A new study finds that AI-generated music stirs stronger emotional and physical responses than music composed by humans.


Normally, T cells naturally identify cancer cells by recognizing specific protein fragments, known as peptides, presented on the cell surface by molecules called pMHCs. It is a slow and challenging process to utilize this knowledge for therapy, often because the variation in the body’s own T-cell receptors makes it challenging to create a personalized treatment.
In the study, the researchers tested the strength of the AI platform on a well-known cancer target, NY-ESO-1, which is found in a wide range of cancers. The team succeeded in designing a minibinder that bound tightly to the NY-ESO-1 pMHC molecules. When the designed protein was inserted into T cells, it created a unique new cell product named ‘IMPAC-T’ cells by the researchers, which effectively guided the T cells to kill cancer cells in laboratory experiments.
“It was incredibly exciting to take these minibinders, which were created entirely on a computer, and see them work so effectively in the laboratory,” says a co-author of the study.
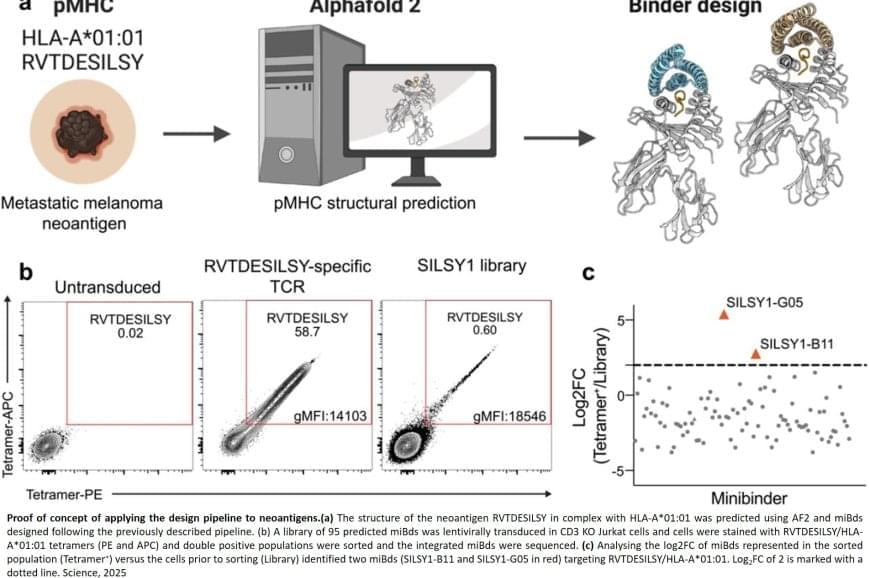
The researchers also applied the pipeline to design binders for a cancer target identified in a metastatic melanoma patient, successfully generating binders for this target as well. This documented that the method also can be used for tailored immunotherapy against novel cancer targets.
A crucial step in the researchers’ innovation was the development of a ‘virtual safety check’. The team used AI to screen their designed minibinders and assess them in relation to pMHC molecules found on healthy cells. This method enabled them to filter out minibinders that could cause dangerous side effects before any experiments were carried out.
Precision cancer treatment on a larger scale is moving closer after researchers have developed an AI platform that can tailor protein components and arm the patient’s immune cells to fight cancer. The new method, published in the scientific journal Science, demonstrates for the first time, that it is possible to design proteins in the computer for redirecting immune cells to target cancer cells through pMHC molecules.
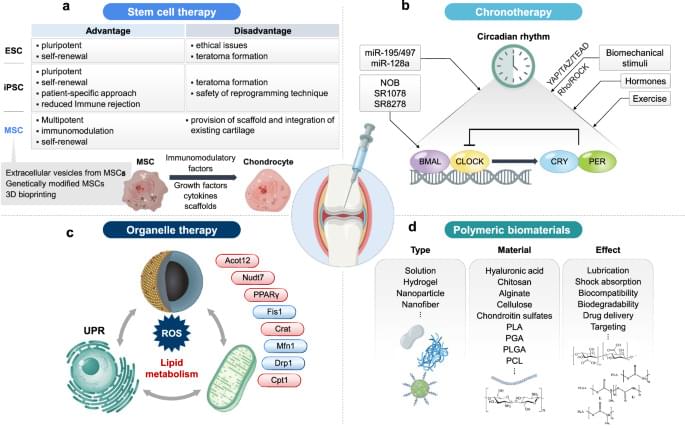
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disease that causes pain and stiffness, especially in older adults. Researchers are exploring new therapies to address this issue, here focusing on regenerative medicine, which uses stem cells to repair damaged cartilage. This involves injecting stem cells into joints to promote healing. However, challenges such as cell survival and long-term effectiveness remain. This study also examines gene therapy, which targets specific genes to reduce inflammation and cartilage breakdown. Biomaterials such as hydrogels and nanoparticles are used to deliver these therapies directly to the joint, improving treatment precision. In addition, this research highlights the role of circadian rhythms in OA, suggesting that timing treatments could enhance their effectiveness. These advancements aim to provide more personalized and effective OA treatments. Future research will focus on refining these approaches for better patient outcomes.
This summary was initially drafted using artificial intelligence, then revised and fact-checked by the author.
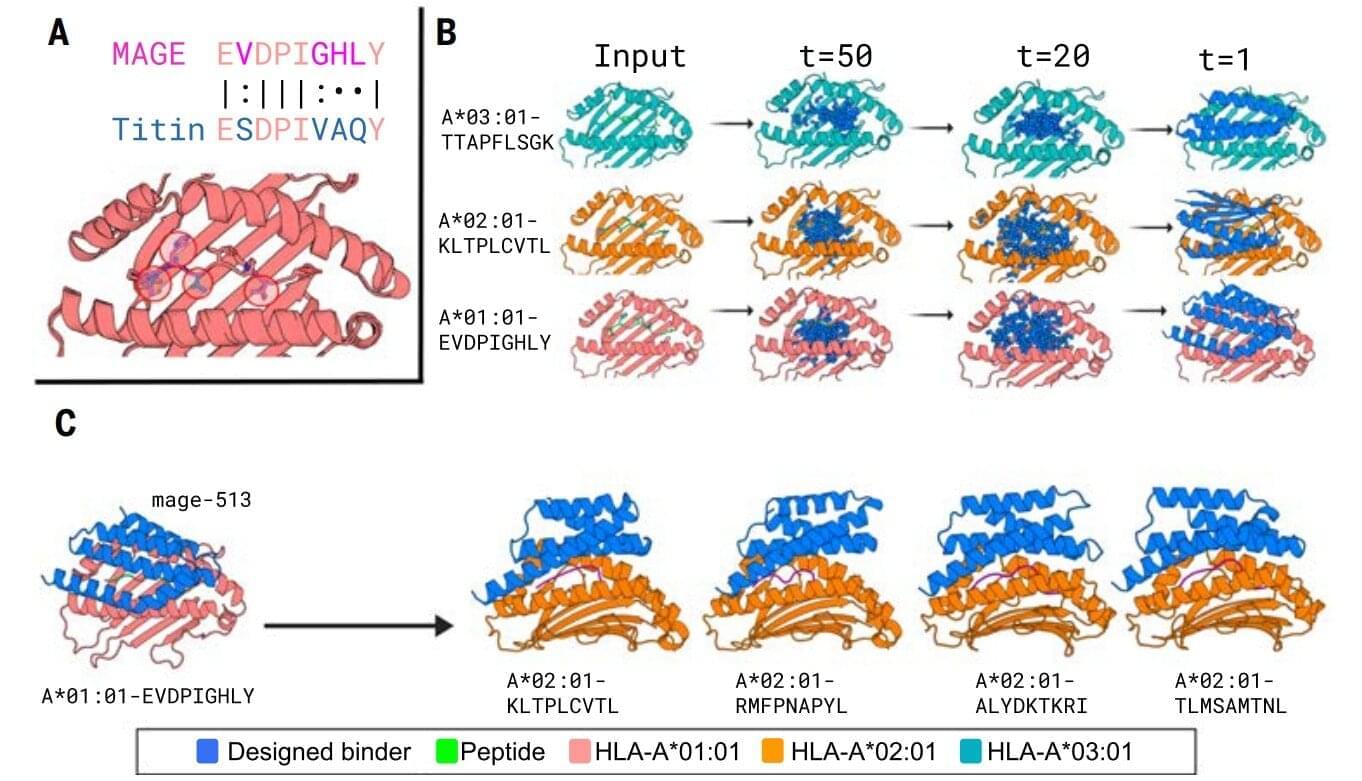
New designer proteins created using an AI tool can selectively target peptide segments that bind to markers on diseased cancer cells, acting like molecular flags that signal immune cells to attack and destroy the threats.
In a recent breakthrough, a team of researchers from the U.S. presented protein binders that specifically recognized the peptide portion of 11 diverse pMHCI complexes—amino-acid fragments found on the surface of almost all cells in the body that play a central role in the immune system’s ability to recognize and respond to abnormal or diseased cells, such as cancer cells.
These proteins, designed with the aid of AI, help human immune cells identify the correct targets and function more effectively, according to findings published in Science.


