Year 2021 face_with_colon_three
Codex, from OpenAI, can turn normal, conversational commands into programming, taking text to code.

Using a quantum processor, researchers made microwave photons uncharacteristically sticky. After coaxing them to clump together into bound states, they discovered that these photon clusters survived in a regime where they were expected to dissolve into their usual, solitary states. As the finding was first made on a quantum processor, it marks the growing role that these platforms are playing in studying quantum dynamics.
Photons — quantum packets of electromagnetic radiation like light or microwaves — usually don’t interact with one another. For example, two crossed flashlight beams pass through one another undisturbed. However, microwave photons can be made to interact in an array of superconducting qubits.
Researchers at Google Quantum AI describe how they engineered this unusual situation in “Formation of robust bound states of interacting photons,” which was published on December 7 in the journal Nature. They investigated a ring of 24 superconducting qubits that could host microwave photons. By applying quantum gates to pairs of neighboring qubits, photons could travel around by hopping between neighboring sites and interacting with nearby photons.

The buzz will likely ramp up even more when OpenAI releases a superior next version of the A.I. chatbot, reportedly sometime next year.
Speaking of buzz, few people have been generating more of it lately than Elon Musk, who leads Tesla, SpaceX, and now Twitter, among other companies. As it turns out, Musk has ties to OpenAI, including as an original backer, and has been involved in both supporting artificial intelligence and warning about its dangers.
This month Musk called ChatGPT “scary good” and warned, “We are not far from dangerously strong AI.”
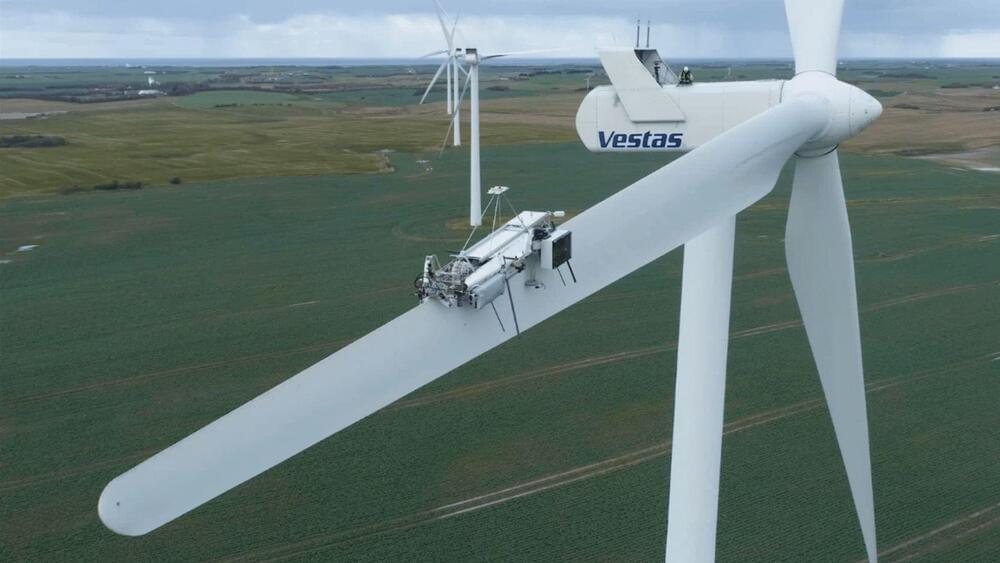

AI is used by the robotic solution to swiftly adapt to all types of blades used in the sector.
Danish energy solutions provider Vestas has unveiled BladeRobots as a stand-alone business with an automated robotic technology solution for the maintenance of wind turbines.
The robot performs automated blade-leading edge maintenance up to “four times faster” than traditional manual methods, according to a press release by the company published on Wednesday.

After all, the AI chatbot seems to be slaying a great deal of search engine responses.
ChatGPT is the latest and most impressive artificially intelligent chatbot yet. It was released two weeks ago, and in just five days hit a million users. It’s being used so much that its servers have reached capacity several times.
But what if we never know the secret sauce behind ChatGPT’s capabilities?
Imaginima/iStock.
