Not without human level hands. and should be 1. on list. and i dont see it til 2030 at earliest.
 Robots are making their first tentative steps from the factory floor into our homes and workplaces. In a recent report, Goldman Sachs Research estimates a $6 billion market (or more) in people-sized-and-shaped robots is achievable in the next 10 to 15 years. Such a market would be able to fill 4% of the projected US manufacturing labor shortage by 2030 and 2% of global elderly care demand by 2035.
Robots are making their first tentative steps from the factory floor into our homes and workplaces. In a recent report, Goldman Sachs Research estimates a $6 billion market (or more) in people-sized-and-shaped robots is achievable in the next 10 to 15 years. Such a market would be able to fill 4% of the projected US manufacturing labor shortage by 2030 and 2% of global elderly care demand by 2035.
GS Research makes an additional, more ambitious projection as well. “Should the hurdles of product design, use case, technology, affordability and wide public acceptance be completely overcome, we envision a market of up to US$154bn by 2035 in a blue-sky scenario,” say the authors of the report The investment case for humanoid robots. A market that size could fill from 48% to 126% of the labor gap, and as much as 53% of the elderly caregiver gap.
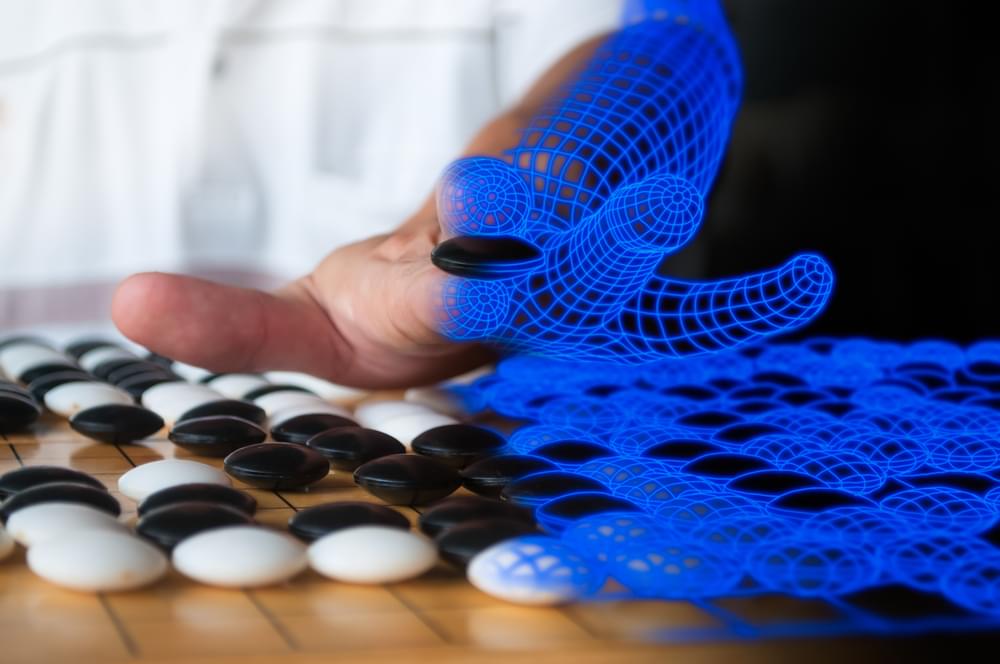
Obstacles remain: Today’s humanoid robots can work in only short one-or two-hour bursts before they need recharging. Some humanoid robots have mastered mobility and agility movements, while others can handle cognitive and intellectual challenges – but none can do both, the research says. One of the most advanced robot-like technologies on the commercial market is a self-driving vehicle, but a humanoid robot would have to have greater intelligence and processing abilities than that – by a significant order. “In the history of humanoid robot development,” the report says, “no robots have been successfully commercialized yet.”