There may be a new artificial intelligence-driven tool to turbocharge scientific discovery: virtual labs.

A personalized brain stimulation system powered by artificial intelligence (AI) that can safely enhance concentration from home has been developed by researchers from the University of Surrey, the University of Oxford and Cognitive Neurotechnology. Designed to adapt to individual characteristics, the system could help people improve focus during study, work, or other mentally demanding tasks.
Published in npj Digital Medicine, the study is based on a patented approach that uses non-invasive brain stimulation alongside adaptive AI to maximize its impact.
The technology uses transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS)—a gentle and painless form of electrical brain stimulation—and an AI algorithm that learns to personalize stimulation based on individual features, including attention level and head size.

Refraction—the bending of light as it passes through different media—has long been constrained by physical laws that prevent independent control over how light waves along different directions bend. Now, UCLA researchers have developed a new class of passive materials that can be structurally engineered to “program” refraction, enabling arbitrary control over the bending of light waves.
In a study published in Nature Communications, a team led by Dr. Aydogan Ozcan, the Chancellor’s Professor of Electrical & Computer Engineering at UCLA, has introduced a novel device called a refractive function generator (RFG) that can independently tailor the output direction of refracted light for each input direction. This device allows light to be steered, filtered, or redirected according to custom-designed rules—far beyond what standard materials or traditional metasurfaces can achieve.
Standard refraction, described by Snell’s law, links the input and output directions of light using fixed material properties. Even advanced metasurface designs only allow limited tunability of refraction.

A vulnerability in Google’s Gemini CLI allowed attackers to silently execute malicious commands and exfiltrate data from developers’ computers using allowlisted programs.
The flaw was discovered and reported to Google by the security firm Tracebit on June 27, with the tech giant releasing a fix in version 0.1.14, which became available on July 25.
Gemini CLI, first released on June 25, 2025, is a command-line interface tool developed by Google that enables developers to interact directly with Google’s Gemini AI from the terminal.