A fashion designer made a dress powered by your brain.



U.S. robotics company Boston Dynamics unveiled a new robot called ‘Stretch,’ designed to perform one very specific warehouse job: moving boxes https://reut.rs/3wc6SOW


When most Americans think of the infrastructure projects the Biden administration is proposing in the American Jobs Plan, they think of concrete, steel, and labor. But what if the biggest predictor of the success of the infrastructure plan is not in the materials but in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)?
Electrek spoke with Monte Zweben, CEO of Splice Machine, a database company that helps utilities and industrial companies implement data, about how AI/ML technologies could determine whether the American Jobs Plan succeeds as the US transitions to clean energy.

Despite artificial intelligence and robotics adapting to many other areas of life and the work force, construction has long remained dominated by humans in neon caps and vests. Now, the robotics company Baubot has developed a Printstones robot, which they hope to supplement human construction workers onsite.
Baubot manufacturers built this robot with the capacity to transport heavy loads, lay bricks and even sand sheetrock. So far, the Austria-based company has come out with two robots – a smaller prototype with a 40-inch arm and a larger robot with an 82-inch arm.
Users can switch out the type of digits at the end of each arm depending on what type of task they need the bot to perform. For example, an arm tip has the ability to cut, drill, sand and also use a suction feature to elevate heavy rocks into the proper location. Both types of robot can transport over one ton of material.

