Apple’s new Vision Pro headset can scan a user’s face and use advanced machine learning to create a photorealistic “Persona” of them for video calls. And in a future visionOS update, these avatars will become even more realistic.


Imagine building a billion-dollar company that competes with the biggest companies in the industry, and doing it with a modest 3 person team powered by AI.
We’re living through a time of rapid change and endless possibilities and opportunities, what are you going to do about it?
While the fear of AI has a lot of people scrambling, anxious, or in denial about the implications of AI in their life and ability to earn a living and provide for their families, there are people like Peter Diamandis, Salim Ismail, and Tom Bilyeu that are going to leverage AI to the max to create a massive impact. Peter Diamondis and Salim Ismail have co-authored the book Exponential Organizations 2.0 where they break down the framework and key differences to exponential growth and success between Fortune 500 companies and some of the most successful unicorn companies of our time.
The Honda Riding Assist is an electric vehicle that has a low center-of-gravity and a very low seat height. In a global debut at CES, Honda unveiled the Honda Riding Assist motorcycle, which leverages our robotics technology to create a self-balancing motorcycle that greatly reduces the possibility of failing over while the motorcycle is at rest.
source/image: Alpha SQUAD official.

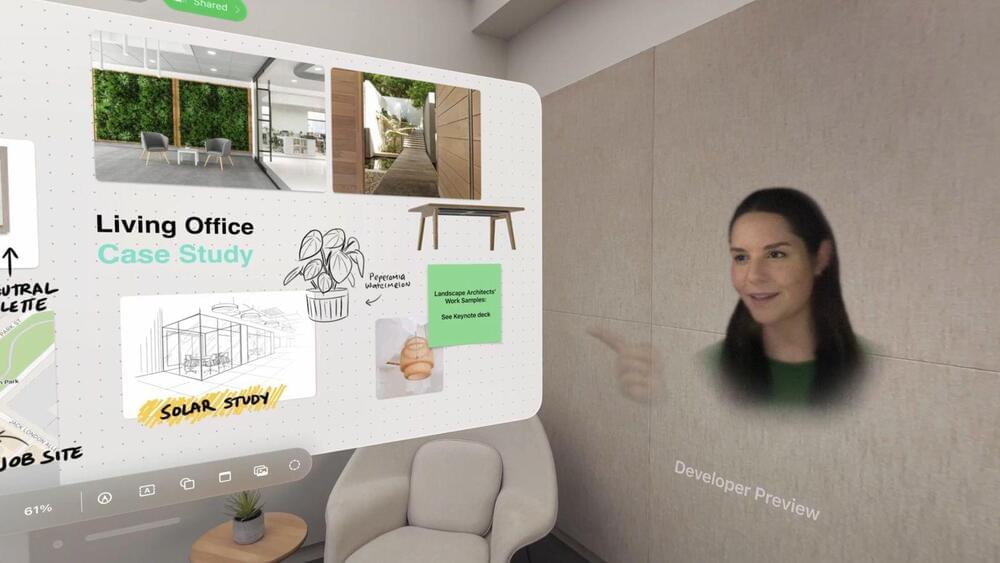
The current education landscape requires close collaboration between edtech and AI developers to leverage their expertise and maximize the impact of AI technology in the sector. It also aims to avoid the negative consequences of redundant efforts, wasted resources and less effective solutions. By effectively applying best practices such as clear communication, alignment of goals, and interdisciplinary collaboration, edtech and AI developers can develop innovative, scalable and effective solutions. The “AI and the Future of Learning: Expert Panel Report” underscores key strategies for successful collaboration between edtech and AI developers. The report highlights key strengths and weaknesses of AI as well as the respective opportunities and barriers to employing AI technologies in the education sector.
Education plays a critical role in promoting social and economic development in a region, and when communities recognize its potential, they are more likely to support educational reforms. These reforms can address any challenges in the sector, such as funding constraints, lack of access to quality education and cultural attitudes that may deny education to particular groups. With the increased adoption of AI in the education sector, potential future developments—including ITS, adaptive assessment, gamification and the use of machine learning—can promote the efficiency of personalized learning.
In the long run, the collaboration between edtech and AI developers holds great potential for transforming education and improving learning outcomes. For this to happen, it is necessary to establish industry standards for AI in education, foster interdisciplinary collaboration between educators and AI experts, and invest in research on AI’s impact on learning outcomes. In this way, we can ensure that AI-powered tools are used effectively and ethically to improve student learning in the 21st century.

