In an interview with Meta CTO Andrew Bosworth, the filmmaker weighs in on Stability AI and VFX, “in the style of” prompts, and whether input or outputs of models should be targeted: “We’re all models.”


How does the brain work? Where, and when, and why do neurons connect and send their signals? Scientists have created the largest wiring diagram and functional map of an animal brain to date to learn more. Research teams at Allen Institute, @BCMweb and @princeton worked together to map half a billion synapses, over 200,000 cells, and 4km of axons from a cubic millimeter of mouse brain, providing unparalleled detail into its structure and functional properties. The project is part of the Machine Intelligence from Cortical Networks (MICrONS) program, which seeks to revolutionize machine learning by reverse-engineering the algorithms of the brain. Research findings reveal key insights into brain activity, connectivity, and structure—shedding light on both form and function—within a region of the mouse visual cortex that plays a critical role in brain health and is often disrupted in neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, autism, and addiction. These insights could revolutionize our ability to treat neuropsychiatric diseases or study the influence of drugs and other changes on the brain.
This extraordinary achievement begins to reveal the elusive language the brain uses to communicate amongst its millions of cells and the cortical mechanisms of intelligence—one of the holy grails of science.
Learn more about this research: https://alleninstitute.org/news/scien… open science data: https://www.microns-explorer.org/ Explore the publications in Nature: https://www.nature.com/immersive/d428… Follow us on social media: Bluesky — https://bsky.app/profile/alleninstitu… Facebook — / alleninstitute X —
/ alleninstitute Instagram —
/ alleninstitute LinkedIn —
/ allen-institute TikTok —
/ allen.institute.
Access open science data: https://www.microns-explorer.org/
Explore the publications in Nature: https://www.nature.com/immersive/d428…
Follow us on social media:
Bluesky — https://bsky.app/profile/alleninstitu…
Facebook — / alleninstitute.
X — / alleninstitute.
Instagram — / alleninstitute.
LinkedIn — / allen-institute.
TikTok — / allen.institute
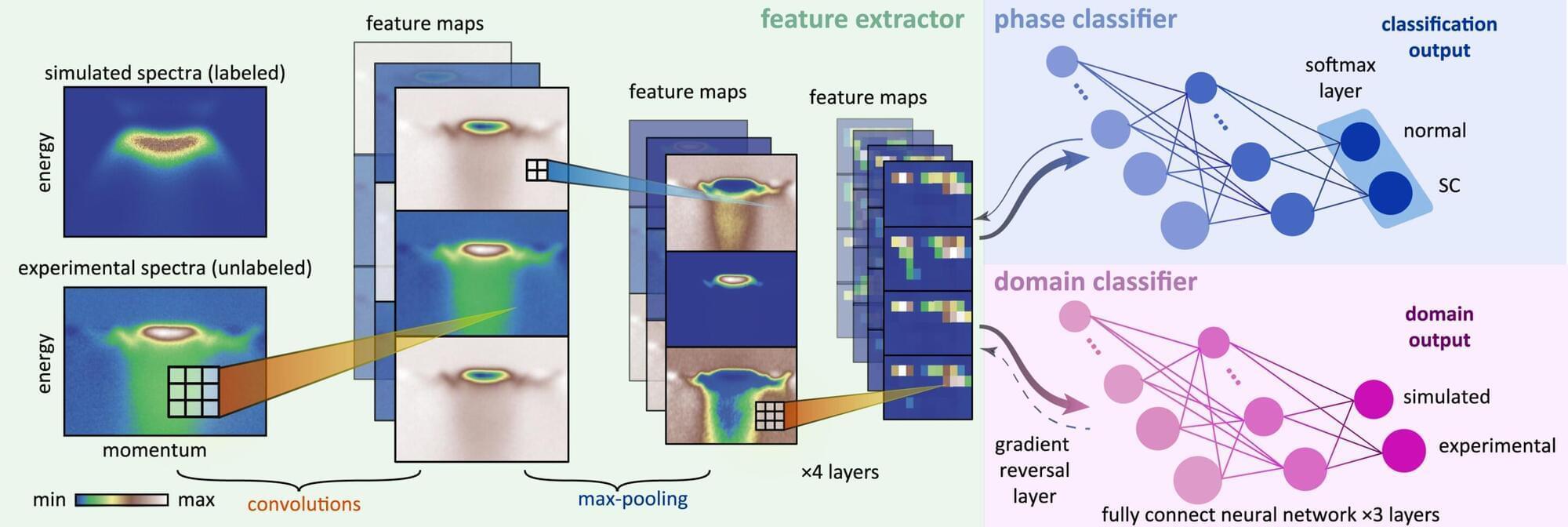
Using artificial intelligence shortens the time to identify complex quantum phases in materials from months to minutes, finds a new study published in Newton. The breakthrough could significantly speed up research into quantum materials, particularly low-dimensional superconductors.
The study was led by theorists at Emory University and experimentalists at Yale University. Senior authors include Fang Liu and Yao Wang, assistant professors in Emory’s Department of Chemistry, and Yu He, assistant professor in Yale’s Department of Applied Physics.
The team applied machine-learning techniques to detect clear spectral signals that indicate phase transitions in quantum materials—systems where electrons are strongly entangled. These materials are notoriously difficult to model with traditional physics because of their unpredictable fluctuations.
A machine learning method has the potential to revolutionize multi-messenger astronomy. Detecting binary neutron star mergers is a top priority for astronomers. These rare collisions between dense stellar remnants produce gravitational waves followed by bursts of light, offering a unique opportunit

