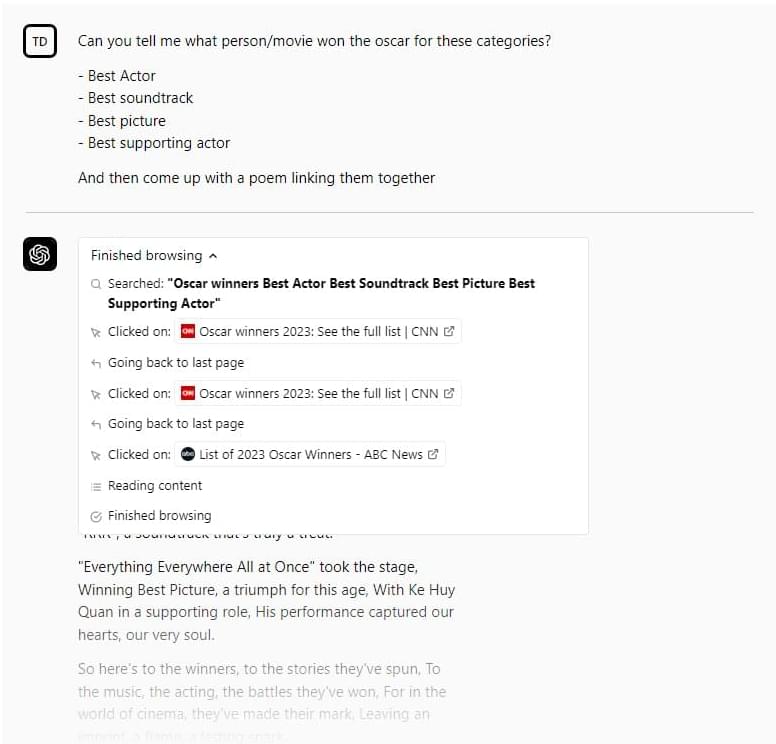
OpenAI’s viral AI-powered chatbot, ChatGPT, can now browse the internet — in certain cases. OpenAI today launched plugins for ChatGPT, which extend the bot’s functionality by granting it access to third-party knowledge sources and databases, including the web. Available in alpha to ChatGPT users and developers on the waitlist, OpenAI says that it’ll initially prioritize a small number of developers and subscribers to its premium ChatGPT Plus plan before rolling out larger-scale and API access.
OpenAI today launched plugins for ChatGPT, which extend the bot’s functionality by granting it access to third-party knowledge sources and databases, including the web. Available in alpha to ChatGPT users and developers on the waitlist, OpenAI says that it’ll initially prioritize a small number of developers and subscribers to its premium ChatGPT Plus plan before rolling out larger-scale and API access.
Easily the most intriguing plugin is OpenAI’s first-party web-browsing plugin, which allows ChatGPT to draw data from around the web to answer the various questions posed to it. (Previously, ChatGPT’s knowledge was limited to dates, events and people prior to around September 2021.) The plugin retrieves content from the web using the Bing search API and shows any websites it visited in crafting an answer, citing its sources in ChatGPT’s responses.