Former Google engineer and esteemed futurist Ray Kurzweil has made another bold prediction: Immortality is within reach for humans by 2030, thanks to the help of nanorobots. You read that right — humans could potentially live forever, according to Kurzweil.
Kurzweil, who has a track record of accurate predictions such as foreseeing a computer beating humans in chess by 2000, shared his prediction in a recent YouTube series by tech vlogger Adagio. The 75-year-old computer scientist believes that advancements in genetics, robotics and nanotechnology will allow tiny robots to run through veins, repairing any damage and keeping people alive indefinitely.
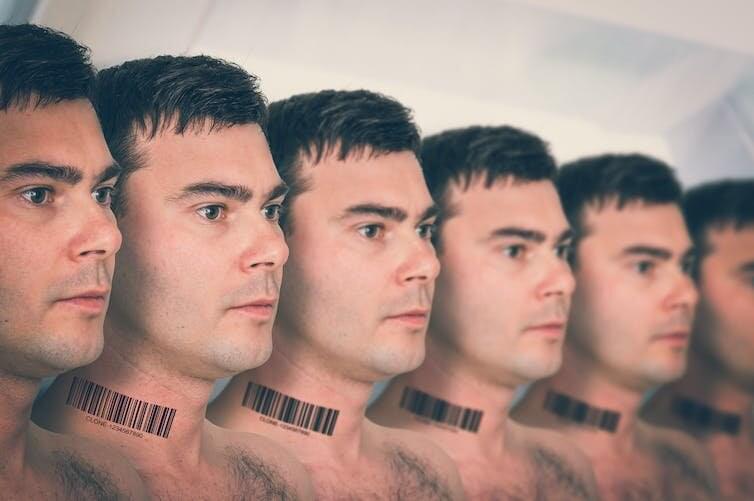

