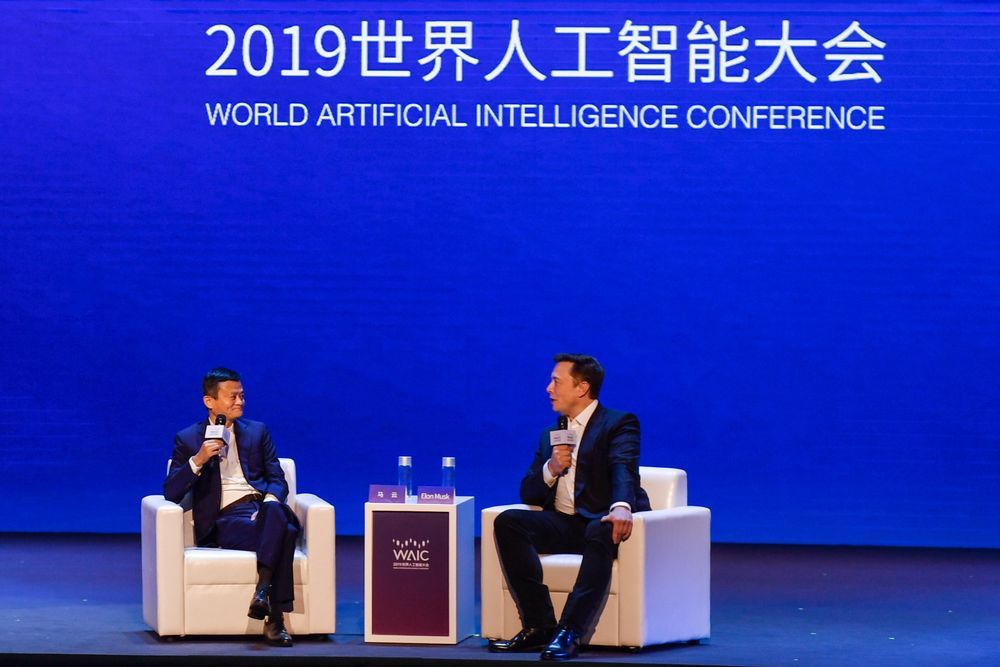
Tesla CEO Elon Musk pointed to advances in artificial intelligence as evidence that we are smarter than computers in fewer and fewer realms.



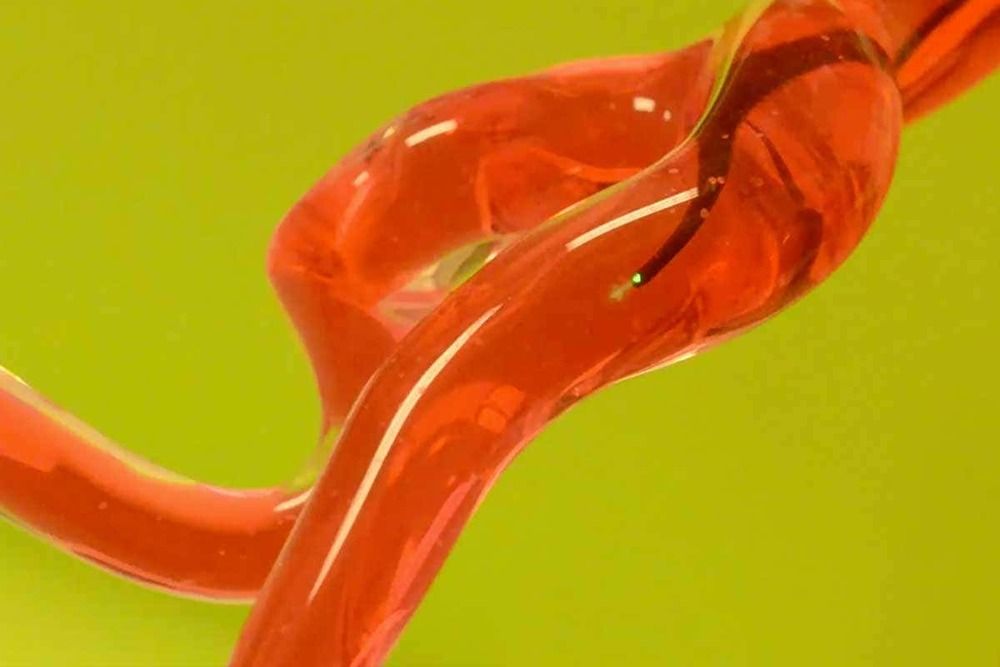
Robotics engineers at MIT have built a threadlike robot worm that can be magnetically steered to deftly navigate the extremely narrow and winding arterial pathways of the human brain. One day it could be used to quickly clear blockages and clots that contribute to strokes and aneurysms, while at the same time making the current state of robotic evolution even more unsettling.
