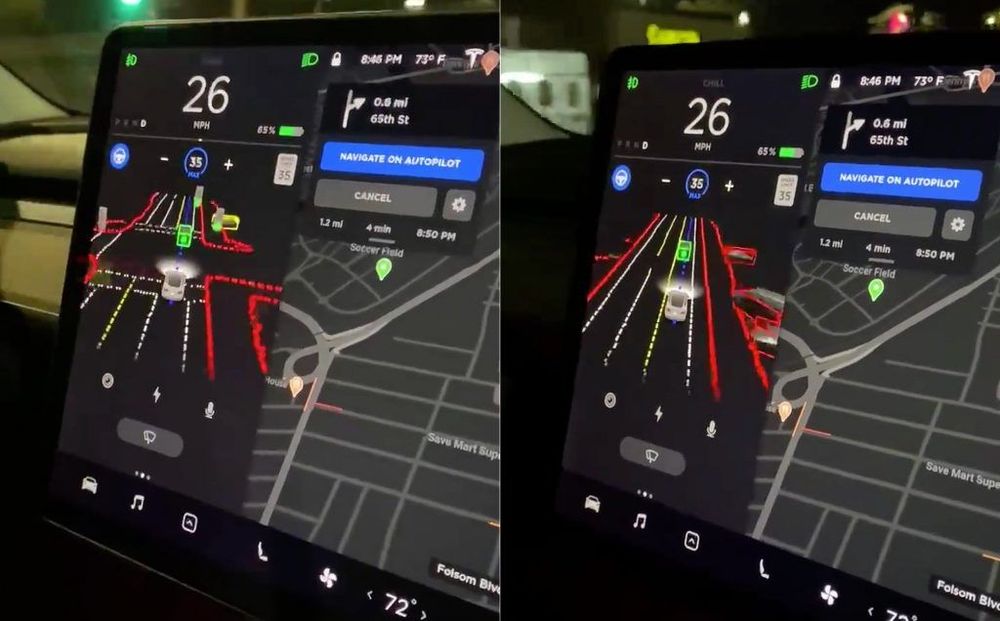
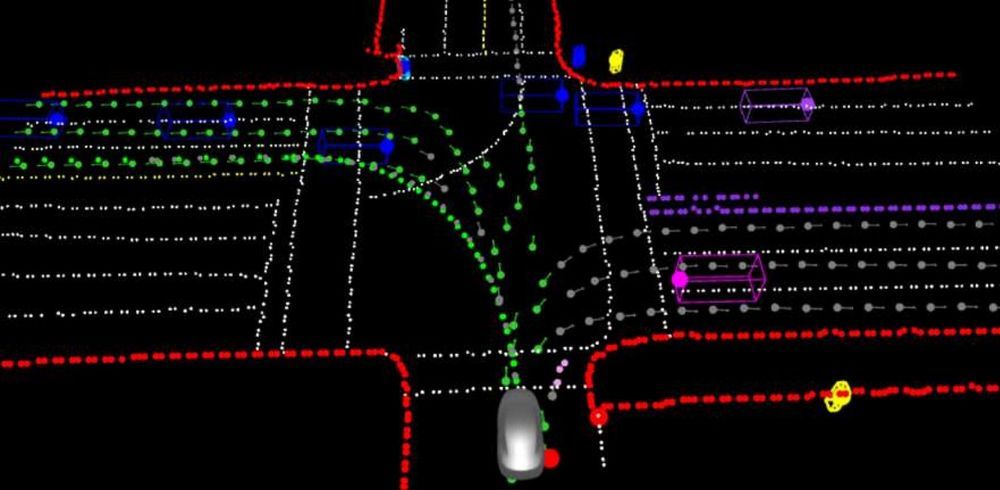
Tesla owners who are part of the limited Full Self-Driving rollout have started sharing some images and videos of the advanced driver-assist features in action. Based on videos and the Release Notes of the limited beta, it appears that Tesla is heavily emphasizing safety.
Among the lucky Tesla owners who received the update were @brandonee916 and the @teslaownerssv group, both of whom shared a images and short clips of the limited Full Self-driving beta in action.
Overall, the UI of the limited beta seems to be quite rough in its current state. With this in mind, there seems to be a good chance that the visuals of FSD will be more refined by the time it gets a wider release.