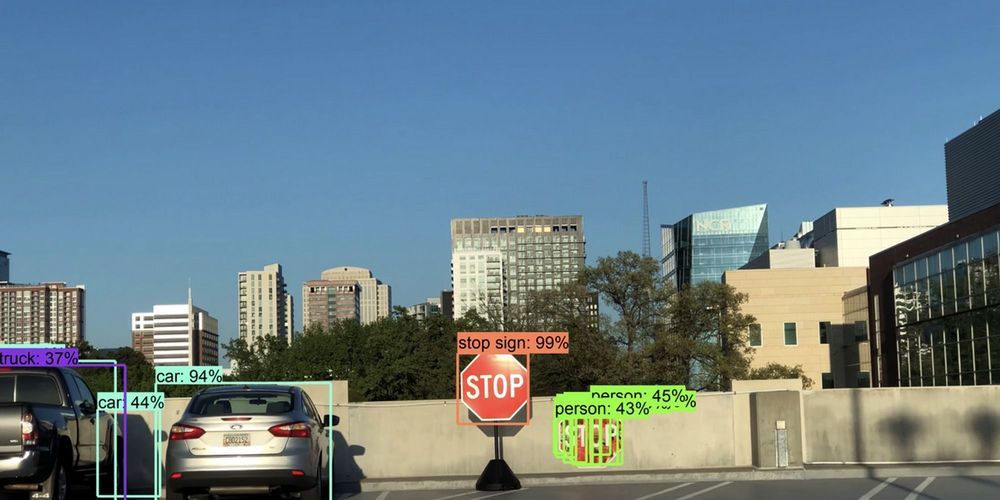
Is that a person or a stop sign? Intel and Georgia Tech are spearheading efforts against adversarial attacks that fool machine learning systems into making such mistakes.
Photo: Georgia Institute of Technology.

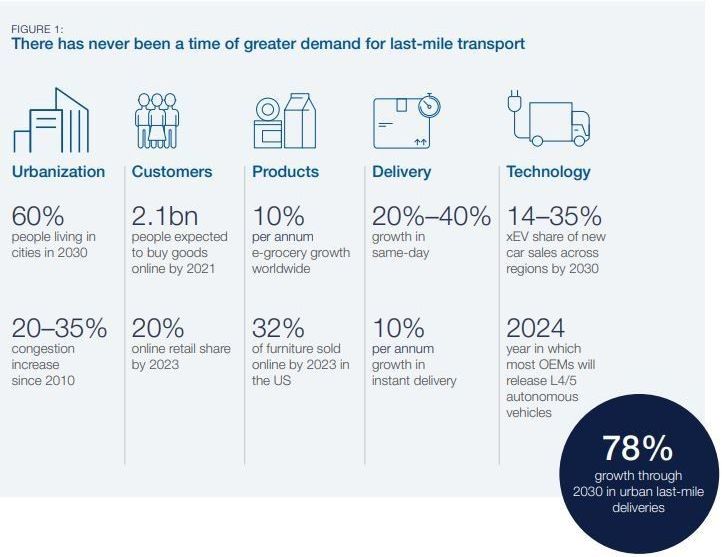
The COVID-19 pandemic has put an incredible strain on global supply chains, from medical supplies to household goods, as spikes in demand stress-test logistics infrastructures. There is an opportunity for unmanned delivery vehicles to assist in addressing this demand and help to reduce the risk of spreading infection.
Here’s a look at some of the challenges and opportunities for automated vehicles (AVs) in last-mile deliveries and local logistics.

Starship Technologies has launched a robot food delivery service in Tempe, Ariz., as part of the autonomous delivery startup’s expansion plans following a $40 million funding round announced last August.
Starship Technologies, which was launched in 2014 by Skype co-founders Ahti Heinla and Janus Friis, has been ramping up commercial services in the past year, including a plan to expand to 100 universities by late summer 2021.
Now, with the COVID-19 pandemic forcing traditional restaurants to close and placing more pressure on gig economy workers, Starship Technologies has an opportunity to accelerate that growth.


