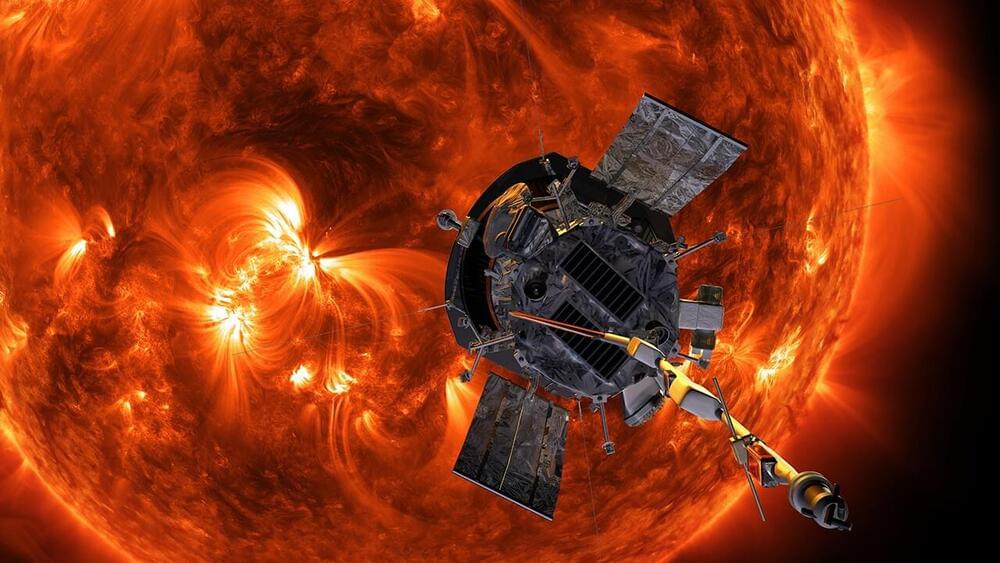
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has set a new pair of records after it survived its 10th close encounter with the Sun. On November 21, 2021 at 4:25 am EST (08:25 GMT), the robotic deep-space explorer came within 5.3 million miles (8.5 million km) of the Sun’s surface and reached a speed of 363,660 mph (586,864 km/h), making it both the closest satellite to survive such a near pass of the Sun and the fastest-ever artificial object.
The Parker Solar Probe was launched on August 12, 2018 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket, and this latest solar flyby between November 16 and 26 marks the halfway point in the spacecraft’s seven-year mission to study the Sun at such close quarters that it will eventually fly through the Sun’s corona.
Having easily beaten the record holder, the Helios-2 spacecraft and its maximum speed of 157,078 mph (252,792 km/h), Parker is now in a league of its own. Its latest speed record beats its own previous record, as will be the case for the future record speeds the probe is expected to reach in later flybys.