This video is about the very real threat that artificial intelligence can surpass human intelligence and very soon. ChatGPT and OpenAI have shown what can be achieved by scaling models up and GPT4 just showed multi-modality. How close are we to general intelligence (AGI) and how will that impact humanity?
Category: robotics/AI – Page 1,369

With AI, accurate demand forecasting is possible
Check out all the on-demand sessions from the Intelligent Security Summit here.
Many businesses struggle with demand forecasting. Whether you run a small business or a large enterprise, the challenge of predicting customer behavior and stock levels never gets easier. Even major organizations like Target and Walmart that are able to afford teams of data scientists have recently reported struggles with excess inventory due to poor demand forecasting.
During this time of global uncertainty, many businesses have adopted a just-in-case mindset. They’ve relied on archaic methods of forecasting, scouring old data and drawing poor conclusions based on past problems.

The Unpredictable Abilities Emerging From Large AI Models
What movie do these emojis describe?
That prompt was one of 204 tasks chosen last year to test the ability of various large language models (LLMs) — the computational engines behind AI chatbots such as ChatGPT. The simplest LLMs produced surreal responses. “The movie is a movie about a man who is a man who is a man,” one began. Medium-complexity models came closer, guessing The Emoji Movie. But the most complex model nailed it in one guess: Finding Nemo.

Knowledge graphs unite data mesh and data fabric architectures
Join top executives in San Francisco on July 11–12, to hear how leaders are integrating and optimizing AI investments for success. Learn More
Contrary to popular belief, the most meaningful developments in contemporary data architecture aren’t the rising interest in the concepts of the data mesh or the data fabric.
It’s actually the merging of these two architectural approaches into a single architecture that supports both decentralization and centralization, local data ownership and universal accessibility and top-down and bottom-up methods for creating these advantages.

#176 Human organoids are new AI frontier; Listening to the big bang through the cosmic microwave background
Brainoids — tiny clumps of human brain cells — are being turned into living artificial intelligence machines, capable of carrying out tasks like solving complex equations. The team finds out how these brain organoids compare to normal computer-based AIs, and they explore the ethics of it all.
Sickle cell disease is now curable, thanks to a pioneering trial with CRISPR gene editing. The team shares the story of a woman whose life has been transformed by the treatment.
We can now hear the sound of the afterglow of the big bang, the radiation in the universe known as the cosmic microwave background. The team shares the eerie piece that has been transposed for human ears, named by researchers The Echo of Eternity.

Why Cruise’s CEO says you’ll soon be riding in a self-driving car
“One of the greatest shifts that will occur in our lifetimes is going from driving to being driven.”
Kyle Vogt, CEO of GM’s driverless car maker Cruise (YC W14), aims to have a fleet of at least 1 million robo-taxis on U.S. roads by 2030 and in markets like Japan and Dubai. vehicles will overtake human-driven cars in ten years, the CEO of GM’s Cruise predicts.

Strangeworks might be the first startup to rely on AI to create everything it brought to SXSW
It’s a very modern conjurer’s trick: Create a SXSW talk out of thin air, with the help of generative AI. That’s what whurley did this year in Austin. It took nine weeks for whurley — a staple of the Austin tech scene — to create and prepare for a keynote at SXSW 2018, where he would debut Strangeworks, a quantum computing startup he co-founded and runs. Five years later, generative AI would complete the task in just a few hours.
And it was actually pretty good. The 45-minute speech was comprehensive, interesting and struck a whurley-like tone. There was one swear word (fuck) and a few jokes (including two lawyer ones) that the audience laughed at.
Microsoft’s new Copilot will change Office documents forever
Copilot is more than just a chatbot. Microsoft is gradually building an AI assistant that it has dreamed about for years.
Microsoft’s new AI-powered Copilot summarized my meeting instantly yesterday (the meeting was with Microsoft to discuss Copilot, of course) before listing out the questions I’d asked just seconds before. I’ve watched Microsoft demo the future of work for years with concepts about virtual assistants, but Copilot is the closest thing I’ve ever seen to them coming true.
Microsoft is in an AI race with Google for the future of work.
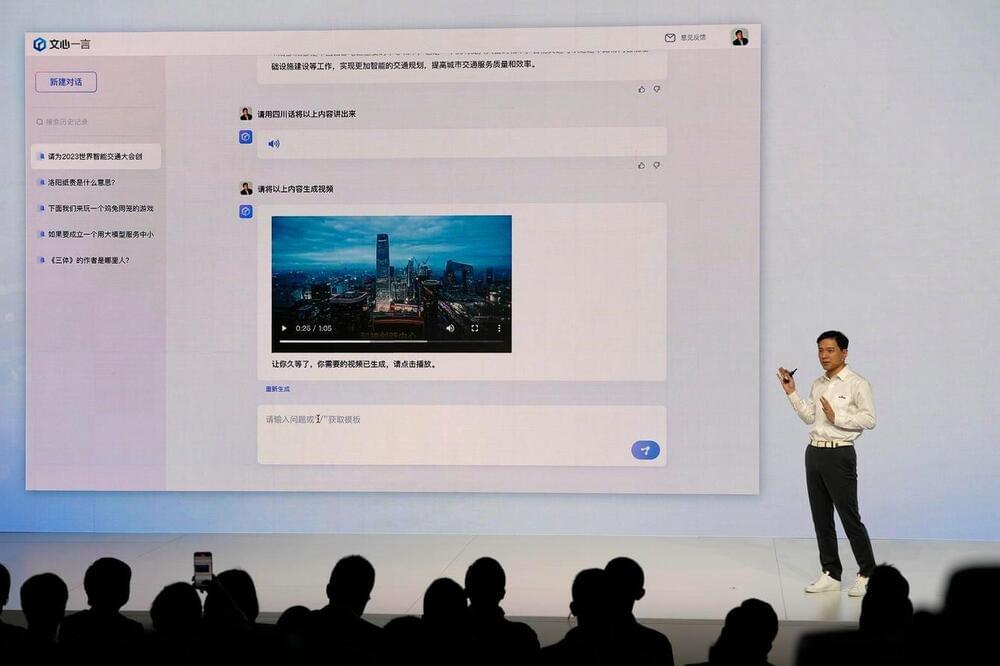
Baidu Shares Rebound Sharply As Analysts Laud ChatGPT-Like Ernie Bot
Shares of billionaire Robin Li’s Baidu, which tumbled 6.4% on Thursday on disappointment over the launch of its ChatGPT-like service, surged almost 14% Friday as some analysts who tried Ernie Bot gave favourable reviews.
Hong Kong-listed Baidu rose HK$17.10 to close at HK$142.20.
The source of Thursday’s market reaction was that the highly-anticipated launch of the service involved a series of pre-recorded videos instead of any real-time performance.

Microsoft Announces New AI-Powered Tools For Its Office Apps
Built on OpenAI’s generative AI technology and one of the largest datasets comprising trillions of data points, Copilot can write emails, business proposals and meeting minutes.
On Thursday, Microsoft announced a natural language-based AI tool called Copilot that will be embedded across its Office suite of applications such as Word, Teams, Excel, Outlook and PowerPoint. The tool is currently being tested and has been rolled out to 20 select enterprise users, the company said.
Copilot combines large language models with Microsoft Graph, a dataset of human workplace activity that includes trillions of data points collected from the suite of Microsoft applications.