A new iOS game from NASA asks players to identify the coral in 3D images of the ocean floor. Doing so will help train AI to do it automatically.


If you enjoyed this article or found it informative and wish to share it, you can do so from the following link: https://www.facebook.com/383136302314720/posts/564255487536133/
A.I. has already gotten to almost sci-fi levels of emulating brain activity, so much so that amputees can experience mind-controlled robotic arms, and neural networks might soon be a thing. That still wasn’t enough for the brains behind one ambitious startup, though.
Cortical Labs sounds like it could have been pulled from the future. Co-founder and CEO Hong Wen Chong and his team are merging biology and technology by embedding real neurons onto a specialized computer chip. Instead of being programmed to act like a human brain, it will use those neurons to think and learn and function on its own. The hybrid chips will save tremendous amounts of energy with an actual neuron doing the processing for them.
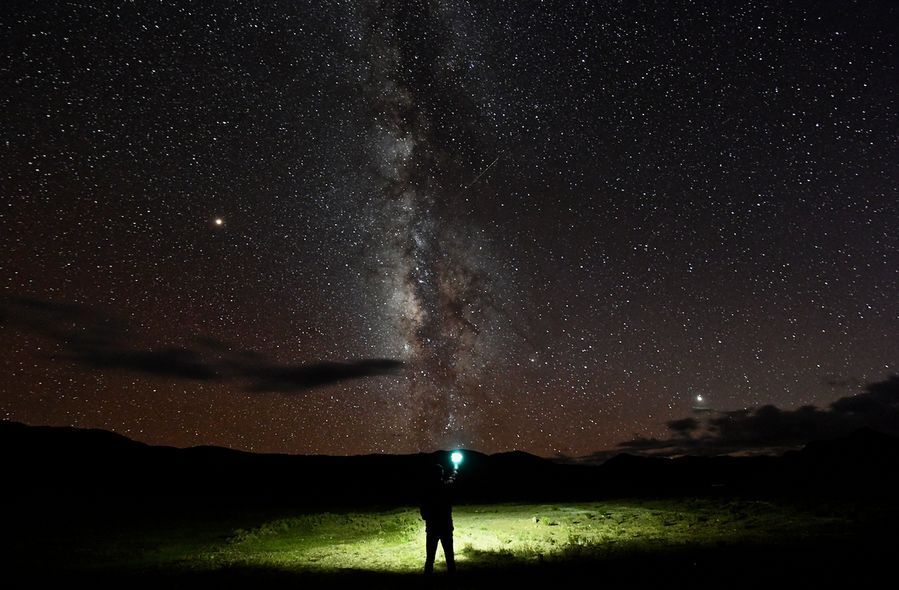


The Milky Way in the sky of Ali Prefecture, southwest China’s Tibet Autonomous Region, Sept.27, 2018. (Xinhua/Purbu Zhaxi)
The star, named LAMOST J040643.69+542347.8, has an estimated rotational velocity of 540 km per second, which is about 100 km per second faster than that of the previous record holder, HD 191423.
BEIJING, April 9 (Xinhua) — A Chinese astronomer has discovered the fastest rotating star in the Milky Way galaxy based on data from the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) located in Xinglong, in northern China’s Hebei Province.
I rarely use the words transformative or breakthrough for neuroscience findings. The brain is complex, noisy, chaotic, and often unpredictable. One intriguing result under one condition may soon fail for a majority of others. What’s more, paradigm-shifting research trends often require revolutionary tools. When we’re lucky, those come once a decade.
But I can unabashedly say that the 2010s saw a boom in neuroscience breakthroughs that transformed the field and will resonate long into the upcoming decade.
In 2010, the idea that we’d be able to read minds, help paralyzed people walk again, incept memories, or have multi-layered brain atlases was near incomprehensible. Few predicted that deep learning, an AI model loosely inspired by neural processing in the brain, would gain prominence and feed back into decoding the brain. Around 2011, I asked a now-prominent AI researcher if we could automatically detect dying neurons in a microscope image using deep neural nets; we couldn’t get it to work. Today, AI is readily helping read, write, and map the brain.
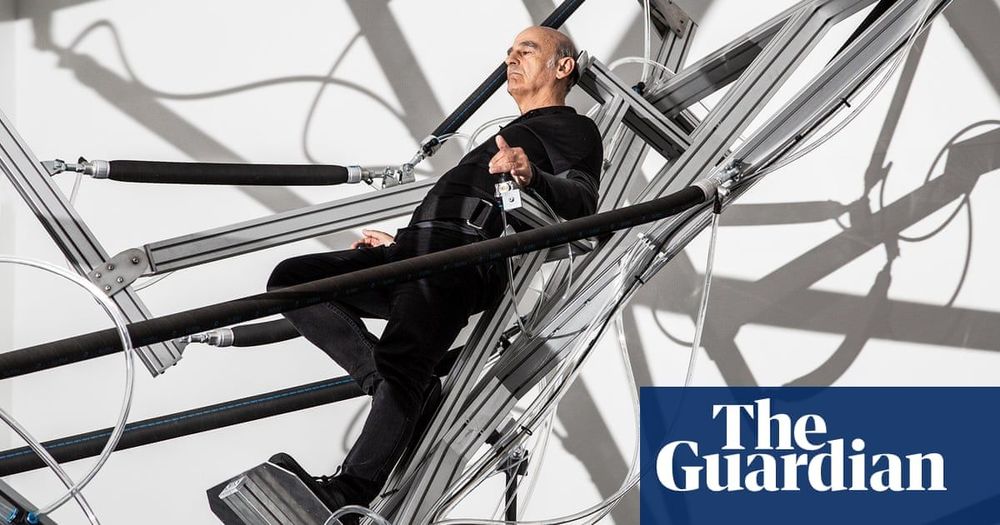

Stelarc has suspended himself from hooks and had an ear surgically constructed on his arm. Now his Adelaide biennial work puts the audience at the helm.

