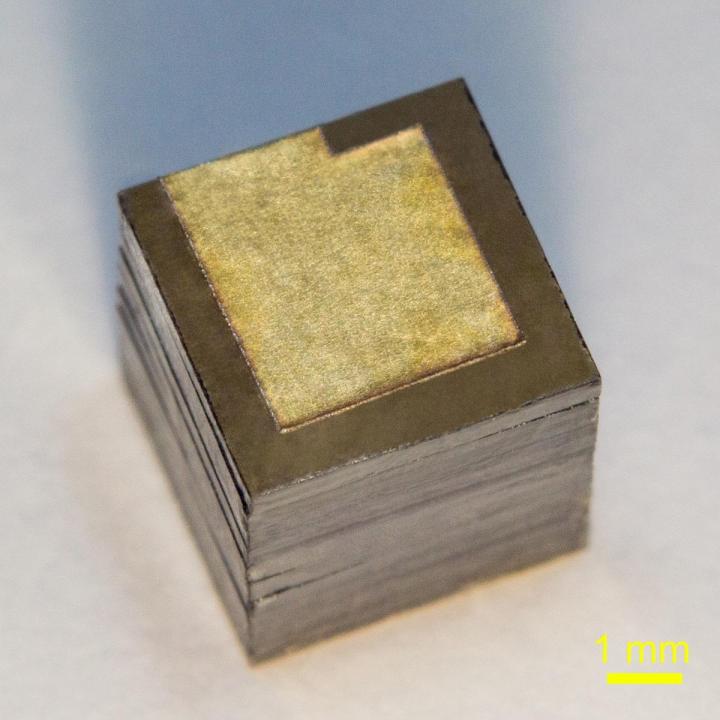
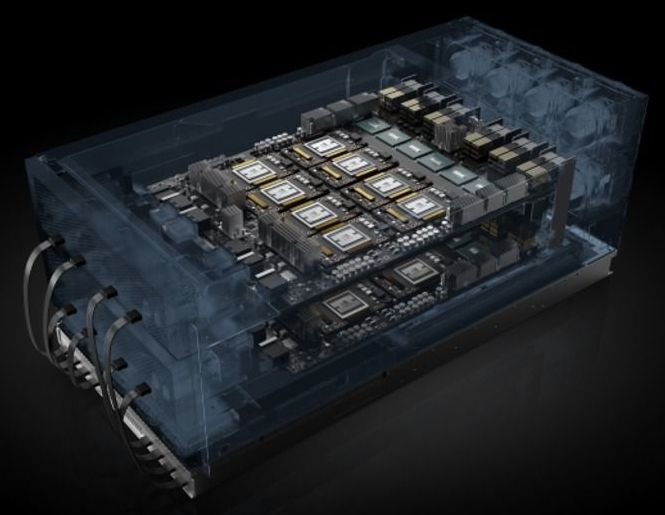
Russian researchers from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT), the Technological Institute for Superhard and Novel Carbon Materials (TISNCM), and the National University of Science and Technology MISIS have optimized the design of a nuclear battery generating power from the beta decay of nickel-63, a radioactive isotope. Their new battery prototype packs about 3,300 milliwatt-hours of energy per gram, which is more than in any other nuclear battery based on nickel-63, and 10 times more than the specific energy of commercial chemical cells. The paperwas published in the journal Diamond and Related Materials.
Conventional batteries
Ordinary batteries powering clocks, flashlights, toys, and other compact autonomous electrical devices use the energy of so-called redox chemical reactions. In them, electrons are transferred from one electrode to another via an electrolyte. This gives rise to a potential difference between the electrodes. If the two battery terminals are then connected by a conductor, electrons start flowing to remove the potential difference, generating an electric current. Chemical batteries, also known as galvanic cells, are characterized by a high power density — that is, the ratio between the power of the generated current and the volume of the battery. However, chemical cells discharge in a relatively short time, limiting their applications in autonomous devices. Some of these batteries, called accumulators, are rechargeable, but even they need to be replaced for charging. This may be dangerous, as in the case of a cardiac pacemaker, or even impossible, if the battery is powering a spacecraft.
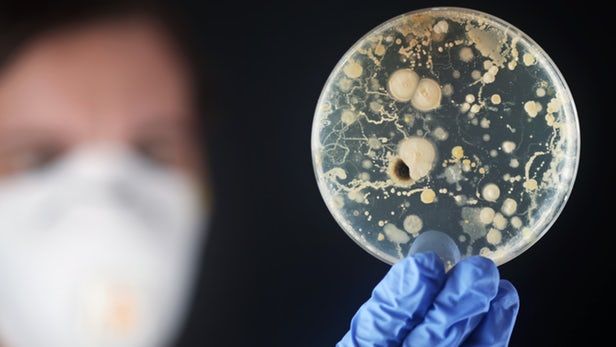
Forget zombies or killer robots – the most likely doomsday scenario in the near future is the threat of superbugs. Bacteria are evolving resistance to our best antibiotics at an alarming rate, so developing new ones is a crucial area of study. Now, inspired by a natural molecule produced by marine microorganisms, researchers at North Carolina State University have synthesized a new compound that shows promising antibacterial properties against resistant bugs.
Decades of overuse and overprescription of antibiotics has led to more and more bacteria becoming resistant to them, and the situation is so dire that a recent report warned that they could be killing up to 10 million people a year by 2050. Worse still, the bugs seem to be on schedule, with the ECDC reporting that our last line of defense has already begun to fail in large numbers.



The new field of biohybrid robotics involves the use of living tissue within robots, rather than just metal and plastic.
Researchers have developed a novel method of growing whole muscles from hydrogel sheets impregnated with myoblasts. They then incorporated these muscles as antagonistic pairs into a biohybrid robot, which successfully performed manipulations of objects. This approach overcame earlier limitations of a short functional life of the muscles and their ability to exert only a weak force, paving the way for more advanced biohybrid robots.

In 2022, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) collides with the smaller body of the Didymos binary asteroid system in an attempt to measurably shift its orbit.
ESA’s Hera mission, now under study, will examine the aftermath of this impact to help determine whether humans can deflect threatening asteroids.
Hera will also demonstrate the ability to operate at close proximity around a low-gravity asteroid with some on-board autonomy similar in scope to a self-driving car, going on to deploy Europe’s first deep-space CubeSats, and potentially also a micro-lander, to test out a new multi-point intersatellite link technology.

All Nippon Airways’ parent company ANA Holdings has made a Y200 million ($1.8 million) investment in commercial space flight company PD Aerospace.
The equity infusion, via a third-party allotment, comes on top of a Y20.4 million investment that the company made in October 2016.
“ANA is excited about the future of transportation and how PD Aerospace’s space technology will play an integral role,” says Yoshiaki Tsuda, vice-president of ANA Digital Design Lab. “We are increasing our support to help expedite the project’s timeline of testing and launching an unmanned spacecraft to an altitude of 100km.”
This weed-pulling robot is cheaper and better for the environment.