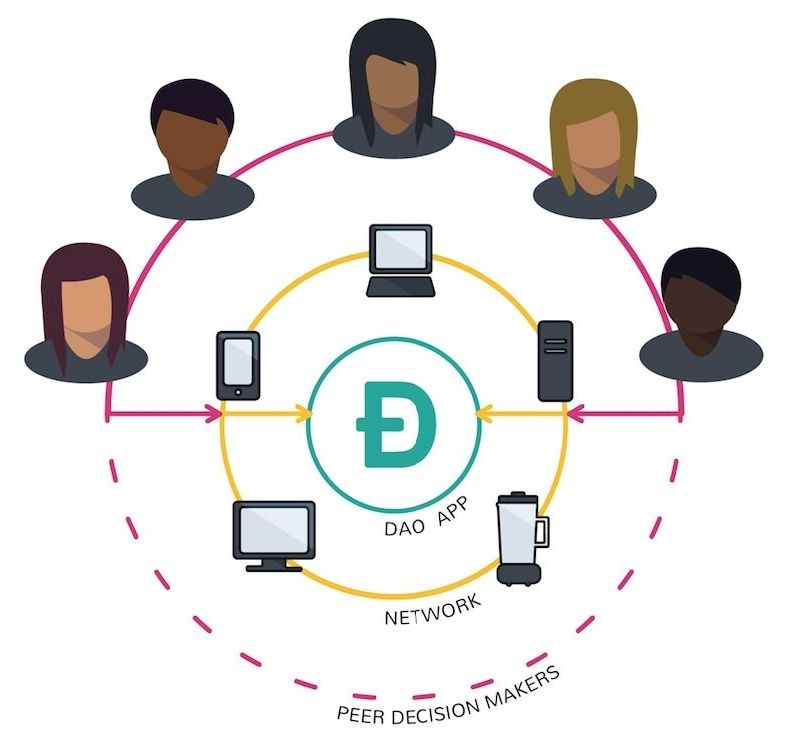
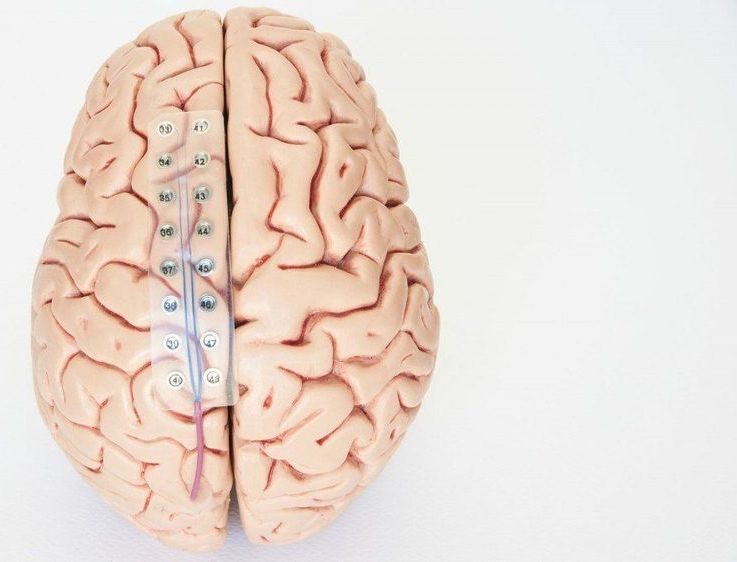
Over the last decade, military theorists and authors in the fields of future warfare and strategy have examined in detail the potential impacts of an ongoing revolution in information technology. There has been a particular focus on the impacts of automation and artificial intelligence on military and national security affairs. This attention on silicon-based disruption has nonetheless meant that sufficient attention may not have been paid to other equally profound technological developments. One of those developments is the field of biotechnology.
There have been some breathtaking achievements in the biological realm over the last decade. Human genome sequencing has progressed from a multi-year and multi-billion dollar undertaking to a much cheaper and quicker process, far outstripping Moore’s Law. Just as those concerned with national security affairs must monitor disruptive silicon-based technologies, leaders must also be literate in the key biological issues likely to impact the future security of nations. One of the most significant matters in biotechnology is that of human augmentation and whether nations should augment military personnel to stay at the leading edge of capability.
Military institutions will continue to seek competitive advantage over potential adversaries. While this is most obvious in the procurement of advanced platforms, human biotechnological advancement is gaining more attention. As a 2017 CSIS report on the Third Offset found most new technological advances will provide only a temporary advantage, assessed to be no more than five years. In this environment, some military institutions may view the newer field of human augmentation as a more significant source of a future competitive edge.