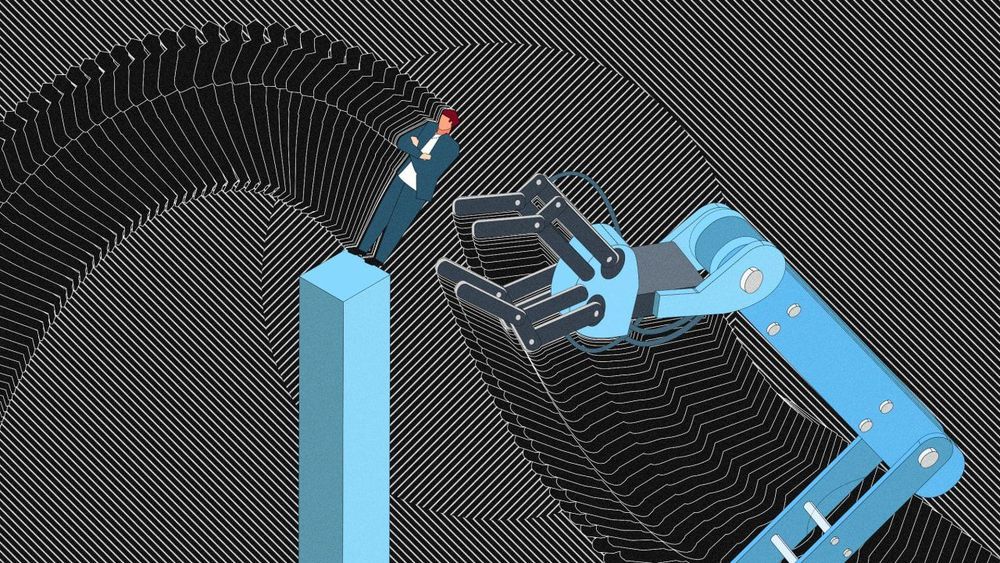
A robot might be great at its job. But that’s not enough to engender trust.
[Source Image: z_wei/iStock, AlfazetChronicles/iStock].

the photo series by vintner and fletcher illustrates three gradual stages of transhumanism from ‘testing ground’, ‘patient zero’ to ‘humanity 2.0’. at the lowest tier, ‘testing ground’ looks into individuals who have created wearable technology to expand their human abilities, improving everything from concentration to mental health.‘patient zero’ studies those who have taken permanent action to become half human and half robot. in the final chapter, ‘humanity 2.0’, the transhumanist subjects focus on life extension and immortality.



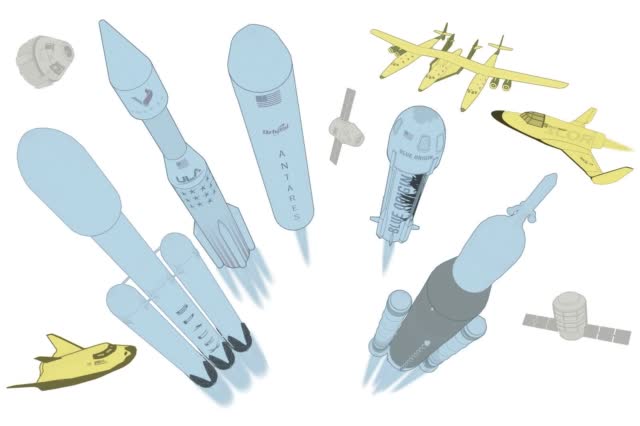
Boeing, an important player in the US space program for decades, hopes that its Starliner manned spacecraft will deliver astronauts to the International Space Station and the moon.
A software issue that prevented an unmanned test capsule from docking with the space station caused NASA to launch a review; preliminary results highlight serious safety concerns.
Boeing may have to attempt another test launch to meet the requirements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Development Program, which would cost it $410 million.


{{#pricinghref}} View pricing & plans {{/pricinghref}} {{^pricinghref}} {{#pricing.billedYearly.weekly.amount}} {{value}} per week {{/pricing.billedYearly.weekly.amount}} {{^pricing.billedYearly.weekly.amount}} {{#pricing.billedMonthly.trial.amount}} {{pricing.billedMonthly.trial.amount}} for 4 weeks {{/pricing.billedMonthly.trial.amount}} {{/pricing.billedYearly.weekly.amount}} {{/pricinghref}}.
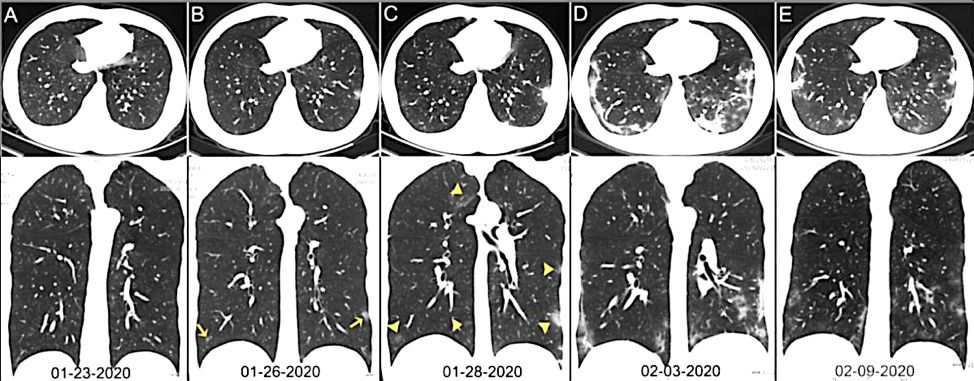
“At the moment, the YITU “Coronavirus Chest CT Smart Evaluation System” can compress the diagnosis of suspected cases to 2–3 seconds. The company also designed a chatbot doctor that can help the public with self-diagnosis through Q&A and recommend nearby hospitals and appointment booking services.”
An article published in medical journal the Lancelet on February 25 finds that reduced medical resource levels will trigger a spike in the coronavirus death rate in the local population beyond the current estimates. The study shows that death rates are over 3 percent in Wuhan city, 2.9 percent in Hubei province, while only 0.7 percent across the rest of China.
Close to 30,000 medical staff from across China have been dispatched to Hubei province to help overworked local medical professionals in the fight against COVID-19. Fast and accurate diagnosis is critical on the front line, and now an AI-powered diagnostic assessment system is helping Hubei medical teams do just that.
Currently, CT lung scans and nucleic acid tests are the two main diagnostic tools doctors use in confirming COVID-19 infections. CT imaging is crucial for diagnosis verification, and also allows doctors to access lung infection severity.