Imagine, if you will, a digital doppelgänger. A clone that looks, talks and behaves just like you, created from the depths of artificial intelligence, reflecting your every mannerism with eerie precision. As thrilling as it might sound, how would you feel about it?
Our research at the University of British Columbia turns the spotlight onto this very question. With advancements in deep-learning technologies such as interactive deepfake applications, voice conversion and virtual actors, it’s possible to digitally replicate an individual’s appearance and behavior.
This mirror image of an individual created by artificial intelligence is referred to as an “AI clone.” Our study dives into the murky waters of what these AI clones could mean for our self-perception, relationships and society. In our paper published as part of the Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, we identified three types of risks posed by AI replicas: doppelgänger-phobia, identity fragmentation and living memories.
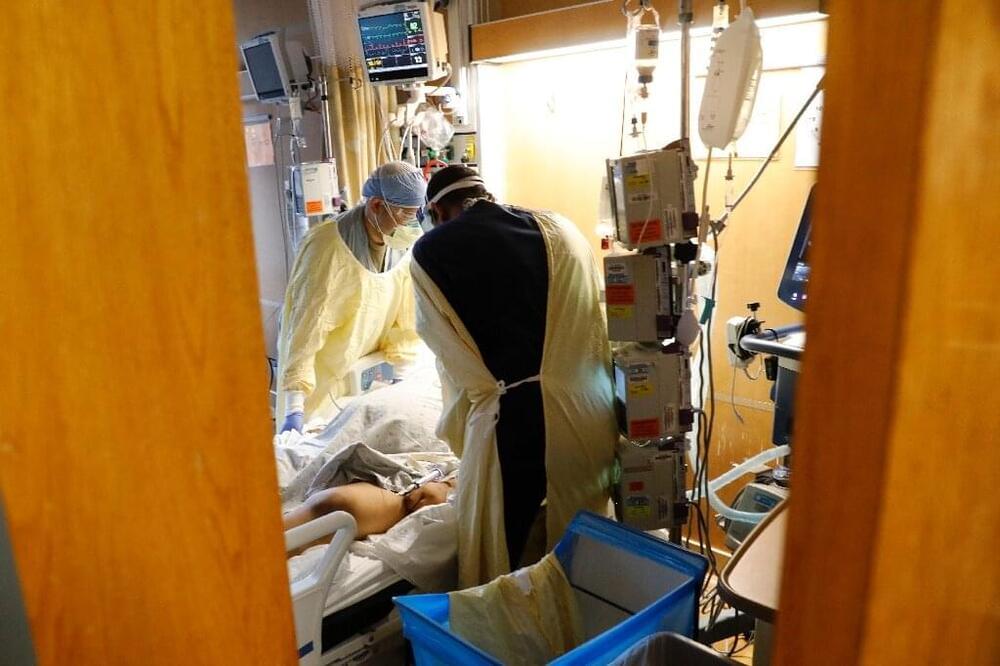
Artificial intelligence has proven itself useful in reading medical imaging and even shown it can pass doctors’ licensing exams.
Now, a new AI tool has demonstrated the ability to read physicians’ notes and accurately anticipate patients’ risk of death, readmission to hospital, and other outcomes important to their care.
Designed by a team at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the software is currently in use at the university’s affiliated hospitals throughout New York, with the hope that it will become a standard part of health care.
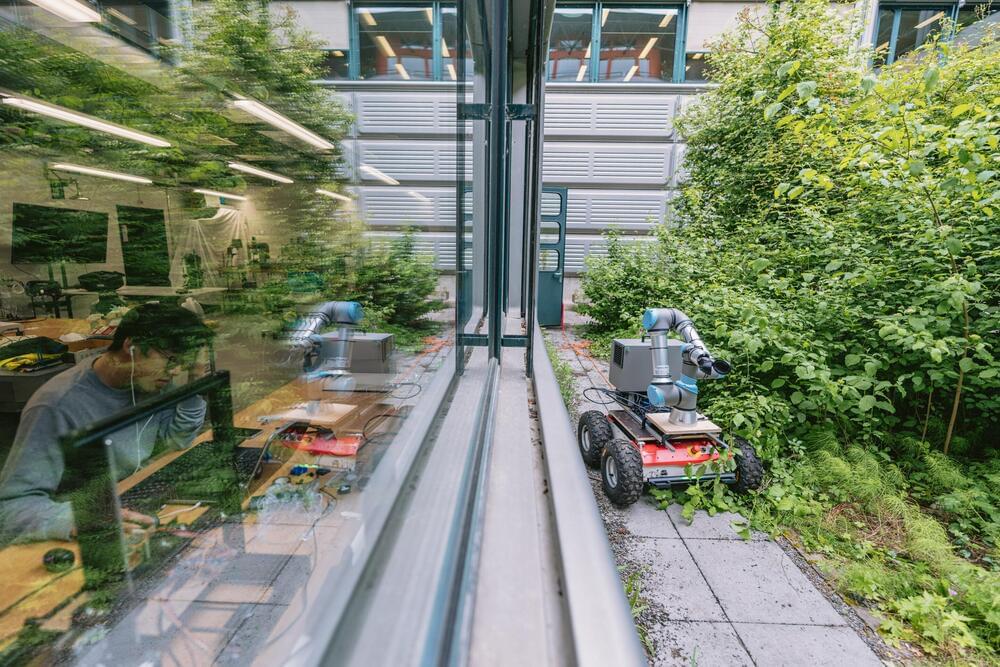

Poems, essays and even books—is there anything the open AI platform ChatGPT can’t handle? These new AI developments have inspired researchers at TU Delft and the Swiss technical university EPFL to dig a little deeper: For instance, can ChatGPT also design a robot? And is this a good thing for the design process, or are there risks? The researchers published their findings in Nature Machine Intelligence.
What are the greatest future challenges for humanity? This was the first question that Cosimo Della Santina, assistant professor, and Ph.D. student Francesco Stella, both from TU Delft, and Josie Hughes from EPFL, asked ChatGPT.
“We wanted ChatGPT to design not just a robot, but one that is actually useful,” says Della Santina. In the end, they chose food supply as their challenge, and as they chatted with ChatGPT, they came up with the idea of creating a tomato-harvesting robot.

“It’s an interesting new approach,” says Peter Sanders, who studies the design and implementation of efficient algorithms at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany and who was not involved in the work. “Sorting is still one of the most widely used subroutines in computing,” he says.
DeepMind published its results in Nature today. But the techniques that AlphaDev discovered are already being used by millions of software developers. In January 2022, DeepMind submitted its new sorting algorithms to the organization that manages C++, one of the most popular programming languages in the world, and after two months of rigorous independent vetting, AlphaDev’s algorithms were added to the language. This was the first change to C++’s sorting algorithms in more than a decade and the first update ever to involve an algorithm discovered using AI.
Ray Kurzweil is known for making predictions in technology that have come true — and now he is sure humans will reach immortality in our lifetime. He also explains how robots will make it happen.