Circa 2010
Unmanned aerial vehicles, or UAVs, are used in many applications to gather intelligence without risking human lives. These aircraft, however, have limited flight time because of their reconnaissance payload requirements coupled with their limited scale. A microwave-powered flight vehicle would be able to perform a reconnaissance mission continuously.
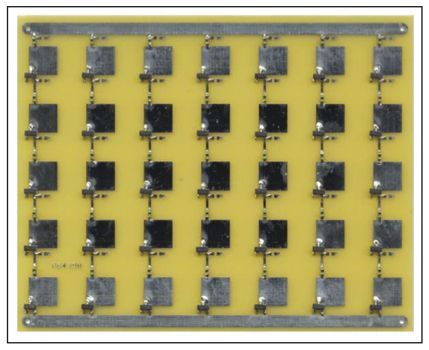
Using beamed microwave energy from a remote source on the ground, the airplane gathers energy using onboard antennas. A rectifying antenna, or rectenna, harvests power and rectifies it into a form usable by an onboard electric motor that drives the propeller, providing thrust. Using a rectenna array affixed to the underside of the aircraft, the power needed to maintain flight can be remotely transmitted.
The idea of a fuel-less flight vehicle, or an aircraft that does not carry its own fuel, has been pursued in few different forms over the past decades. There are many different approaches for how to power these vehicles; however, the common theme is that power must be transmitted from a source remote to the aircraft. Some of the possibilities for power transmission include solar power, the heating of air underneath the aircraft to cause thrust, and using antennas to convert microwave radiation into electrical power.