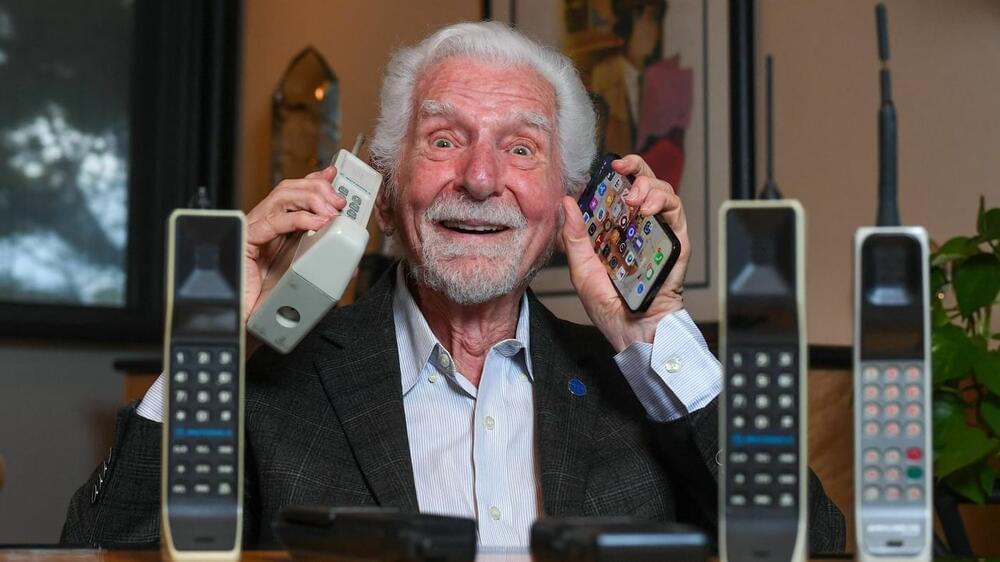
Martin Cooper made the first-ever cellphone call exactly 50 years ago. He says artificial intelligence is the new frontier.


Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/daveshap.
GitHub: https://github.com/daveshap.
Discord: https://discord.gg/yqaBG5rh4j.
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/ArtificialSentience/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/HeuristicImperatives/
DISCLAIMER: This video is not medical, financial, or legal advice. This is just my personal story and research findings. Always consult a licensed professional.
I work to better myself and the rest of humanity.
Progress is speeding up even as the world barrels toward one of innumerable disasters. What lies ahead, and what should we do when we get there? In the best-case scenario, we may still have control over our direction.
BECOME A PATRON: https://www.patreon.com/TonyTalksBack
Or, make a one-time donation here: https://paypal.me/TonyTalksBack
Follow on social media for updates on new content and releases:
https://www.facebook.com/TonyTalksBack/
https://twitter.com/TonyTalksBack.
All photos made with Wonder AI:
https://www.wonder-ai.com/
Music credits:
“Half Mystery” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License.
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.
“Hypnothis” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
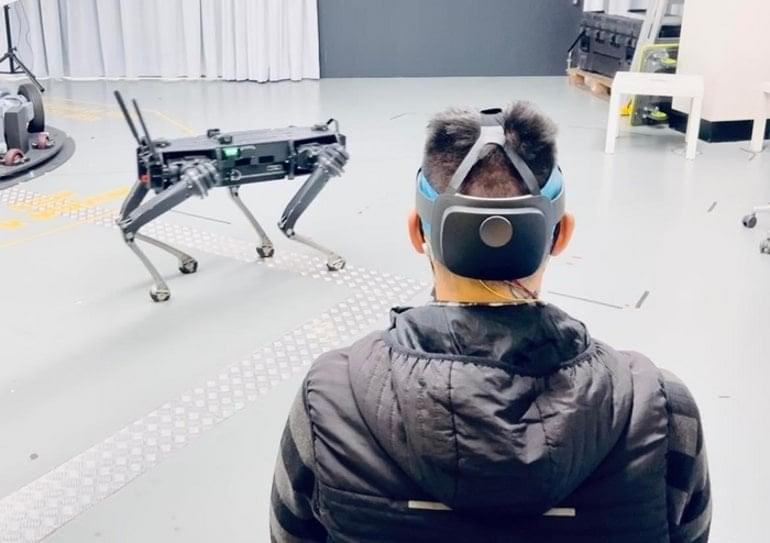

Summary: A newly designed dry sensor that can measure brain activity may someday enable mind control of robotic systems.
Source: American Chemical Society.
It sounds like something from science fiction: Don a specialized, electronic headband and control a robot using your mind. But now, recent research published in ACS Applied Nano Materials has taken a step toward making this a reality.
