To get greater efficiency, Google DeepMind’s researchers did what chip designers have long done, built a pipeline so that the learning rule for machine learning — backpropagation — is more efficient.

A new prototype uses ultrasound waves to move objects.
In a recent IEEE Spectrum article, learn how engineers are taking machine learning to the smallest microprocessors, while facing challenges in energy consumption, compressing neural networks, and privacy practices. #tinyML #neuralnetworks #machinelearning
IN FEBRUARY, a group of researchers from Google, Microsoft, Qualcomm, Samsung, and half a dozen universities will gather in San Jose, Calif., to discuss the challenge of bringing machine learning to the farthest edge of the network, specifically microprocessors running on sensors or other battery-powered devices.
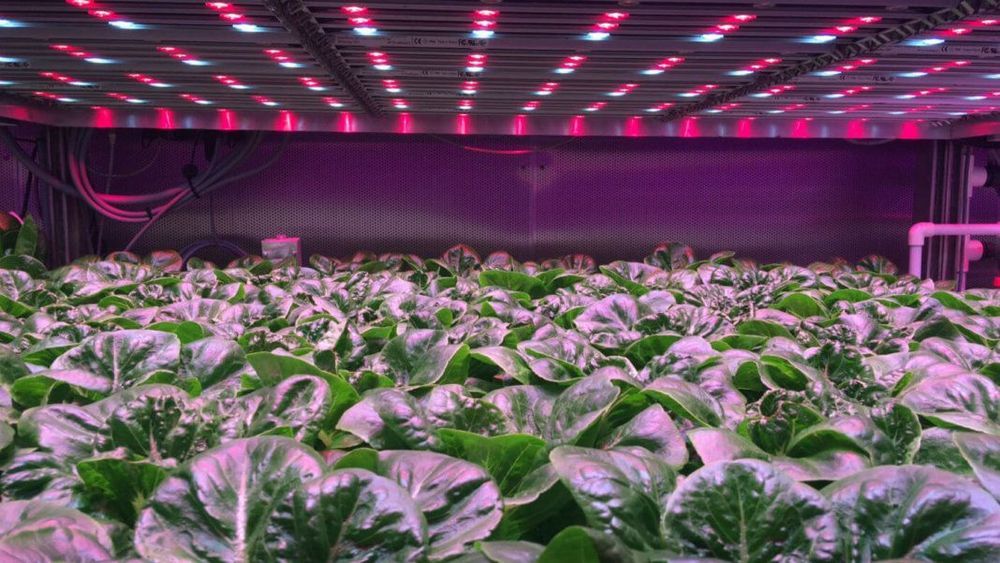

Within the next 10 years, what we eat and how it’s grown will be fundamentally transformed.
And converging exponential technologies—from materials science to AI-driven digital agriculture—are not slowing down. Today’s breakthroughs will soon allow our planet to boost its food production by nearly 70 percent, using a fraction of the real estate and resources, to feed 9 billion by mid-century.
What you consume, how it was grown, and how it will end up in your stomach will all ride the wave of converging exponentials, revolutionizing the most basic of human needs.
[Note: This article is an excerpt from my next book The Future Is Faster Than You Think, co-authored with Steven Kotler, to be released January 28th, 2020.]
Printing Food
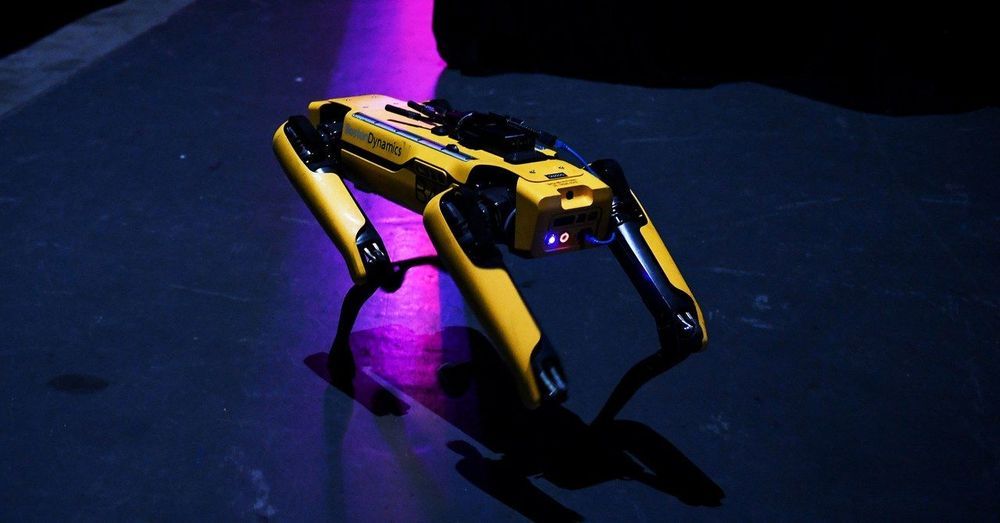

The founder of robot maker Boston Dynamics, Marc Raibert, is moving from CEO to chairman as the company prepares for a “new stage of growth.” The firm, well-known for its robotic creations, has been researching and developing its technology for decades, and it started leasing its first commercial robot, Spot, in 2019.

Evolutionary cyberneticist and digital philosopher Alex M. Vikoulov, author of The Syntellect Hypothesis, is interviewed by Agah Bahari, host and producer of NeoHuman podcast.
On this recent podcast, Alex Vikoulov, author of The Syntellect Hypothesis, is interviewed by NeoHuman podcaster Agah Bahari. Topics include evolutionary cybernetics, computational physics, consciousness, the simulation theory, the transcension hypothesis, the Global mind, AGI, VR, AR, psychedelics, technological singularities, transhumanism, Fermi Paradox, Digital Physics, objective reality, philosophy of mind, the extended mind hypothesis, absolute idealism, physics of time, the Omega Point cosmology, mind-uploading, synthetic telepathy, and more.
Watch a short intro here ↴.

Machines, especially through the power of AI, will surpass humans in Intelligence, effectiveness, and functionality.
Though there are some areas where humans will hold the dominance; mostly areas that require feeling and emotion.
But overall, machines will have capabilities that far surpass even the most Intelligent of humans.