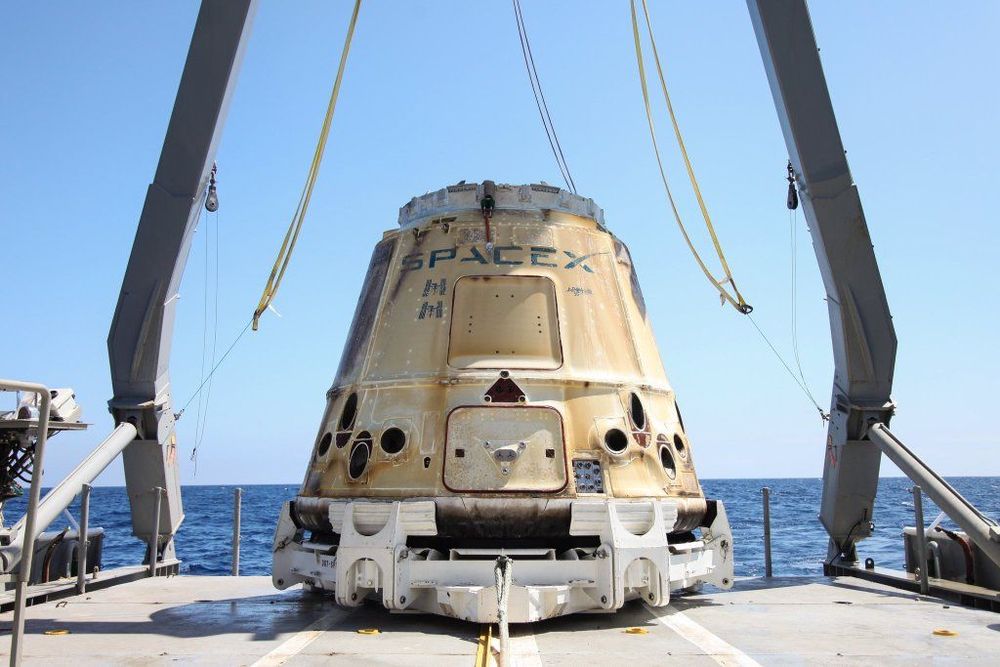

A SpaceX Dragon capsule that set down in the Pacific Ocean on Tuesday after having been docked at the International Space Station since late July became the first such vehicle to do three of those trips. SpaceX uses its Dragon cargo capsule to ferry experiment materials, supplies and more to and from the ISS, and it also refurbishes and reflies these capsules when possible as part of its ongoing mission to make spaceflight more reusable, and therefore more economical.
After it splashed down yesterday, SpaceX recovered the capsule from the ocean and returned it to shore. The vehicle is loaded with return cargo from the ISS, with almost 2,700 pounds of materials and results from experiments, which NASA staff on the ground will now examine and study. Dragon carried more than 5,000 pounds of stuff to the Space Station, and over half of that was related to science and research missions. One of the return cargo items is actually a spherical robot called CIMON, and is basically a space-based smart speaker companion.

