For centuries, mathematicians have tried to prove that Euler’s fluid equations can produce nonsensical answers. A new approach to machine learning has researchers betting that “blowup” is near.



Back in 1993, AI pioneer Jürgen Schmidhuber published the paperA Self-Referential Weight Matrix, which he described as a “thought experiment… intended to make a step towards self-referential machine learning by showing the theoretical possibility of self-referential neural networks whose weight matrices (WMs) can learn to implement and improve their own weight change algorithm.” A lack of subsequent practical studies in this area had however left this potentially impactful meta-learning ability unrealized — until now.
In the new paper A Modern Self-Referential Weight Matrix That Learns to Modify Itself, a research team from The Swiss AI Lab, IDSIA, University of Lugano (USI) & SUPSI, and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) presents a scalable self-referential WM (SRWM) that leverages outer products and the delta update rule to update and improve itself, achieving both practical applicability and impressive performance in game environments.
The proposed model is built upon fast weight programmers (FWPs), a scalable and effective method dating back to the ‘90s that can learn to memorize past data and compute fast weight changes via programming instructions that are additive outer products of self-invented activation patterns, aka keys and values for self-attention. In light of their connection to linear variants of today’s popular transformer architectures, FWPs are now witnessing a revival. Recent studies have advanced conventional FWPs with improved elementary programming instructions or update rules invoked by their slow neural net to reprogram the fast neural net, an approach that has been dubbed the “delta update rule.”
10 people will take the better part of a year to port a new technology library. Now we can do it with a couple of GPUs running for a few days.
Nvidia has been quick to hop on the artificial intelligence bus一with many of its consumer facing technologies, such as Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) and AI-accelerated denoising exemplifying that. However, it has also found many uses for AI in its silicon development process and, as Nvidia’s chief scientist Bill Dally said in a GTC conference, even designing new hardware.
Dally outlines a few use cases for AI in its own development process of the latest and greatest graphic cards (among other things), as noted by HPC Wire.
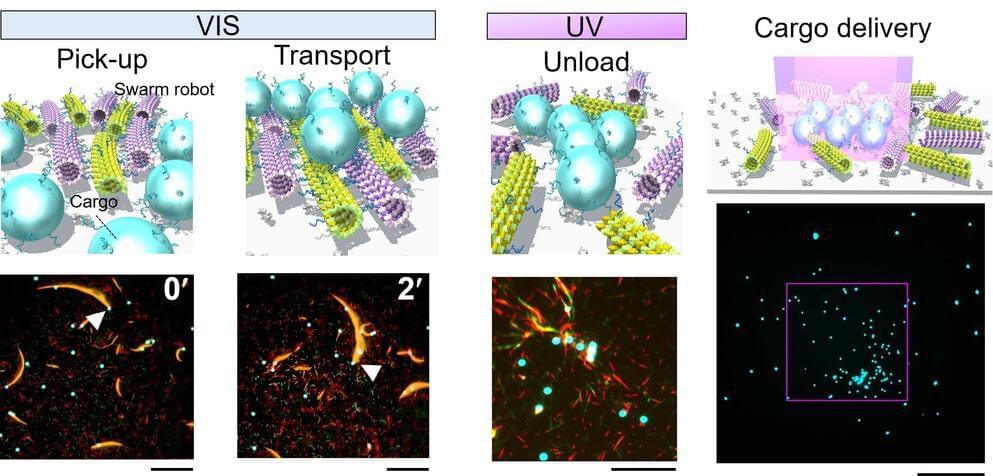
In a global first, scientists have demonstrated that molecular robots are able to accomplish cargo delivery by employing a strategy of swarming, achieving a transport efficiency five times greater than that of single robots.
Swarm robotics is a new discipline, inspired by the cooperative behavior of living organisms, that focuses on the fabrication of robots and their utilization in swarms to accomplish complex tasks. A swarm is an orderly collective behavior of multiple individuals. Macro-scale swarm robots have been developed and employed for a variety of applications, such as transporting and accumulating cargo, forming shapes, and building complex structures.
A team of researchers, led by Dr. Mousumi Akter and Associate Professor Akira Kakugo from the Faculty of Science at Hokkaido University, has succeeded in developing the world’s first working micro-sized machines utilizing the advantages of swarming. The findings were published in the journal Science Robotics. The team included Assistant Professor Daisuke Inoue, Kyushu University; Professor Henry Hess, Columbia University; Professor Hiroyuki Asanuma, Nagoya University; and Professor Akinori Kuzuya, Kansai University.



The processing of food at high volumes has traditionally posed many problems for robots and cobots, and has lagged behind other industries. Foods have a variety of shapes and sizes and can be delicate in nature. These variables can be challenging when a robot tries to grasp an item. The delicate often has strict requirements for quality, making them even harder to grasp (think: strawberries).
Non-automotive robot orders now represent 58% of the North American total. Unit sales to the food and consumer goods sector alone increased 29% in 2021 over 2020, according to Association for Advancing Automation (A3).
