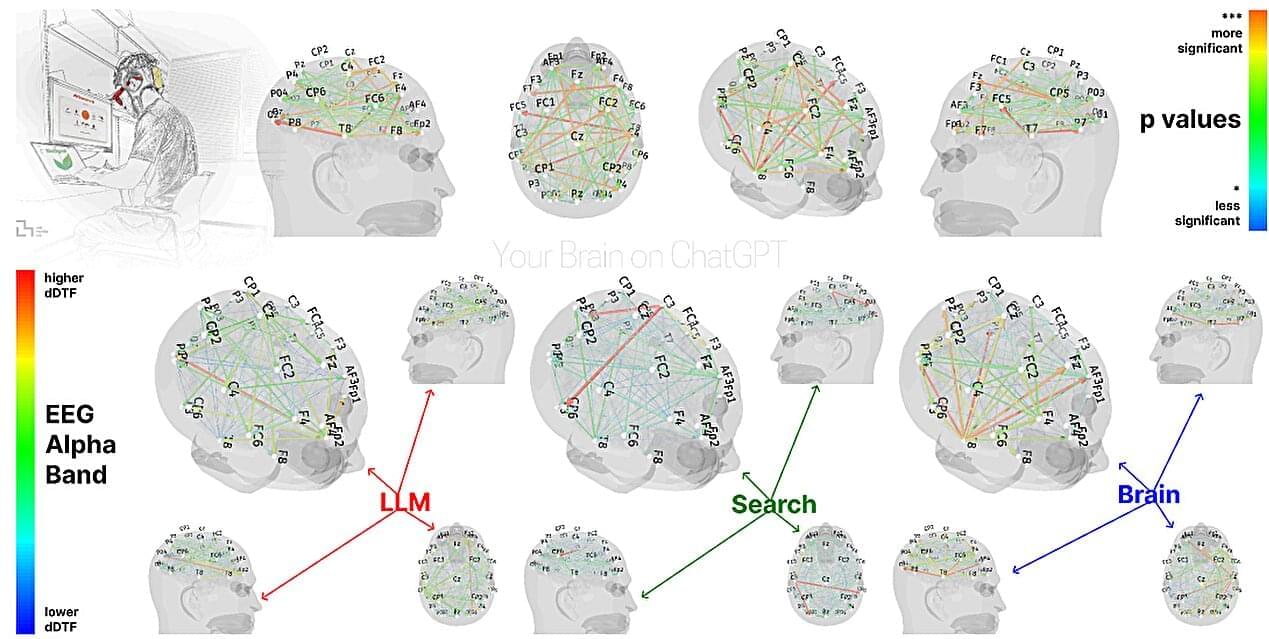
In this engaging new eighth episode of the AI Bros podcast, hosts John Lawson III and Bruce Burke delve into the dynamic world of artificial intelligence and its profound impact on various industries. The conversation kicks off with a discussion on the latest developments in AI, highlighting the massive investments being made by tech giants like Mark Zuckerberg, who recently acquired a significant stake in Scale AI. This move underscores the growing importance of data labeling in training AI models and the relentless pursuit of achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
The hosts explore the implications of AI on global infrastructure, particularly focusing on the energy demands required to support AI advancements. They discuss the necessity of building new data centers and the potential role of nuclear energy in meeting these demands. The conversation touches on the strategic moves by companies to secure energy resources, emphasizing the critical need for the U.S. to catch up with countries like China in terms of infrastructure development.
Transitioning to the realm of marketing and content creation, John and Bruce highlight how AI is revolutionizing these fields. They share insights into how AI tools are being used to automate tasks that were traditionally outsourced, such as virtual assistance, graphic generation, and scriptwriting. The hosts discuss the potential of AI to create high-quality content quickly and cost-effectively, as demonstrated by a recent AI-generated commercial aired during the NBA finals.
The episode also addresses the broader societal implications of AI, including the potential need for universal basic income (UBI) as AI continues to displace jobs. The hosts debate the feasibility of UBI in the U.S. and the challenges of implementing such a system. They reflect on historical technological advancements and the new job opportunities that AI might create, while acknowledging the uncertainty surrounding the pace and scale of these changes.
Throughout the episode, John and Bruce provide a balanced perspective on the opportunities and challenges presented by AI. They emphasize the importance of staying informed and adaptable in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. The hosts conclude with a forward-looking discussion on the future of AI in entertainment, speculating on the possibility of AI-generated feature films and the evolving role of AI in creative industries.
This episode is a must-listen for anyone interested in the intersection of technology, business, and society. It offers valuable insights into the transformative power of AI and its potential to reshape our world.
Join Bruce and John for the latest episode of The AI Bros Podcast. Subscribe, like, follow and share with your network. Thank you!