Neuralink is building a brain-machine interface as well as a little robot that installs it into your skull.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 2,071
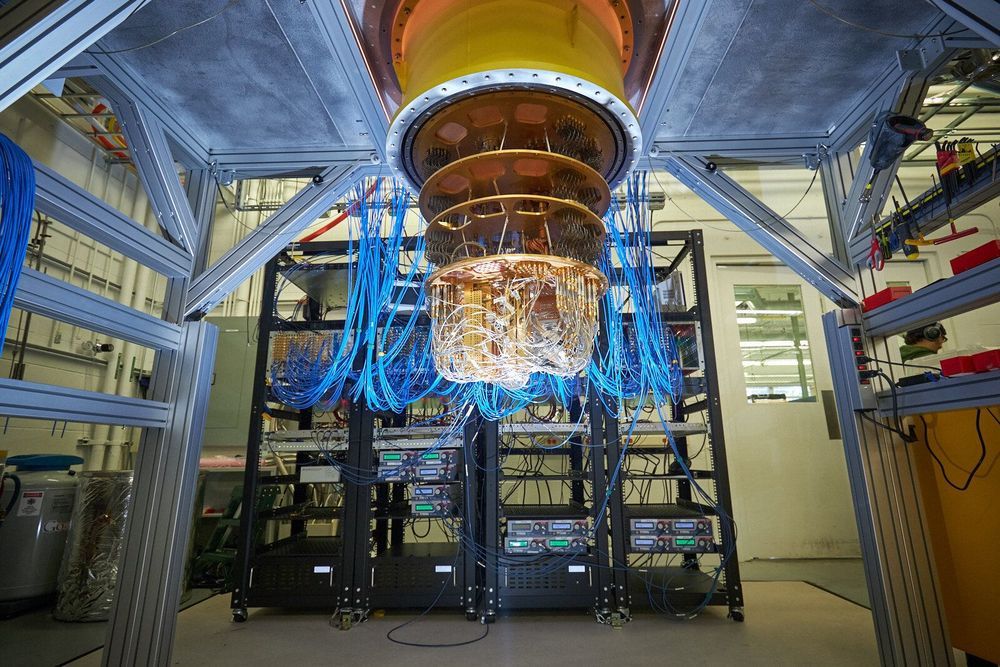

Google conducts largest chemical simulation on a quantum computer to date
A team of researchers with Google’s AI Quantum team (working with unspecified collaborators) has conducted the largest chemical simulation on a quantum computer to date. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes their work and why they believe it was a step forward in quantum computing. Xiao Yuan of Stanford University has written a Perspective piece outlining the potential benefits of quantum computer use to conduct chemical simulations and the work by the team at AI Quantum, published in the same journal issue.
Developing an ability to predict chemical processes by simulating them on computers would be of great benefit to chemists—currently, they do most of it through trial and error. Prediction would open up the door to the development of a wide range of new materials with still unknown properties. Sadly, current computers lack the exponential scaling that would be required for such work. Because of that, chemists have been hoping quantum computers will one day step in to take on the role.
Current quantum computer technology is not yet ready to take on such a challenge, of course, but computer scientists are hoping to get them there sometime in the near future. In the meantime, big companies like Google are investing in research geared toward using quantum computers once they mature. In this new effort, the team at AI Quantum focused their efforts on simulating a simple chemical process—the Hartree-Fock approximation of a real chemical system—in this particular case, a diazene molecule undergoing a reaction with hydrogen atoms, resulting in an altered configuration.


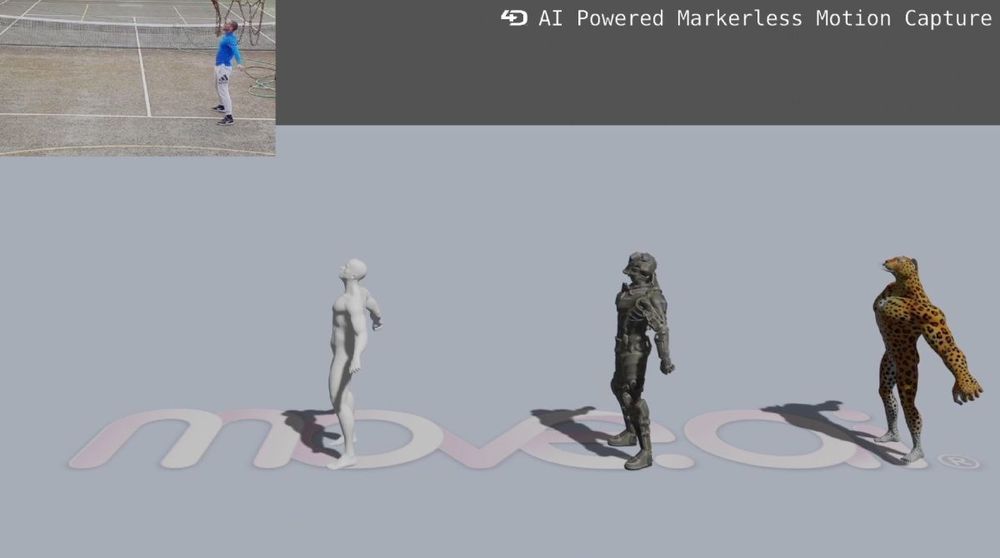
Move.ai enables AI motion capture without the hassle for video game production
Move.ai can use artificial intelligence to capture a 3D representation of an actor in a process known as motion capture. But it doesn’t need actors in Lycra suits with lots of white balls attached to them. And it enables game companies to do motion capture in a remote way during the pandemic.
That’s an important technological advancement, because the hassles of motion-capture systems have led to a stall in production for both movie makers and video game companies. Move.ai hopes to fix that with “markerless” motion capture that can lower the costs and hassles of doing the work.
The technology comes from a London company that started out capturing the images of sports athletes and turning them into digital animated objects. But the pandemic hobbled that business with the closing of physical sports events. Luckily, games need better realism to give players total immersion and engagement in an alternate reality, and that means that they need motion capture.