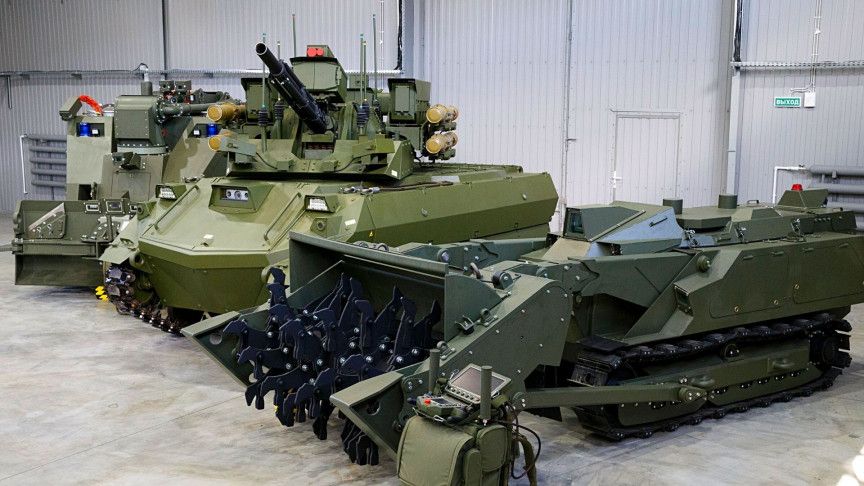
Composite membrane origami has been an efficient and effective method for constructing transformable mechanisms while considerably simplifying their design, fabrication, and assembly; however, its limited load-bearing capability has restricted its application potential. With respect to wheel design, membrane origami offers unique benefits compared with its conventional counterparts, such as simple fabrication, high weight-to-payload ratio, and large shape variation, enabling softness and flexibility in a kinematic mechanism that neutralizes joint distortion and absorbs shocks from the ground. Here, we report a transformable wheel based on membrane origami capable of bearing more than a 10-kilonewton load. To achieve a high payload, we adopt a thick membrane as an essential element and introduce a wireframe design rule for thick membrane accommodation. An increase in the thickness can cause a geometric conflict for the facet and the membrane, but the excessive strain energy accumulation is unique to the thickness increase of the membrane. Thus, the design rules for accommodating membrane thickness aim to address both geometric and physical characteristics, and these rules are applied to basic origami patterns to obtain the desired wheel shapes and transformation. The capability of the resulting wheel applied to a passenger vehicle and validated through a field test. Our study shows that membrane origami can be used for high-payload applications.
Origami has been a rich source of inspiration for art, education, and mathematics, and it has proven to be an efficient and effective method for realizing transformable structures in nature (1–3) and artificial systems (4–8). Composite membrane origami, the design technique based on the laminar composition of flexible membranes with rigid facet constraints, opens a new field for robotics by the transition from component assembly to lamination, which considerably simplifies design, fabrication, and assembly. This transition simplifies and speeds up fabrication and enables reaching size scales that were difficult to access before (9, 10). In addition, membrane origami provides a versatile shape-changing ability that has been exploited in various applications (11–15), and its applicability has been extended by additional design dimensions obtained from material characteristics such as softness and stretchability (16–19).
Beyond the aforementioned benefits, origami has been an effective design tool for constructing a high payload-to-weight structure, such as a honeycomb panel, by markedly increasing the buckling strength using unique geometric configurations (20, 21). Combining this feature with reconfigurability, various stiffness transition mechanisms have also been introduced (22–24). The rigidity of components is another important factor to secure high load capacity and closely related to the thickness. Origami design is, traditionally, a matter of organizing fold lines under fundamental and ideal assumptions—zero facet thickness and zero fold line width (25–27). However, in response to growing interest in origami-inspired applications that require load-bearing capability, various thickness accommodation methods have been introduced (28–30).
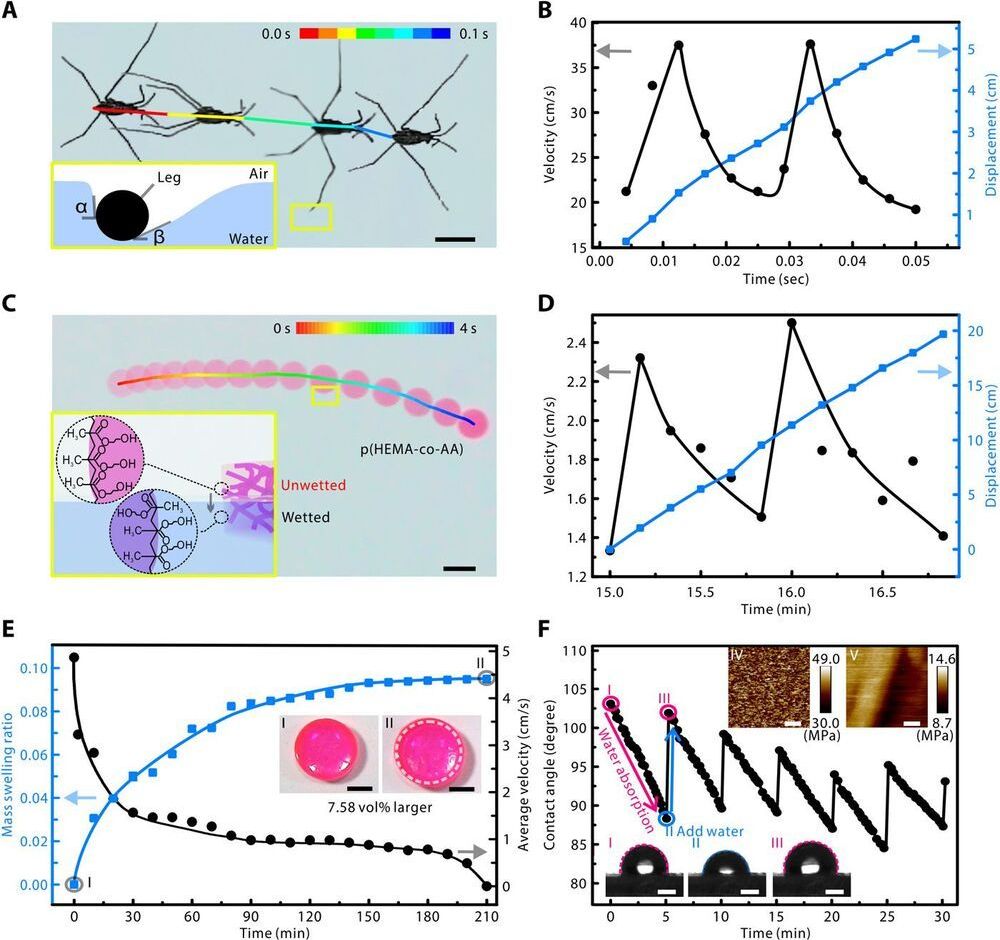
Hydrogels are an exciting class of materials for new and emerging robotics. For example, actuators based on hydrogels have impressive deformability and responsiveness. Studies into hydrogels with autonomous locomotive abilities, however, are limited. Existing hydrogels achieve locomotion through the application of cyclical stimuli or chemical modifications. Here, we report the fabrication of active hydrogels with an intrinsic ability to move on the surface of water without operated stimuli for up to 3.5 hours. The active hydrogels were composed of hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups and underwent a dynamic wetting process to achieve spatial and temporal control of surface tension asymmetry. Using surface tension, the homogeneous active hydrogels propelled themselves and showed controlled locomotion on water, similar to common water striders.
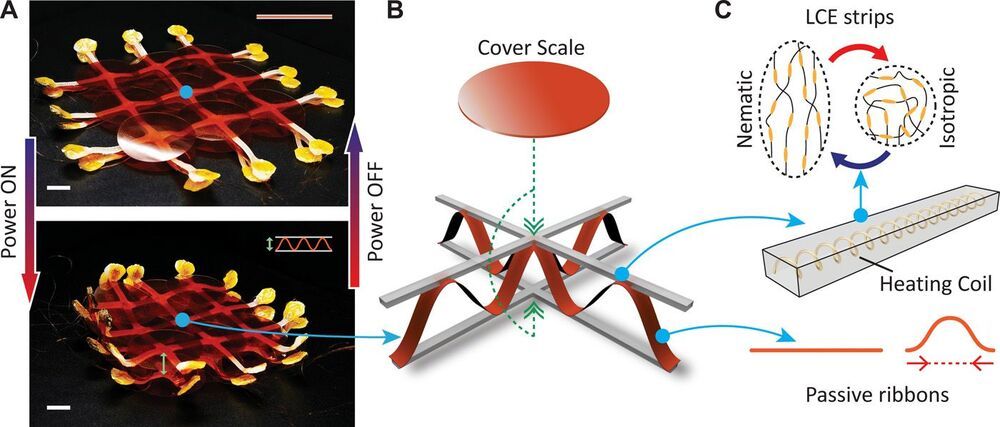
Continuous and controlled shape morphing is essential for soft machines to conform, grasp, and move while interacting safely with their surroundings. Shape morphing can be achieved with two-dimensional (2D) sheets that reconfigure into target 3D geometries, for example, using stimuli-responsive materials. However, most existing solutions lack the ability to reprogram their shape, face limitations on attainable geometries, or have insufficient mechanical stiffness to manipulate objects. Here, we develop a soft, robotic surface that allows for large, reprogrammable, and pliable shape morphing into smooth 3D geometries. The robotic surface consists of a layered design composed of two active networks serving as artificial muscles, one passive network serving as a skeleton, and cover scales serving as an artificial skin.