In 2021, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) released a report detailing recently declassified information on Unidentified Aerial Phenomena (UAP).
Since then, the Department of Defense has released annual reports on UAP through the All-domain Anomaly Resolution Office (AARO). Nevertheless, there is still a lack of publicly available scientific data.
To address this, a new study led by the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) and the Galileo Project proposes an All-Sky Infrared Camera (Dalek) to search for potential indications of extraterrestrial spacecraft.


Hackers started exploiting a high-severity flaw that allows bypassing authentication in the OttoKit (formerly SureTriggers) plugin for WordPress just hours after public disclosure.
Users are strongly recommended to upgrade to the latest version of OttoKit/SureTriggers, currently 1.0.79, released at the beginning of the month.
The OttoKit WordPress plugin allows users to connect plugins and external tools like WooCommerce, Mailchimp, and Google Sheets, automate tasks like sending emails and adding users, or updating CRMs without code. Statistics show that the product is active on 100,000 websites.

How will AI shape our understanding of our creativity and ourselves?
In February, artist and technologist K Allado-McDowell delivered a fascinating Long Now Talk that explored the dimensions of Neural Media — their term for an emerging set of creative forms that use artificial neural networks inspired by the connective design of the human brain.
Their Long Now Talk is a journey through the strange valleys and outcroppings of this age of neural media, telling a story involving statistical distributions, anti-aging influencers at war with death itself, and vast quantities of “AI Slop,” the low-quality, faintly surreal output of cheap, rapidly proliferating image models.
Yet even in this morass of slop Allado-McDowell sees reason for optimism. Referring to the title of their 2020 book Pharmako-AI, which was co-written with GPT-3, Allado-McDowell notes that the Greek word pharmakon could mean both drug and cure. What may seem poisonous or dangerous in this new paradigm of neural media could also unlock for us new and deeper ways of understanding ourselves, our planet, and all of the intelligent networks that live within it.
This talk was presented February 25, 02025 at the Cowell Theatre in San Francisco. The event livestream is here: https://www.youtube.com/live/AsCGRjl3zac?si=KBfIfkqatLwdMr8M
Episode notes: https://longnow.org/ideas/neural-media/
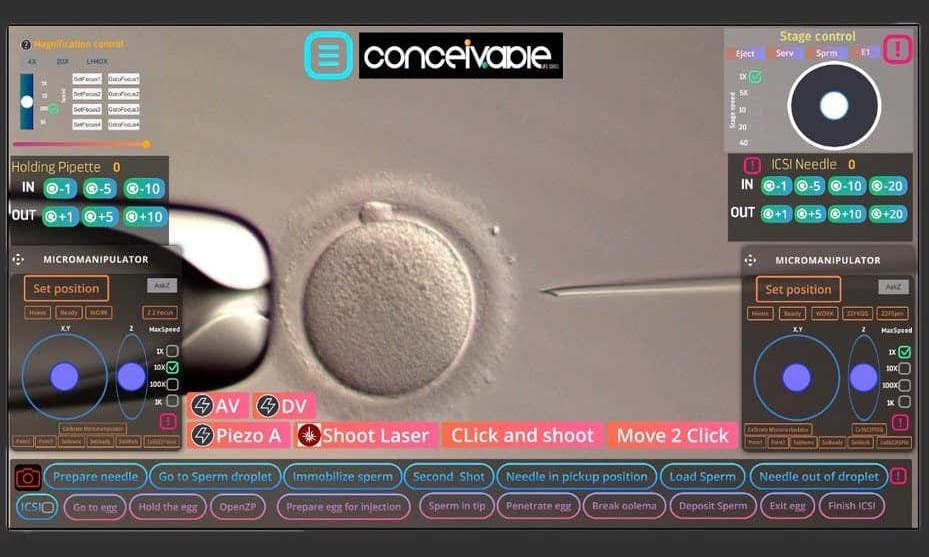
A highly automated form of in vitro fertilisation (IVF) has led to a successful birth, raising hopes that this approach could cut the risk of human error during such procedures.
One method of IVF is intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where sperm is injected into eggs in a lab dish. This is commonly used in cases of male infertility, as the sperm don’t have to work to reach an egg. Any resulting embryos are then inserted into the uterus. IVF can also be done by mixing sperm and eggs in a lab dish in the hope that fertilisation will take place, which is generally less successful, but also requires less medical intervention.
Image: Conceivable Life Sciences
A baby has been born after being conceived via IVF performed by a machine, with a medical professional merely overseeing the process.
By Carissa Wong