We could essentially use deep learning to get to the theory of everything if we digitize all processes.
By Rajat Jain, SAP
No single technology can ever replace humans and their unique value. Yet, the addition of hyperautomation is opening a world of new possibilities for the strategic nature of the employee experience – turning highly manual, labor-intensive tasks into nearly no-touch, rules-based processes.
Unquestionably, hyperautomation brings businesses closer to their vision of an intelligent enterprise that is customer-centric and operationally efficient. But first, innovation teams will need to rethink how they will deliver this technology capability. According to McKinsey, 70% of such complex and large digital initiatives do not achieve their stated goals. So it’s no wonder that only 6% of executives are satisfied with the performance of these efforts.
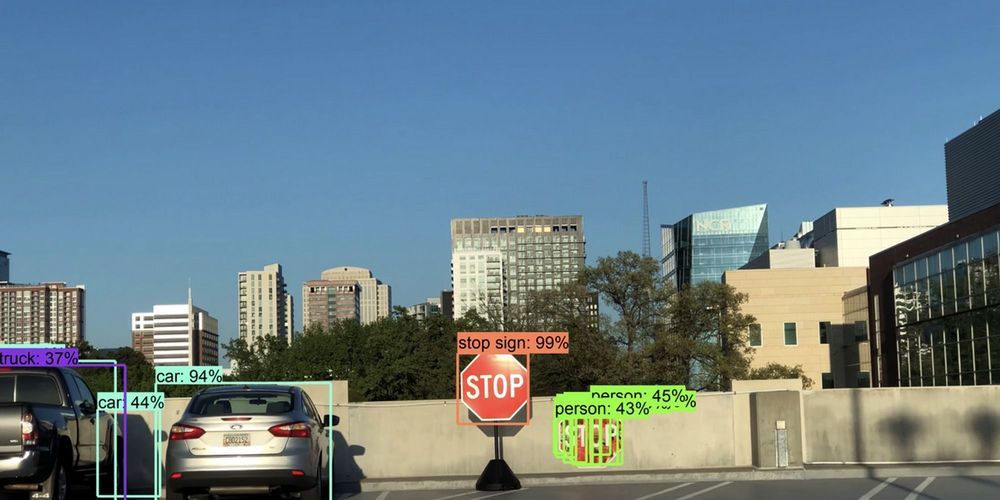

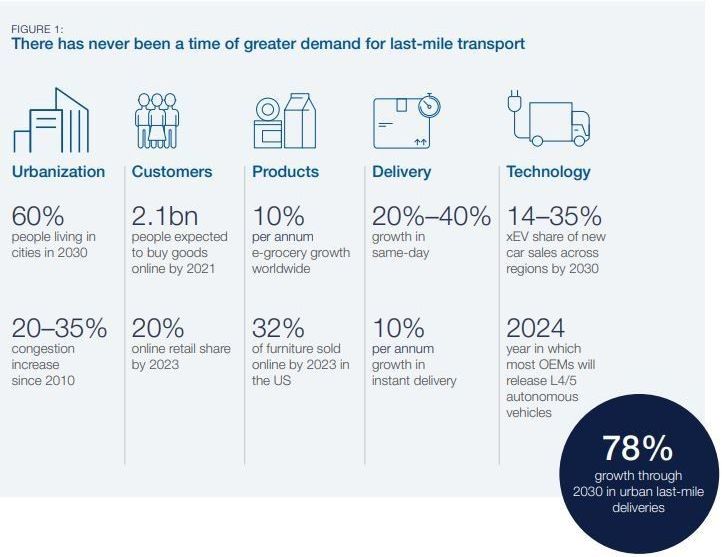
The COVID-19 pandemic has put an incredible strain on global supply chains, from medical supplies to household goods, as spikes in demand stress-test logistics infrastructures. There is an opportunity for unmanned delivery vehicles to assist in addressing this demand and help to reduce the risk of spreading infection.
Here’s a look at some of the challenges and opportunities for automated vehicles (AVs) in last-mile deliveries and local logistics.

Starship Technologies has launched a robot food delivery service in Tempe, Ariz., as part of the autonomous delivery startup’s expansion plans following a $40 million funding round announced last August.
Starship Technologies, which was launched in 2014 by Skype co-founders Ahti Heinla and Janus Friis, has been ramping up commercial services in the past year, including a plan to expand to 100 universities by late summer 2021.
Now, with the COVID-19 pandemic forcing traditional restaurants to close and placing more pressure on gig economy workers, Starship Technologies has an opportunity to accelerate that growth.