Around 1,500 Latin inscriptions are discovered every year, offering an invaluable view into the daily life of ancient Romans—and posing a daunting challenge for the historians tasked with interpreting them.
But a new artificial intelligence tool, partly developed by Google researchers, can now help Latin scholars piece together these puzzles from the past, according to a study published on Wednesday.
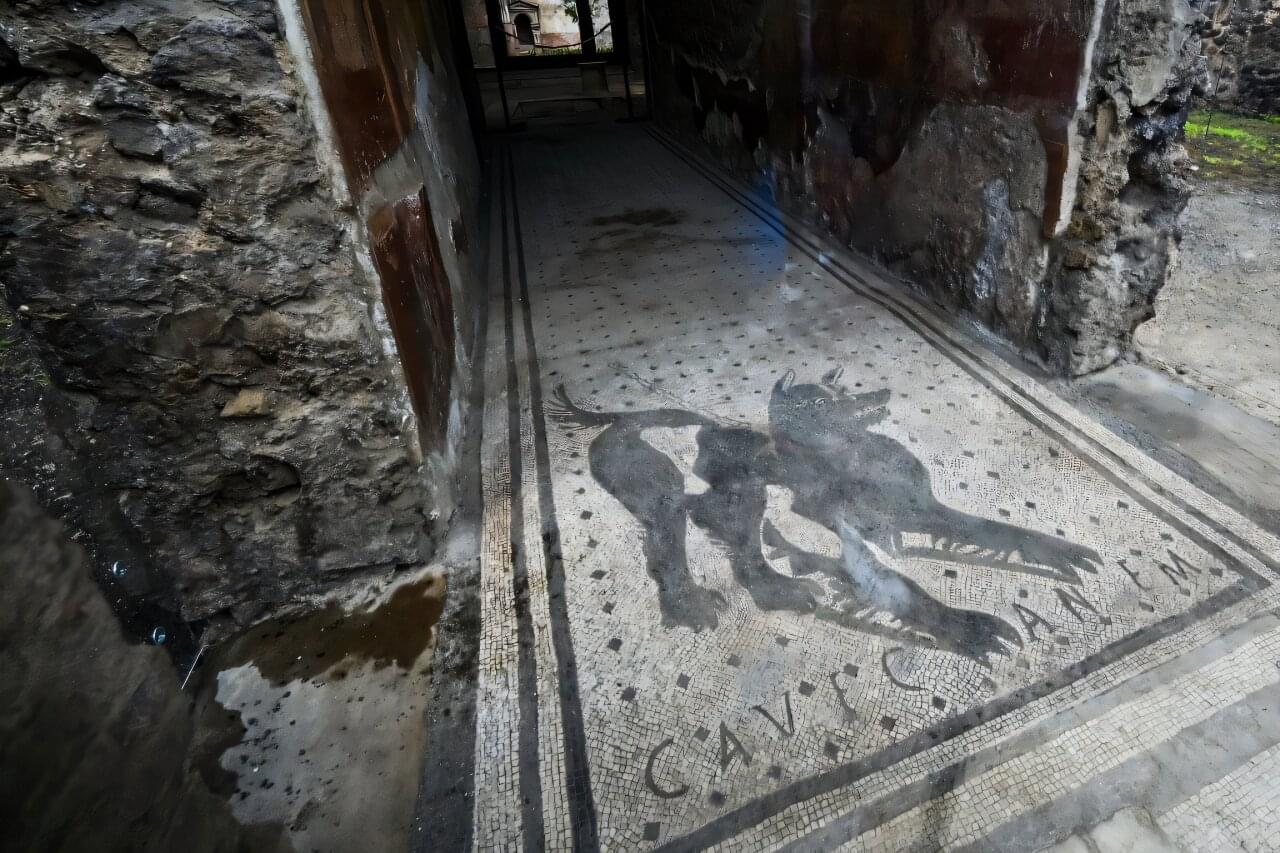
Inscriptions in Latin were commonplace across the Roman world, from laying out the decrees of emperors to graffiti on the city streets. One mosaic outside a home in the ancient city of Pompeii even warns: “Beware of the dog”