LiGO is a new machine-learning technique developed by MIT researchers that cuts by about 50 percent the computational cost required to train large vision and language models.

When pondering the probability of discovering technologically advanced extraterrestrial life, the question that often arises is, if they’re out there, why h…

“AlphaFold was a huge advance in protein structure prediction. We were inspired by the advances they made, which led to a whole new wave of using deep learning,” said Professor David Baker, a biochemist and computational biologist at the University of Washington.
“The advantage of ESMFold is that it is very fast, and so can be used to predict the structures of a larger set of proteins than AlphaFold, albeit with slightly lower accuracy, similar to that of RoseTTAFold,” Dr. Baker said, referring to a tool that emerged from his lab in 2021.
DeepMind open-sourced the code for AlphaFold2, making it freely available to the community. Nearly all proteins known to science—about 214 million—can be looked up in the public AlphaFold Protein Structure Database. Meta’s ESM Metagenomic Atlas includes 617 million proteins.
A leading neuroscientist claims that a pong-playing clump of about a million neurons is “sentient”. What does that mean? Why did they teach a lab-grown brain to play pong? To study biological self-organization at the root of life, intelligence, and consciousness. And, according to their website, “to see what happens.”
CORRECTIONS/Clarifications:
- The cells aren’t directly frozen in liquid nitrogen — they are put in vials and stored in liquid nitrogen: https://www.atcc.org/products/pcs-201-010
- The sentience of some invertebrates, like octopuses, is generally agreed upon. Prominent scientists affirmed non-human consciousness in the Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness: https://philiplow.foundation/consciousness/
DISCLAIMER: The explanations in this video are those proposed by the researchers, or my opinion. We are far from understanding how brains, or even neurons, work. The free energy principle is one of many potential explanations.
Support the channel: https://www.patreon.com/IhmCurious.
Footage from Cortical Labs: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=neV3aZtTgVM
NASJAQ’s interview with founder Hon Weng Chong: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y1R5k5QWPsY
Cortical Labs website: https://corticallabs.com.
Full paper on DishBrain: https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(22)00806-6
Stanford’s Alpaca AI performs similarly to the astonishing ChatGPT on many tasks – but it’s built on an open-source language model and cost less than US$600 to train up. It seems these godlike AIs are already frighteningly cheap and easy to replicate.
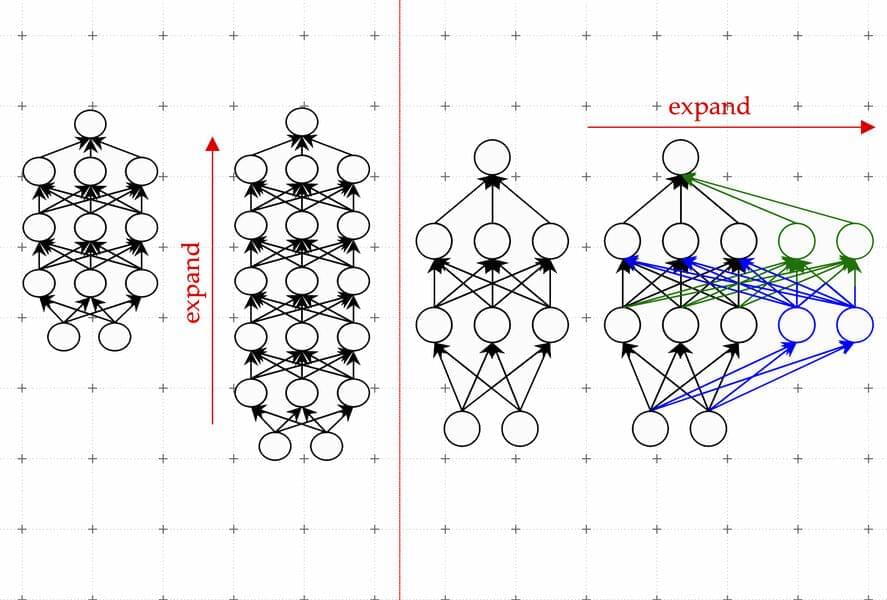
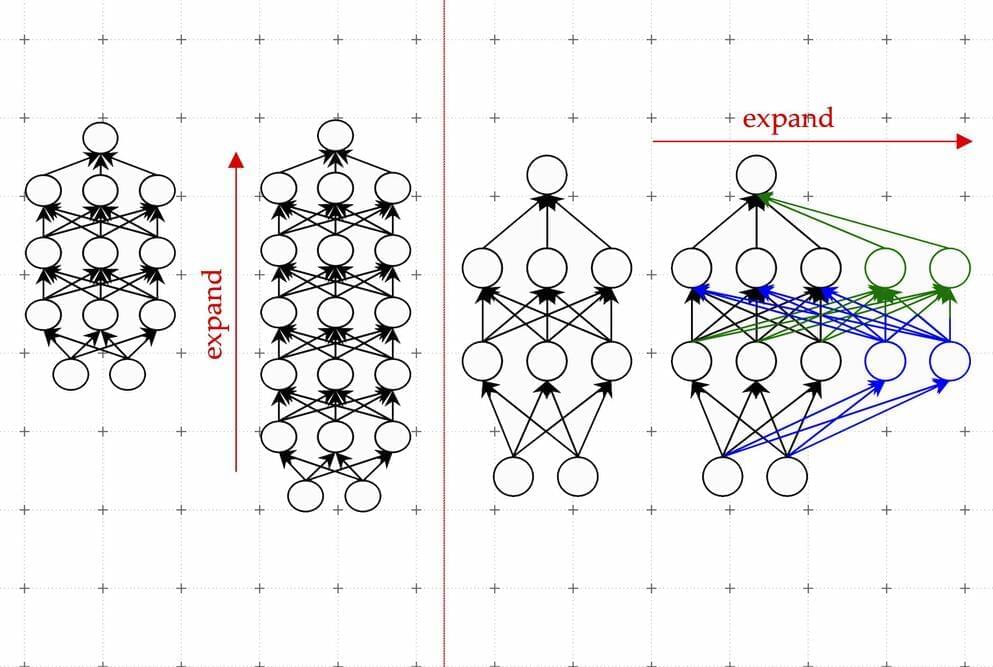
It’s no secret that OpenAI’s ChatGPT has some incredible capabilities—for instance, the chatbot can write poetry that resembles Shakespearean sonnets or debug code for a computer program. These abilities are made possible by the massive machine-learning model that ChatGPT is built upon. Researchers have found that when these types of models become large enough, extraordinary capabilities emerge.
But bigger models also require more time and money to train. The training process involves showing hundreds of billions of examples to a model. Gathering so much data is an involved process in itself. Then come the monetary and environmental costs of running many powerful computers for days or weeks to train a model that may have billions of parameters.
“It’s been estimated that training models at the scale of what ChatGPT is hypothesized to run on could take millions of dollars, just for a single training run. Can we improve the efficiency of these training methods, so we can still get good models in less time and for less money? We propose to do this by leveraging smaller language models that have previously been trained,” says Yoon Kim, an assistant professor in MIT’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and a member of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL).