One day in the future, we may interact with our electronic devices not with physical input or even voice commands, but simply by thinking about what we want to do. Such brain–computer interfaces (BCIs), combined with machine learning, could allow us to turn our ideas into reality faster and with less effort than ever before — imagine being able to produce a PCB design simply by thinking about how the completed circuit would work. Of course as an assistive technology, BCIs would be nothing less than life-changing for many.
Today BCIs are in their infancy, but that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for hackers and makers to experiment with the concept. [Ildar Rakhmatulin] has been working on low-cost open source BCIs for years, and with the recent release of his PiEEG on Crowd Supply, thinks he’s finally found an affordable solution that will let individuals experiment with this cutting edge technology.
Implemented as a shield that can be connected to a Raspberry Pi 3 or 4, the PiEEG features 8 channels for connecting wet or dry electrodes that can measure biosignals such as those used in electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), and electrocardiography (ECG). With the electrodes connected, reading these biosignals is as easy as running a Python script. While primarily designed for neuroscience experimentation, [Ildar] says the device is also useful for learning more about signal processing, filters, and machine learning.
Researchers from Tel Aviv University, Israel, have created a micro-robot the size of a single biological cell that navigates using both electricity and magnetic fields and can identify and capture a single cell, opening the door to a vast array of applications.
Inspired by biological “swimmers” such as bacteria and sperm, the researchers developed a micro-robot (about 10 microns across) with the ability to move around the body autonomously or controlled by an operator.
Using a magnetic field to propel the micro-robot, also called a micro-motor, was attractive; it doesn’t require fuel or direct contact between the magnet and body tissues, can be steered accurately, and can function in a wide range of temperatures and solution conductivities. Electrically powered micro-motors offer advantages, such as selective cargo loading, transport and release and the ability to use electricity to “deform” cells, but they have some downsides. So, combining the two was a no-brainer.
Are you ready for the future of #ai? In this video, we will showcase the top 10 AI-tools to watch out for in 2023. From advanced machine learning algorithms to cutting-edge deep learning #technologies, these tools will revolutionize the way we work, learn, and interact with the world. Join us as we explore the #innovative capabilities of these AI-tools and discover how they can boost your productivity, streamline your operations, and enhance your decision-making process. Don’t miss out on this exciting glimpse into the future of artificial intelligence!
As more private data is stored and shared digitally, researchers are exploring new ways to protect data against attacks from bad actors. Current silicon technology exploits microscopic differences between computing components to create secure keys, but artificial intelligence (AI) techniques can be used to predict these keys and gain access to data. Now, Penn State researchers have designed a way to make the encrypted keys harder to crack.
Led by Saptarshi Das, assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics, the researchers used graphene — a layer of carbon one atom thick — to develop a novel low-power, scalable, reconfigurable hardware security device with significant resilience to AI attacks. They published their findings in Nature Electronics today (May 10).
“There has been more and more breaching of private data recently,” Das said. “We developed a new hardware security device that could eventually be implemented to protect these data across industries and sectors.”
This special edition show is sponsored by Numerai, please visit them here with our sponsor link (we would really appreciate it) http://numer.ai/mlst.
Prof. Karl Friston recently proposed a vision of artificial intelligence that goes beyond machines and algorithms, and embraces humans and nature as part of a cyber-physical ecosystem of intelligence. This vision is based on the principle of active inference, which states that intelligent systems can learn from their observations and act on their environment to reduce uncertainty and achieve their goals. This leads to a formal account of collective intelligence that rests on shared narratives and goals.
To realize this vision, Friston suggests developing a shared hyper-spatial modelling language and transaction protocol, as well as novel methods for measuring and optimizing collective intelligence. This could harness the power of artificial intelligence for the common good, without compromising human dignity or autonomy. It also challenges us to rethink our relationship with technology, nature, and each other, and invites us to join a global community of sense-makers who are curious about the world and eager to improve it.
Pod version: https://podcasters.spotify.com/pod/show/machinelearningstree…on-e208f50
Support us! https://www.patreon.com/mlst.
MLST Discord: https://discord.gg/aNPkGUQtc5
TOC:
Intro [00:00:00]
Numerai (Sponsor segment) [00:07:10]
Designing Ecosystems of Intelligence from First Principles (Friston et al) [00:09:48]
Information / Infosphere and human agency [00:18:30]
Intelligence [00:31:38]
Reductionism [00:39:36]
Universalism [00:44:46]
Emergence [00:54:23]
Markov blankets [01:02:11]
Whole part relationships / structure learning [01:22:33]
Enactivism [01:29:23]
Knowledge and Language [01:43:53]
ChatGPT [01:50:56]
Ethics (is-ought) [02:07:55]
Can people be evil? [02:35:06]
Ethics in Al, subjectiveness [02:39:05]
Final thoughts [02:57:00]
References: