Mind reading technology is here.
Scientists have developed a program that can read your brainwaves and produce an image based on what you’re thinking about.
A few days ago, transhumanist author and politician Zoltan Istvan had an article published on The Maven titled “Transhumanism is Under Siege from Socialism.” It was there that he stated, “Transhumanists must favor the free world and free market to make its movement as powerful and successful as possible,” and must equally “be on their guard against[socialism].” I disagree — at least when it comes to the free market.
In order to survive the impending trend of proliferated automation, transhumanists must prepare for a future that is post-capitalist by nature.

I’m excited to share I’ll be speaking/debating at the upcoming #Biohack the Planet 2018 conference in Oakland on Aug 31 & Sept 1. Many interesting biohackers will be there. Tickets are still available and very reasonably priced right now, but they will likely sell out. Hope to see you there! Here’s the speaker list: http://biohacktheplanet.com/2018-speakers/ #transhumanism #biohacker & ticket page: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/biohack-the-planet-2018-ticket…
Bryan Johnson is the founder and CEO of Kernel, OS Fund and Braintree.
In 2016, Bryan invested $100M in Kernel to build advanced neural interfaces to treat disease and dysfunction, illuminate the mechanisms of intelligence, and extend cognition. Kernel is on a mission to dramatically increase our quality of life as healthy lifespans extend. He believes that the future of humanity will be defined by the combination of human and artificial intelligence (HI +AI). In 2014, Bryan invested $100M to start OS Fund which invests in entrepreneurs commercializing breakthrough discoveries in genomics, synthetic biology, artificial intelligence, precision automation, and new materials development. Bryan founded Braintree in 2007, later acquiring Venmo, which he sold to Ebay in 2013 for $800M. He is an outdoor-adventure enthusiast, pilot, and author of a children’s book, Code 7.

Michael Specter is a staff writer at The New Yorker.
Since joining the magazine in 1998, he has written about agricultural biotechnology, the global AIDS epidemic, avian influenza, malaria, the world’s diminishing freshwater resources, synthetic biology, geoengineering, new ways to edit DNA with CRISPR, and the implications of gene drive technology. His profile subjects include: Ingrid Newkirk, the founder of PETA, Dr. Oz, Peter Singer, Vandana Shiva, Miuccia Prada, and Richard Branson. Specter came to The New Yorker from the New York Times, where he had been a roving foreign correspondent based in Rome. From 1995 to 1998, Specter served as co-chief of The Times Moscow bureau. Before working at the Times he was the New York Bureau Chief of The Washington Post.


Harking back to Soviet big science, a 10-point plan calls for new organizations and focus areas, from job training to a giant new R&D campus.
The Russian Ministry of Defense is pursuing artificial intelligence with an urgency that has only grown since Vladimir Putin’s “rule the world” speech in September. But after several years of watching American and Chinese researchers accumulate breakthroughs and funding, while Russia continues to lack a relevant high-tech culture, Ministry leaders have decided that if they can’t outspend their global competitors, perhaps they can out-organize them.
So in March, the MOD — along with the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, or MES ; and the Russian Academy of Sciences — gathered domestic and international developers and users at a conference intended to take stock of the world’s AI prowess, and develop plans to focus Russia’s academic, scientific, and commercial communities to compete.
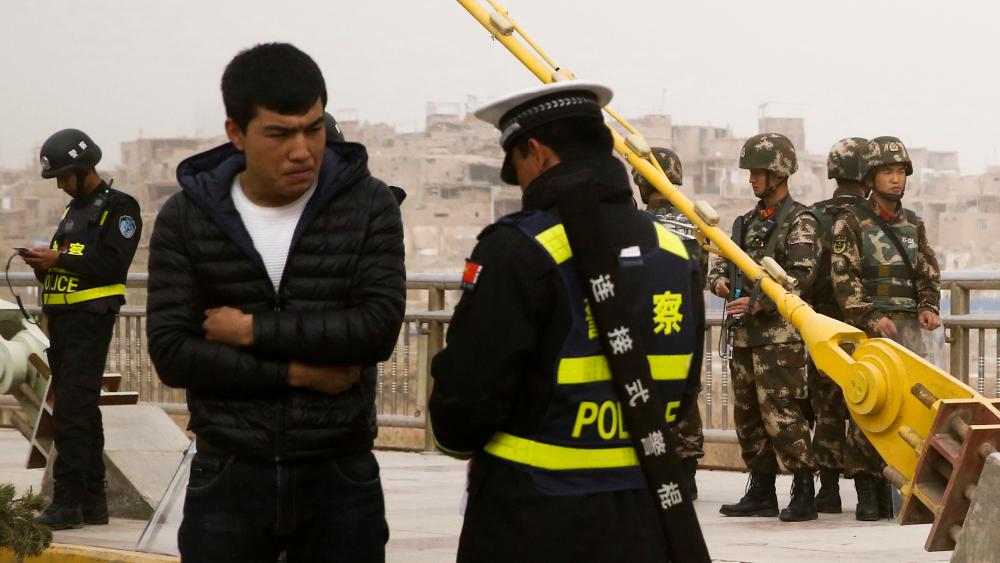

