The idea is to use AI to develop a platform for detecting biomarkers from neural data. Then long-life neural interfaces (connections that allow computers to read and write neural data directly to and from the body) could be combined with a deep intelligence system trained to assess biomarkers directly from neural data.
If the AI platform is able to understand the “language” of the nervous system it could be used in closed-loop experiments to test neuromodulation therapy on new targets. This could accelerate the development of treatments for a number of chronic conditions and would also be a big step closer to real-world clinical applications of AI within the body. This progress could create a new way to investigate medical conditions, accelerate the detection of neural biomarkers, and open the door to a new generation of AI-based neural medical procedures.
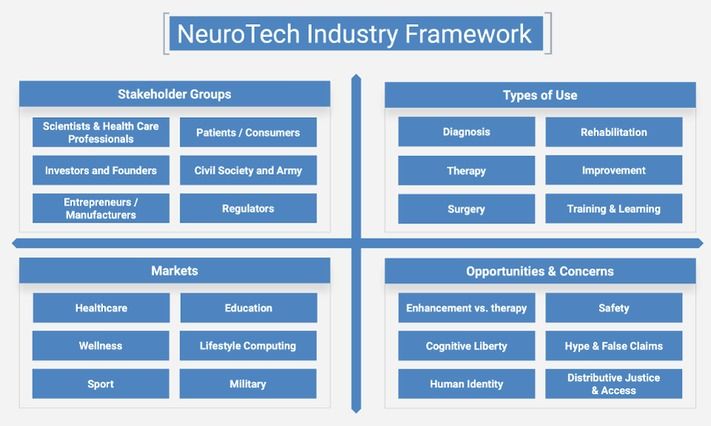
NeuroTech is one of the most promising areas of BioTech. In the last 20 years private capital funds invested more than $19 billion in the sector, and annual growth of investment in the sector is 31%. Some NeuroTech subsectors are already well-established with practical implementations and products on the market. Over the next several years, many early-stage startups will evolve into mature companies and bring new NeuroTech products to market. Advances in AI and increased integration of computers and biology could lead to improved brain health for people all over the world.