OpenAI, the company that developed it, is already being discussed as a potential Google slayer. Why look up something on a search engine when ChatGPT can write a whole paragraph explaining the answer? (There’s even a Chrome extension that lets you do both, side by side.)
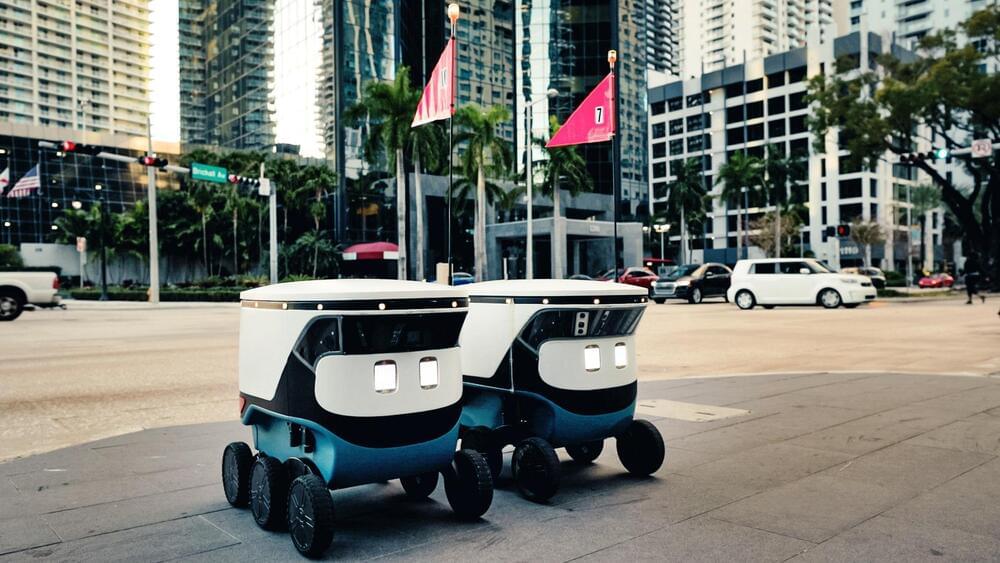

It’s been two years since Uber called it quits trying to make its own driverless cars, but the ride-hauling giant is now speeding to market with a distributed fleet of delivery robots and autonomous vehicles thanks to a recent flurry of partnerships.
Those attending the world’s largest technology show, CES, might have a chance to ride in an all-electric self-driving Uber from Motional, a Hyundai-backed startup based out of Boston. The companies just announced a 10-year agreement to bring millions of autonomous rides across the Uber network. Following deployment in Las Vegas, a broader rollout is being planned for Los Angeles. Motional’s Hyundai IONIQ 5 robotaxis have been making Uber Eats deliveries in Santa Monica since May as part of a pilot.
In Miami, Uber Eats is rolling out sidewalk delivery robots with Cartken’s AI-powered carriers. The robotics company founded by ex-Google engineers currently operates across college campuses with food delivery services like GrubHub. The Uber Eats partnership will be its first beyond college campuses.