Just as competition between liberal democratic, fascist, and communist social systems defined much of the twentieth century, so the struggle between liberal democracy and digital authoritarianism is set to define the twenty-first.
The debate over the effects of artificial intelligence has been dominated by two themes. One is the fear of a singularity, an event in which an AI exceeds human intelligence and escapes human control, with possibly disastrous consequences. The other is the worry that a new industrial revolution will allow machines to disrupt and replace humans in every—or almost every—area of society, from transport to the military to healthcare.
There is also a third way in which AI promises to reshape the world. By allowing governments to monitor, understand, and control their citizens far more closely than ever before, AI will offer authoritarian countries a plausible alternative to liberal democracy, the first since the end of the Cold War. That will spark renewed international competition between social systems.
For decades, most political theorists have believed that liberal democracy offers the only path to sustained economic success. Either governments could repress their people and remain poor or liberate them and reap the economic benefits. Some repressive countries managed to grow their economies for a time, but in the long run authoritarianism always meant stagnation. AI promises to upend that dichotomy. It offers a plausible way for big, economically advanced countries to make their citizens rich while maintaining control over them.


Although i dont really like the idea of a different robot for every job, because you will get nickel and dimed to death.
If you love scrubbing the floors of your kitchen and bathrooms, then don’t get an iRobot Braava Jet 240. If you would rather let a plucky little robot do the mopping for you, then do get one, and leave this thankless household chore behind forever.

The big roll out Was going to be 2022, now looking like maybe 2027. There has been some shady stuff happening in the background in the USA to hold up self driving cars. It seems the people who were set to lose a lot of money on the changeover have found ways to hold it up.
Despite the rapid accumulation of testing miles, Krafcik warned the governors not to end all of their infrastructure investments just yet. Responding to a question about the need for new parking facilities, he responded that there will be a very long period of overlap between personally owned human driven vehicles and shared automated vehicles from Waymo and others. He suggested that it might be possible to slow down on some massive parking structures but was non-committal on timelines.
With Waymo planning to launch its commercial service by the end of 2018, GM coming in 2019 and others including Zoox, Daimler and Voyage in the next 2–3 years, there will be shared automated vehicles on the road. However, these will be limited to locations where they are demonstrated to function reliably and there is a market for ride-hailing despite the optimistic projections of some investors and developers. Widespread adoption in the millions of vehicles globally is unlikely before the latter half of the 2020s.
Krafcik was equally non-committal to Sandoval’s query about when he might be able to purchase his own car with Waymo technology. While Waymo and Fiat Chrysler are in talks about utilizing this virtual driver system on cars for retail sale, Krafcik said it’s going to be some time yet. The emphasis for now is the ride-hailing service, trucking and logistics and working with transit authorities. Supplying systems for personal use cars is last on the timeline.