“More industries recognized that robotics could help reverse productivity declines and fill repetitive jobs human workers don’t want. It is no longer a choice whether to deploy robots and automation,” says Jeff Burnstein, president of A3. “It’s now an absolute imperative. As we’ve long believed—and users continue to confirm—robots help companies compete, ultimately creating more jobs to handle their growth.”
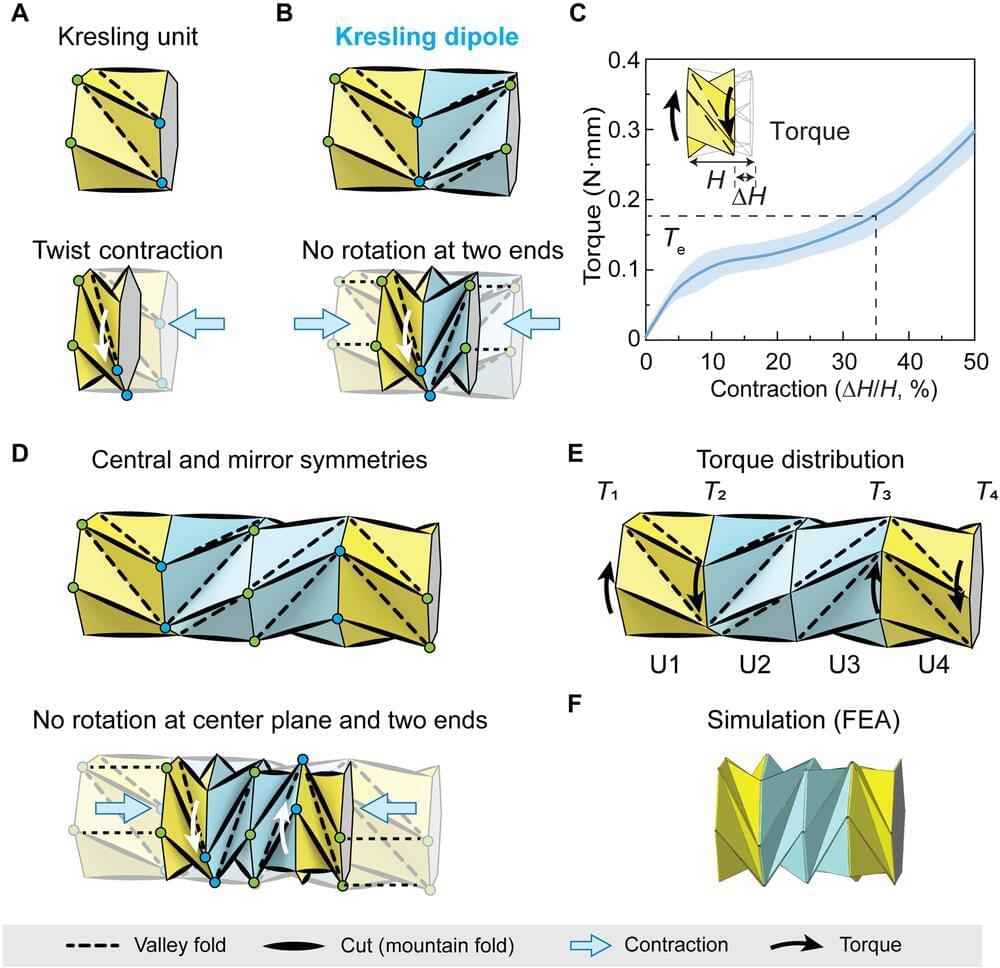
Materials scientists aim to develop biomimetic soft robotic crawlers including earthworm-like and inchworm-like crawlers to realize locomotion via in-plane and out-of-plane contractions for a variety of engineering applications. While such devices can show effective motion in confined spaces, it is challenging to miniaturize the concept due to complex and limited actuation. In a new report now published in Science Advances, Qiji Ze and a team of scientists in mechanical engineering and aerospace engineering at Stanford University and the Ohio State University, U.S., described a magnetically actuated, small-scale origami crawler exhibiting in-plane contraction. The team achieved contraction mechanisms via a four-unit Kresling origami assembly to facilitate the motion of an untethered robot with crawling or steering capacity. The crawler overcame large resistances in severely confined spaces due to its magnetically tunable structural stiffness and anisotropy. The setup provided a contraption for drug storage and release with potential to serve as a minimally invasive device in biomedicine.
Navigating complicated terrains
Bioinspired crawling motion shows adaptation to complicated terrains due to its soft deformable dimensions. Researchers aim to engineer crawling for a variety of applications in limited or confined environments, including extraterrestrial exploration, tube inspection, and gastrointestinal endoscopy. Origami provides an appropriate method to generate contraction relative to structural folding, which can be adapted to engineer robotic crawlers. The team described Kresling patterns; a specific type of bioinspired, origami pattern used to generate axial contraction under torque or compressive force, coupled with a twist from the relative rotation of the device units. Ze et al illustrated a magnetically actuated small-scale origami crawler to induce effective in-plane crawling motions. The scientists developed a four-unit Kresling assembly and verified torque distribution on the crawler using finite element analysis to induce motion.