Presented by Intel.
Every day around the world, companies leverage artificial intelligence to accelerate scientific discovery, and transform consumer and business services. Regrettably, the employment of AI is not occurring evenly. McKinsey’s ‘The State of AI in 2022’ report documents that adoption of AI by organizations has stalled at 50%. AI leaders are pulling ahead of the pack. One reason is 53% of AI projects fail to get to production. As the benefits of AI to everyone are too great and the issues with AI being in the hands of only a few are too concerning, that it is an opportune time to survey the challenges of going from concept to deployment.

Chipmaker Nvidia has announced a new service that will allow users to access supercomputer level computing power from web browsers. The service, called Nvidia DGX Cloud, is an AI supercomputing service that allows enterprises to run workloads on the company’s A100 and H100 chips remotely.
“DGX Cloud provides dedicated clusters of NVIDIA DGX AI supercomputing, paired with NVIDIA AI software. The service makes it possible for every enterprise to access its own AI supercomputer using a simple web browser, removing the complexity of acquiring, deploying and managing on-premises infrastructure,” the company said in a blog post.
As reported by Reuters, however, the service isn’t cheap. Nvidia is charging $37,000 per month for access to eight of the A100 or H100 chips — the company’s flagship chips, which are both designed for AI computing. “Each instance of DGX Cloud features eight Nvidia H100 or A100 80GB Tensor Core GPUs for a total of 640GB of GPU memory per node. A high-performance, low-latency fabric built with Nvidia Networking ensures workloads can scale across clusters of interconnected systems, allowing multiple instances to act as one massive GPU to meet the performance requirements of advanced AI training,” Nvidia’s blog post explained.

GitHub Copilot is also coming to pull requests to help developers create AI-generated descriptions. Tags are automatically completed by GitHub Copilot based on what code has changed, and developers can then review and edit them.
“At GitHub we invented the pull request over a decade ago, so the natural next step for us was to bring Copilot into the pull request,” says Dohmke. “You can actually ask Copilot to describe the pull request to you, or you can ask Copilot to generate tests.”
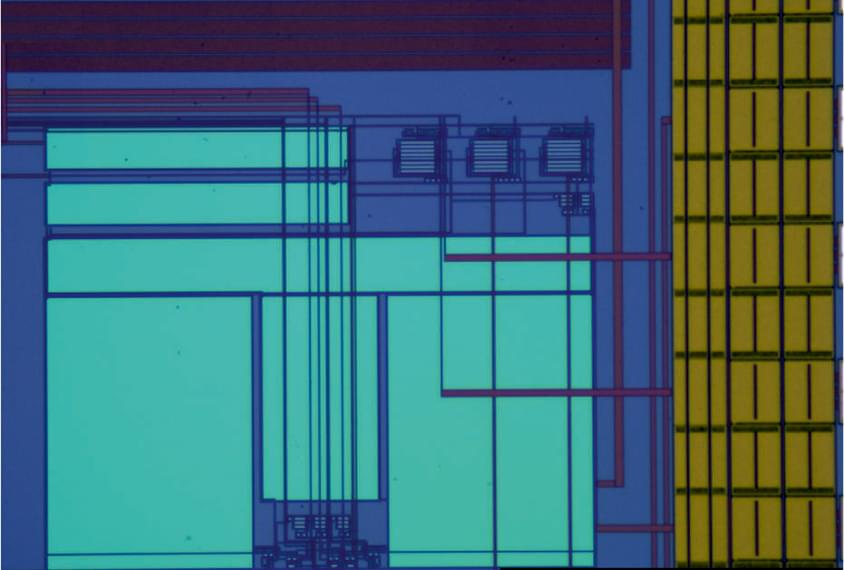
Electronic neurons made from silicon mimic brain cells and could be used to treat autism1.
Researchers plan to use the technology in conjunction with machine learning to retrain damaged or atypical neurons and restore function in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease, autism or other conditions.
Another team attempted to make artificial neurons in 2015 from a conductive organic chemical, but that version oversimplified brain signaling and was too large to implant in a human brain2.