Sept. 9, 2020 By Tom Ward, Senior Vice President, Customer Product, Walmart.
Years ago, our founder Sam Walton famously said, “I have always been driven to buck the system, to innovate, to take things beyond where they’ve been.” It remains a guiding principle at Walmart to this day. From being an early pioneer of universal bar codes and electronic scanning cash registers to our work on autonomous vehicle delivery, we’re working to understand how these technologies can impact the future of our business and help us better serve our customers.
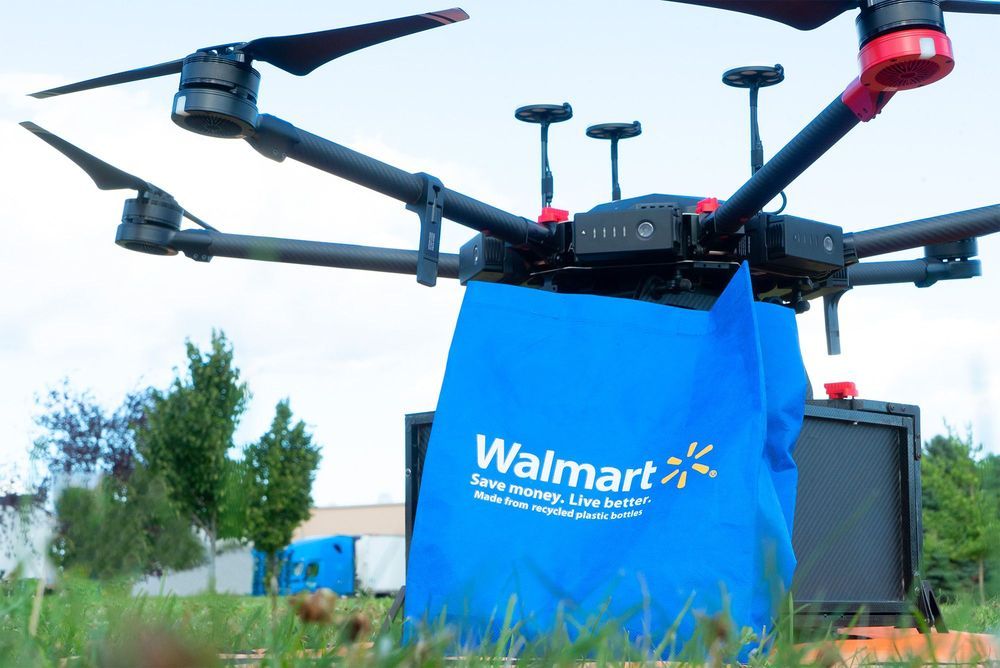
Our latest initiative has us exploring how drones can deliver items in a way that’s convenient, safe, and – you guessed it – fast. Today, we’re taking the next step in our exploration of on-demand delivery by announcing a new pilot with Flytrex, an end-to-end drone delivery company.