Chip maker Intel has been chosen to lead a new initiative led by the U.S. military’s research wing, DARPA, aimed at improving cyber-defenses against deception attacks on machine learning models.
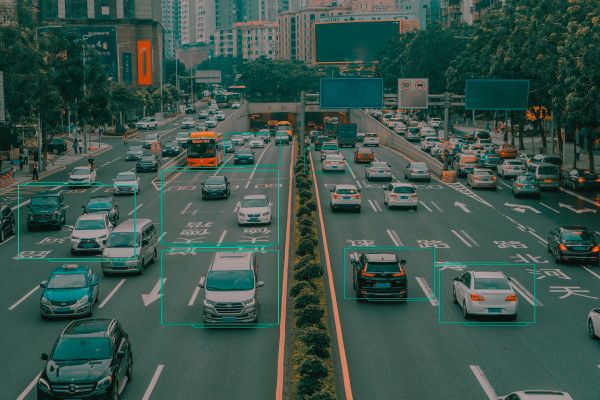
Machine learning is a kind of artificial intelligence that allows systems to improve over time with new data and experiences. One of its most common use cases today is object recognition, such as taking a photo and describing what’s in it. That can help those with impaired vision to know what’s in a photo if they can’t see it, for example, but it also can be used by other computers, such as autonomous vehicles, to identify what’s on the road.
But deception attacks, although rare, can meddle with machine learning algorithms. Subtle changes to real-world objects can, in the case of a self-driving vehicle, have disastrous consequences.

#Technology in #medicine: What will the #future #healthcare be like? https://www.neurozo-innovation.com/post/future-health Technologies have made many great impacts on our medical system in recent years. The article will first give a thorough summarization of them, and then the expectations and potential problems regarding future healthcare will be discussed. #AI #5G #VR #AR #MR #3DPrinting #BrainComputerInterface #telemedicine #nanotechnology #drones #SelfDriving #blockchain #robotics #innovation #trend
Technology has many beneficial effects on modern people’s lives, and one of them is to prolong our lifespan through advancing the medical field. In the past few years, new techniques such as artificial intelligence, robots, wearable tech, and so on have been used to improve the quality of our healthcare system, and some even newer innovations such as flying vehicles and brain computer interface are also considered valuable to the field. In this article, we will first give a thorough discussion about how these new technologies will shape our future healthcare, and then some upcoming problems that we may soon face will be addressed.

Focus is on Physical Sciences Research and Management of Complex Systems
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced a plan to provide up to $30 million for advanced research in machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) for both scientific investigation and the management of complex systems.
The initiative encompasses two separate topic areas. One topic is focused on the development of ML and AI for predictive modeling and simulation focused on research across the physical sciences. ML and AI are thought to offer promising new alternatives to traditional programming methods for computer modeling and simulation.
Replicating human interaction and behavior is what artificial intelligence has always been about. In recent times, the peak of technology has well and truly surpassed what was initially thought possible, with countless examples of the prolific nature of AI and other technologies solving problems around the world.
Think about this: Gary Kasparov stated that he would never lose a game of chess to a computer. For a long time, this seemed like a statement that would withstand all tests.
Roll on 1996, however, and IBM developed Deep Blue, a computer bot/program/application that beat the master Gary Kasparov at his own game.
These days, neural networks, deep learning and all types of sensors allow AI to be used in healthcare, to operate self-driving cars and to tweak our photos on Instagram.
In the #future, the ability to learn, to emulate the creative process and to self-organize may give rise to previously unimagined opportunities and unprecedented threats.
When 20 years ago, a computer beat a human at chess, it marked the dawn of Artificial Intelligence, as we know it.
These days, neural networks, deep learning and all types of sensors allow AI to be used in healthcare, to operate self-driving cars and to tweak our photos on Instagram.
In the #future, the ability to learn, to emulate the creative process and to self-organize may give rise to previously unimagined opportunities and unprecedented threats.
SUBSCRIBE TO RTD Channel to get documentaries firsthand! http://bit.ly/1MgFbVy
FOLLOW US
RTD WEBSITE: https://RTD.rt.com/
#RTD ON TWITTER: http://twitter.com/RT_DOC
RTD ON FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/RTDocumentary
RTD ON INSTAGRAM https://www.instagram.com/rtdocumentaries/
RTD LIVE https://rtd.rt.com/on-air/
#Documentary

As we enter our third decade in the 21st century, it seems appropriate to reflect on the ways technology developed and note the breakthroughs that were achieved in the last 10 years.
The 2010s saw IBM’s Watson win a game of Jeopardy, ushering in mainstream awareness of machine learning, along with DeepMind’s AlphaGO becoming the world’s Go champion. It was the decade that industrial tools like drones, 3D printers, genetic sequencing, and virtual reality (VR) all became consumer products. And it was a decade in which some alarming trends related to surveillance, targeted misinformation, and deepfakes came online.
For better or worse, the past decade was a breathtaking era in human history in which the idea of exponential growth in information technologies powered by computation became a mainstream concept.