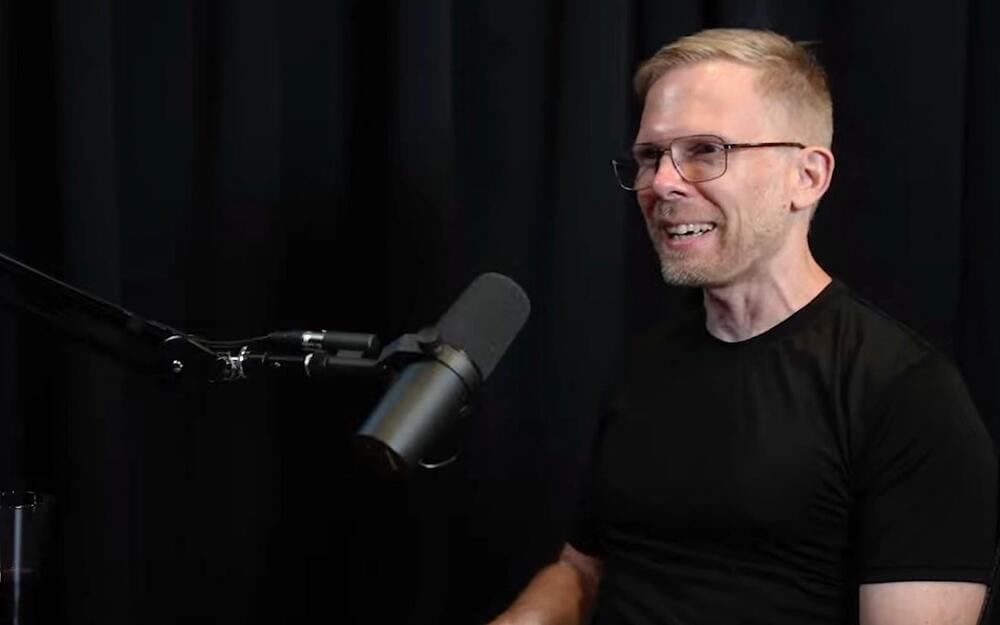

Metaverse was a huge, company destroyin, blunder. Smart move this decade is Drop Everything else and chase Agi.
VR pioneer John Carmack is leaving Meta for good. With his departure, the industry loses a visionary and an important voice.
Carmack published his farewell letter on Facebook after parts of the email were leaked to the press.
In the message to employees, Carmack, as usual, doesn’t mince words. He cites a lack of efficiency and his powerlessness to change anything about this circumstance as reasons.
Is digital immortality possible by uploading your mind? Dr. Paul Thagard discusses Neuralink, artificial intelligence, mind uploading, simulation theory, and the challenges involved with whole brain emulation.
Dr. Paul Thagard is a philosopher, cognitive scientist, and author of many interdisciplinary books. He currently teaches as a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Philosophy at the University of Waterloo, where he founded and directed the Cognitive Science Program.
Dr. Thagard is a graduate of the Universities of Saskatchewan, Cambridge, Toronto (with a PhD in philosophy) and Michigan (with an MS in computer science). He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, the Cognitive Science Society, and the Association for Psychological Science. The Canada Council awarded him a Molson Prize in 2007 and a Killam Prize in 2013.
LINKS & RESOURCES:
Dr. Paul Thagard’s Website:
Balance: How It Works and What It Means.
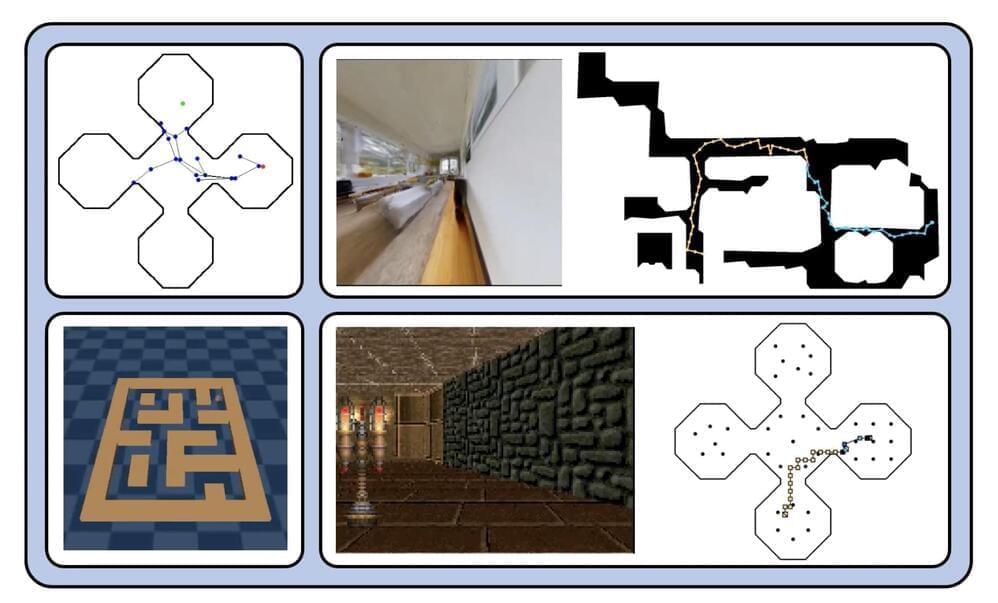
Both animals and people use high-dimensional inputs (like eyesight) to accomplish various shifting survival-related objectives. A crucial aspect of this is learning via mistakes. A brute-force approach to trial and error by performing every action for every potential goal is intractable even in the smallest contexts. Memory-based methods for compositional thinking are motivated by the difficulty of this search. These processes include, for instance, the ability to: recall pertinent portions of prior experience; (ii) reassemble them into new counterfactual plans, and (iii) carry out such plans as part of a focused search strategy. Compared to equally sampling every action, such techniques for recycling prior successful behavior can considerably speed up trial-and-error. This is because the intrinsic compositional structure of real-world objectives and the similarity of the physical laws that control real-world settings allow the same behavior (i.e., sequence of actions) to remain valid for many purposes and situations. What guiding principles enable memory processes to retain and reassemble experience fragments? This debate is strongly connected to the idea of dynamic programming (DP), which using the principle of optimality significantly lowers the computing cost of trial-and-error. This idea may be expressed informally as considering new, complicated issues as a recomposition of previously solved, smaller subproblems.