4 Evolving Technology Areas Of Smart Cybersecurity
By Chuck Brooks In FORBES
The surge in digital connectivity and more sophisticated cyber-threats has promulgated the need for smart cybersecurity. Smart Cybersecurity is a logical reaction to try to manage risk by lessening security gaps often posed by reliance on manual processes that are impacted by a continual cybersecurity skills shortage and the administrative burdens of data security management.
Despite the challenges, there is promise for reducing dependence on humans and bolstering cybersecurity capabilities. A myriad of evolving cognitive technologies can help us enhance cybersecurity and navigate the increasingly malicious and disruptive cyber threat landscape. They include:
• Artificial Intelligence

The Merging Of Human And Machine. Two Frontiers Of Emerging Technologies
An amazing aspect of living in The Fourth Industrial Era is that we are at a new inflection point in bringing emerging technologies to life. We are in an era of scientific breakthroughs that will change the way of life as we currently know it. While there are many technological areas of fascination for me, the meshing of biology with machine is one of the most intriguing. It fuses many elements of technologies especially artificial intelligence and pervasive computing. I have highlighted two frontiers of “mind-bending” developments that are on the horizon, Neuromorphic technologies, and human-machine biology.
Neuromorphic Technologies
Human computer interaction (HCI) was an area of research that started in the 1980s and has come a long way in a short period of time. HCI was the foundation for what we call neuromorphic computing, the integration of systems containing electronic analog circuits to mimic neuro-biological architectures present in the biological nervous system.
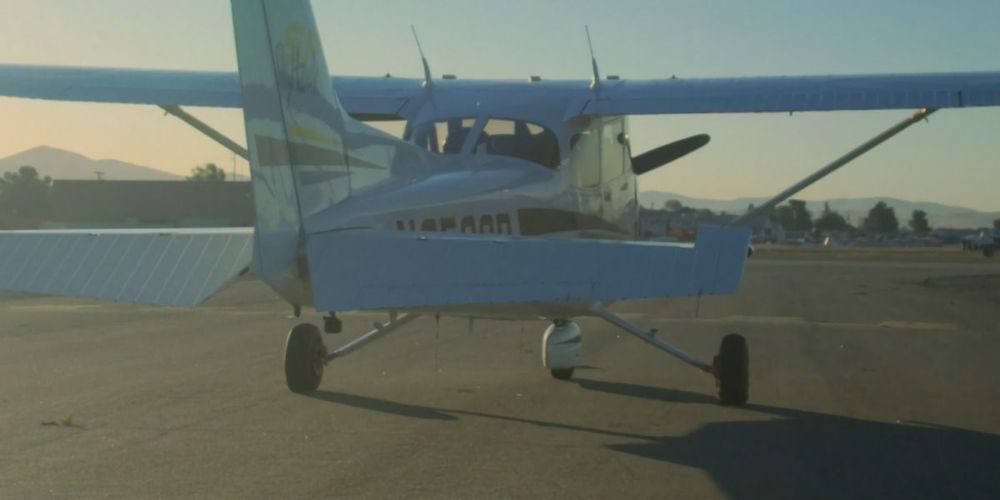

Autonomous aircraft startup Reliable Robotics emerges from stealth with $33.5 million
Reliable Robotics, a startup developing autonomous flight technologies, this week emerged from stealth with $33.5 million in venture capital funding. Cofounder and CEO Robert Rose says the funds will be used to scale production of the company’s products and bring on new engineering talent.
Aviation companies pursuing autonomous transportation include Uber, Boeing, and Honeywell. According to management consulting firm Oliver Wyman, replacing single-pilot operations with autonomous planes could save airlines as much as $60 billion annually. Pandemic headwinds have only reinvigorated the search for cost-cutting opportunities, as Statista estimates airlines will lose at least $314 billion in revenue in 2020.
Looking to expedite their path to market, companies like Xwing, Airbus, and Elroy Air have explored retrofitting existing aircraft rather than developing hardware from scratch. Reliable Robotics, which was founded in 2017 by Rose and VP of engineering Juerg Frefel, aims to develop a platform that imbues any fixed-wing plane with autonomous capabilities.
This robot can make a pizza in just 3 minutes
Robot vending machines designed specifically for pizza is the future we need right now.