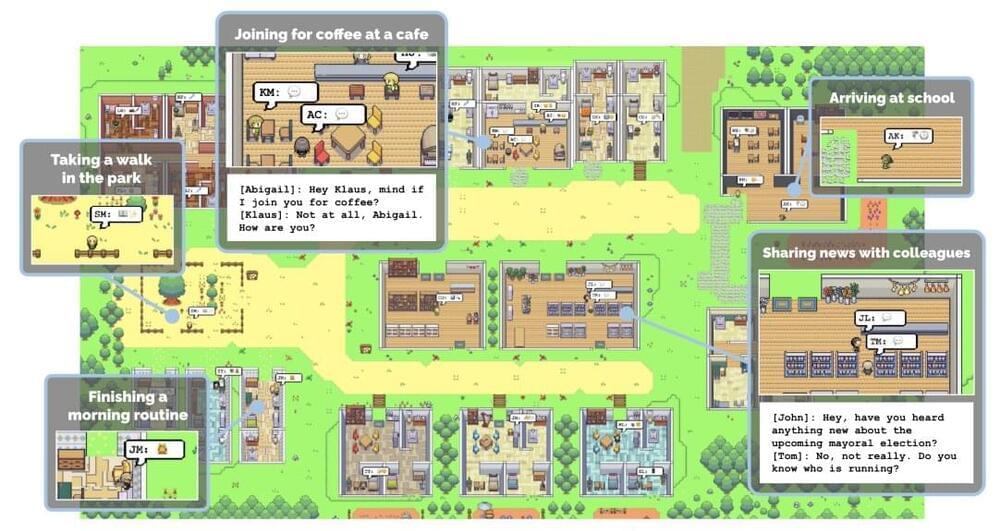
Make a template based on a 1980s virtual reality game, create 25 AI characters, give them personalities and histories, equip them with memory, and throw in some ChatGPT—and what do you get?
A pretty impressive representation of a functioning society with compelling, believable human interactions.
That’s the conclusion of six computer scientists from Stanford University and Google Research who designed a Sims-like environment to observe the daily routines of inhabitants of an AI-generated virtual town.