In a newly published paper, researchers detail an experimental model that can extract device PINs and passphrases from the sounds of tapping fingers.


Circa 2019
Technology has long been helping to hack world hunger. These days most conversations about tech’s impact on any sector of the economy inevitably involves artificial intelligence—sophisticated software that allows machines to make decisions and even predictions in ways similar to humans. Food waste tech is no different.
A report from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation and Google estimates that technologies employing AI to “design out food waste” could help generate up to $127 billion a year by 2030. These technologies range from machine vision that can spot when fruit is ready to be picked to algorithms that forecast demand in order to ensure retailers don’t overstock certain foods.
One London-based startup that has been generating headlines by reducing food waste is Winnow Solutions. The company took in $20 million in October from equity investments and loans to scale its AI platform, Winnow Vision, which identifies and weighs food waste for commercial kitchens. It then automatically assigns a dollar value to each scraped plate of fettuccine Alfredo or bowl of carrots dumped into its smart waste bin.

Key point: Washington knows it needs high-tech weapons and machines to win future wars. That includes robots to haul supplies and assist the Marines in winning any fight.
The U.S. Navy is moving quickly to develop robotic warships that could hunt submarines and other ships, screen aircraft carriers and convoys from air attack and sweep away enemy mines.
But there’s another mission the Navy should consider assigning to unmanned surface vessels, Neil Zerbe, a retired Navy officer, argued for the Center for International Maritime Security: shuttling supplies from ship to shore in the aftermath of an amphibious assault by U.S. Marines.
Along with personal jetpacks for every man, woman, and child (sure, why not), levitation is one of those conveniences that sci-fi has long promised us but has yet to deliver, other than magnetically levitating trains. But at Argonne National Laboratory in Illinois, physicist Chris Benmore and his colleagues are levitating objects with an unlikely tool: sound. It’s called acoustic levitation, and after breaking your brain with what seems to be an optical illusion, it’s poised to deliver advances in pharmacology, chemistry more broadly, and even robotics.
In the future, you can set-up personal mini-networks with people you would like to share your thoughts…
#AI #DL #DataScience #Robotics #FinServ #AI #MachineLearning #DeepLearning #BigData #Fintech #Insurtech #Datascience #Marketing #ML #DL #Robotics #HealthTech #martech #tech
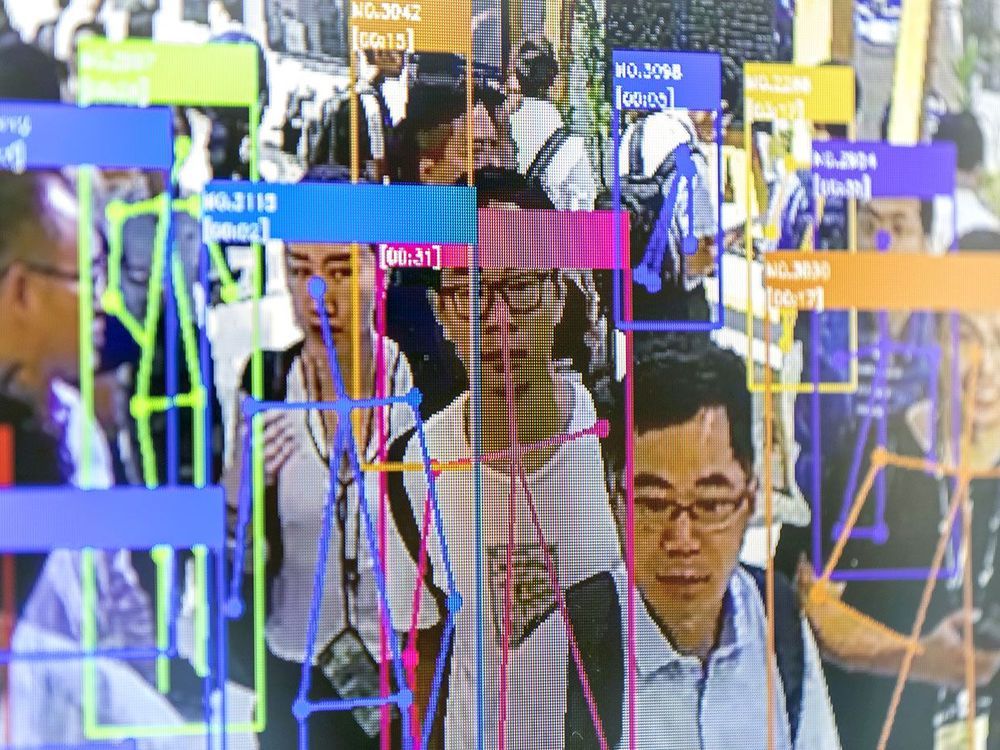

I’m excited to share my new opinion piece on AI facial recognition and privacy for IEEE Spectrum:
The views expressed here are solely those of the author and do not represent positions of IEEE Spectrum or the IEEE.
Many people seem to regard facial-recognition software in much the same way they would a nest of spiders: They recognize, in some abstract way, that it probably has some benefits. But it still gives them the creeps.
It’s time for us to get over this squeamishness and embrace face recognition as the life-enhancing—indeed, life–saving—technology that it is. In many cities, closed-circuit cameras increasingly monitor streets, plazas, and parks around the clock. Meanwhile, the price of recognition software is decreasing, while its capabilities are increasing.
I welcome these trends. I want my 9-year-old daughter tracked while she walks alone to school. I want a face scanner at Starbucks to simply withdraw the payment for my coffee from my checking account. I want to board a plane without fumbling for a boarding pass. Most of all, I want murderers or terrorists recognized as they walk on a city street and before they can cause further mayhem.
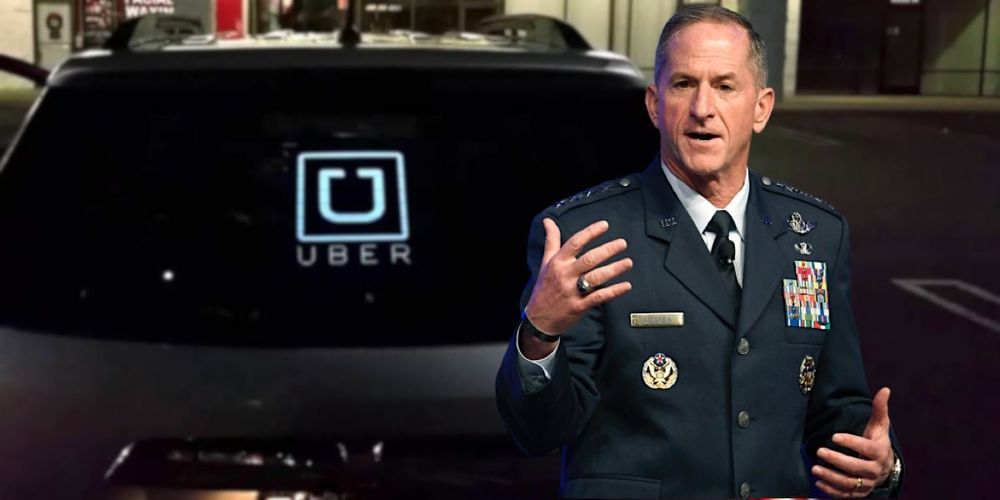

The Air Force’s top general says one of the designers of the ride-sharing app Uber is helping the branch build a new data-sharing network that the Air Force hopes will help service branches work together to detect and destroy targets.
The network, which the Air Force is calling the advanced battle management system (ABMS), would function a bit like the artificial intelligence construct Cortana from Halo, who identifies enemy ships and the nearest assets to destroy them at machine speed, so all the fleshy humans need to do is give a nod of approval before resuming their pipe-smoking.
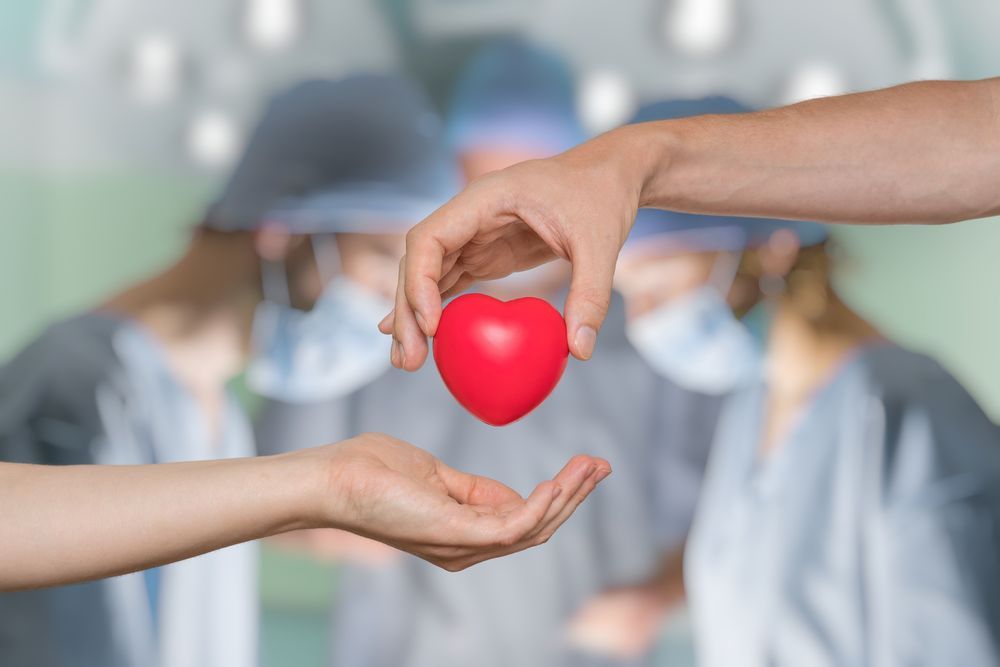

The world’s first completely robotic heart may end the need for transplants from dead humans in as few as 10 years, the hybrid heart made of soft artificial muscles and sensors is hoped to eventually end the need for human transplants.
The hybrid robotic heart is under development and could clear NHS heart transplant waiting lists and save many lives. It is the first hybrid heart made from soft artificial muscles and sensors which are coated in human tissues that are grown in a laboratory.
There are plans partnered with the British Heart Foundation to transplant it into the first person in 2028; the hope is that this hybrid robotic heart will save thousands of lives who would normally have died while waiting for a human organ donor on global waiting lists.
A team of researchers have built what they claim to be the first living robots. The “xenobots,” they say, can move, pick up objects, and even heal themselves after being cut.
The team is hoping the biological machines could one day be used to clean up microplastics in the ocean or even deliver drugs inside the human body, The Guardian reports.
To build the robots, the team used living cells from frog embryos and assembled them into primitive beings.
Taiwan has been the world’s hardware hub for decades, so the shift toward AI makes the most of the existing inexpensive engineering talent. A refocus on AI, however, reduces reliance on hardware, which can easily be made somewhere else, such as China, at lower costs. Multinational tech companies have already shown interest in tapping Taiwan’s talent in software, including AI.
To move things along further, the government of Hsinchu County, near Taipei, will open a 126,000-square-meter (about 1.3 million square feet) AI business park near one of Taiwan’s major all-purpose high-tech zones and two top universities.
“[The park] will not just help [promote] industry-academia cooperation, but also let AI-oriented startups and companies have a demo space to verify AI product services,” says Shirley Tsai, a research manager with IDC Taiwan’s enterprise solution group. “It will be helpful as well to attract the companies who are interested in the AI field and then accelerating the AI ecosystem.”