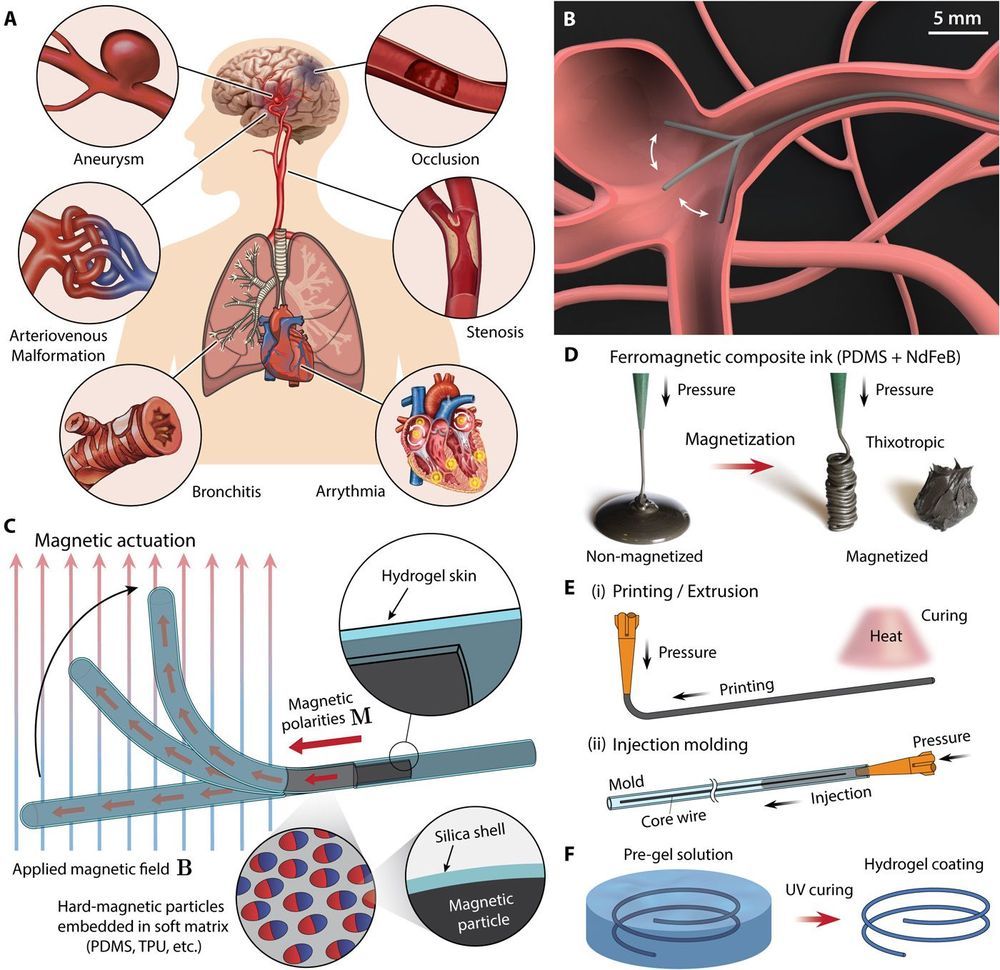
Small-scale soft continuum robots capable of active steering and navigation in a remotely controllable manner hold great promise in diverse areas, particularly in medical applications. Existing continuum robots, however, are often limited to millimeter or centimeter scales due to miniaturization challenges inherent in conventional actuation mechanisms, such as pulling mechanical wires, inflating pneumatic or hydraulic chambers, or embedding rigid magnets for manipulation. In addition, the friction experienced by the continuum robots during navigation poses another challenge for their applications. Here, we present a submillimeter-scale, self-lubricating soft continuum robot with omnidirectional steering and navigating capabilities based on magnetic actuation, which are enabled by programming ferromagnetic domains in its soft body while growing hydrogel skin on its surface. The robot’s body, composed of a homogeneous continuum of a soft polymer matrix with uniformly dispersed ferromagnetic microparticles, can be miniaturized below a few hundreds of micrometers in diameter, and the hydrogel skin reduces the friction by more than 10 times. We demonstrate the capability of navigating through complex and constrained environments, such as a tortuous cerebrovascular phantom with multiple aneurysms. We further demonstrate additional functionalities, such as steerable laser delivery through a functional core incorporated in the robot’s body. Given their compact, self-contained actuation and intuitive manipulation, our ferromagnetic soft continuum robots may open avenues to minimally invasive robotic surgery for previously inaccessible lesions, thereby addressing challenges and unmet needs in healthcare.
Small-scale soft continuum robots capable of navigating through complex and constrained environments hold promise for medical applications (1–3) across the human body (Fig. 1A). Several continuum robot concepts have been commercialized so far, offering a range of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures that are safer for patients owing to their minimally invasive nature (4–6). Surgeons benefit from remotely controlled continuum robots, which allow them to work away from the radiation source required for real-time imaging during operations (5, 6).
Despite these advantages, existing continuum robots are often limited to relatively large scales due to miniaturization challenges inherent in their conventional actuation mechanisms, such as pulling mechanical wires or controlling embedded rigid magnets for manipulation. Tendon-driven continuum robots (7–10) with antagonistic pairs of wires are difficult to scale down to submillimeter diameters due to increasing complexities in the fabrication process as the components become smaller (11–13). The miniaturization challenges have rendered even the most advanced form of commercialized continuum robots, mostly for cardiac and peripheral interventions (14), unsuited for neurosurgical applications due to the considerably smaller and more tortuous vascular structures. Magnetically steerable continuum robots (15–19) have also remained at large scale because of the finite size of the embedded magnets required to generate deflection under applied magnetic fields.

Just imagine what types of treatments, human enhancements, and other disorders could be solved with this technique. No more invasive GBM surgeries, Dystonia is finally treated and no longer a problem as well as other diseases and disorders that are located in areas like the basal ganglia area of the brain.
By Chris Stokel-Walker
A tiny robotic worm can wiggle its way through a model brain. It could eventually be used to make brain surgeries less invasive.
Yoonho Kim and his colleague Xuanhe Zhao at Massachusetts Institute of Technology created the robot out of a polymer with small magnetic particles embedded throughout, meaning it can be directed using a magnet. It is coated in a self-lubricating material and is less 0.6 millimetres in diameter.
One of the most difficult challenges in treating the brain cancer glioblastoma is that few drugs can pass through the blood-brain barrier. Scientists at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles have developed a system to circumvent this hurdle—one that combines a powerful immuno-oncology drug with a polymer-based delivery vehicle that can cross the blood-brain barrier.
The researchers showed that this “nano-immunotherapy” treatment crossed the blood-brain barrier in mouse models of glioblastoma, and that it stopped tumor cells from multiplying. They published their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
The Cedars-Sinai team used the polymer scaffold to deliver two types of immune checkpoint inhibitors, blocking either CTLA-4 or PD-1. When injected into the bloodstream of mice, the drugs quickly infiltrated brain tumors, but not healthy brain tissue, the researchers reported.
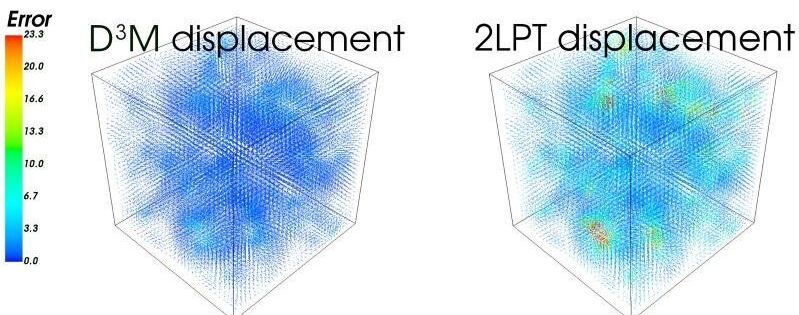
Researchers have successfully created a model of the Universe using artificial intelligence, reports a new study.
Researchers seek to understand our Universe by making model predictions to match observations. Historically, they have been able to model simple or highly simplified physical systems, jokingly dubbed the “spherical cows,” with pencils and paper. Later, the arrival of computers enabled them to model complex phenomena with numerical simulations. For example, researchers have programmed supercomputers to simulate the motion of billions of particles through billions of years of cosmic time, a procedure known as the N-body simulations, in order to study how the Universe evolved to what we observe today.
“Now with machine learning, we have developed the first neural network model of the Universe, and demonstrated there’s a third route to making predictions, one that combines the merits of both analytic calculation and numerical simulation,” said Yin Li, a Postdoctoral Researcher at the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, University of Tokyo, and jointly the University of California, Berkeley.

The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) puts out lots of public requests for scientific research, including high-profile competitions involving robotics and space launch tech. But today, the agency tweeted a very simple plea: it needs a massive, maze-like underground facility for running experiments, and it needs it right now.