This viewpoint has recently been used to create hierarchical reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms for goal-achieving tasks. These techniques develop edges between states in a planning graph using a distance regression model, compute the shortest pathways across it using DP-based graph search, and then use a learning-based local policy to follow the shortest paths. Their essay advances this field of study. The following is a summary of their contributions: They provide a strategy for long-term planning that acts directly on high-dimensional sensory data that an agent may see on its own (e.g., images from an onboard camera). Their solution blends traditional sampling-based planning algorithms with learning-based perceptual representations to recover and reassemble previously recorded state transitions in a replay buffer.
The two-step method makes this possible. To determine how many timesteps it takes for an optimum policy to move from one state to the next, they first learn a latent space where the distance between two states is the measure. They know contrastive representations using goal-conditioned Q-values acquired through offline hindsight relabeling. To establish neighborhood criteria across states, the second threshold this developed latent distance metric. They go on to design sampling-based planning algorithms that scan the replay buffer for trajectory segments—previously recorded successions of transitions—whose ends are adjacent states.
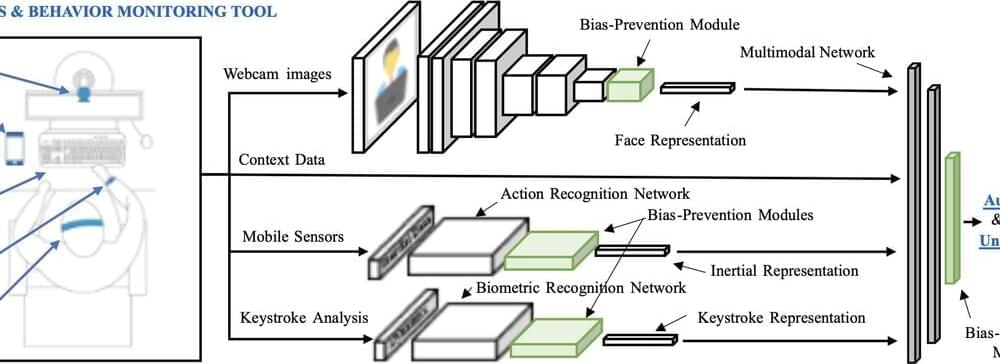
Researchers at Universidad Autónoma de Madrid have recently created an innovative, AI-powered platform that could enhance remote learning, allowing educators to securely monitor students and verify that they are attending compulsory online classes or exams.
An initial prototype of this platform, called Demo-edBB, is set to be presented at the AAAI-23 Conference on Artificial Intelligence in February 2022, in Washington, and a version of the paper is available on the arXiv preprint server.
“Our investigation group, the BiDA-Lab at Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, has substantial experience with biometric signals and systems, behavior analysis and AI applications, with over 300 hundred published papers in last two decades,” Roberto Daza Garcia, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore.