It’s not easy to impress the world’s fourth richest person. But Gates is calling this breakthrough ‘the big thing.’



Meta this week showcased its work on new generative AI technologies for its consumer products, including Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger, as well as those being used internally at the company. At an all-hands meeting, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg announced several AI technologies in various stages of development, including AI chatbots for Messenger and WhatsApp, AI stickers, and other tools that would allow photo editing in Instagram Stories, in addition to internal-only products, like an AI productivity assistant and an experimental interface for interacting with AI agents, powered by Meta’s large language model LLaMA.
Axios had first reported the news of the consumer-facing AI agents and photo-editing tools, specifically. But the larger presentation touched on a number of areas where Meta is developing AI technologies and commentary about where it sees this space going.
In addition, the company announced it’s planning to host an internal AI hackathon in July focused on generative AI, which could result in new AI products that eventually make their way to Meta’s users.
New technologies will be able to wrap around legacy bank systems and create a new layer of data attribution, ushering in a modern era for accounting and business finance.
AI-enabled accounting takes a proactive approach to processing financial information. This means reducing the likelihood of errors, ensuring greater consistency across the ledger and allowing continuous data monitoring.
Where once bad or missing transaction information led to messy books and uninformed business decisions, advances in AI can now use context clues to categorize transactions accurately from the outset—getting us to a world where transactions can actually be “self-documenting.” This will make accountants’ and business owners’ lives easier while improving overall operating efficiencies.

Enter Kim’s class, 2.74 (Bio-Inspired Robotics).
According to Kim, researchers need to understand this cognitive bias, this tendency toward anthropomorphism, in order to even begin developing robots that can help humans with their physical movements. While Kim’s research interest is in building robots that could help people, such as the elderly in an aging population with fewer young people to perform services, such advancement is not even possible without understanding biology, biomechanics, and how much we don’t understand about our own everyday movements.
“One big thing students should learn in this class is not necessarily to understand how we move our body but the fact that we don’t understand how we move,” Kim says. “One of our ultimate goals in robotics is to develop robots that help elderly people by mimicking how we use our arms and legs, but if you don’t realize how little we know about how we move, we cannot even start tackling this problem.”

Google announced the general availability (GA) of generative AI services based on Vertex AI, the Machine Learning Platform as a Service (ML PaaS) offering from Google Cloud. With the service becoming GA, enterprises and organizations could integrate the platform’s capabilities with their applications.
With this update, developers can use several new tools and models, such as the world completion model driven by PaLM 2, the Embeddings API for text, and other foundation models in the Model Garden. They can also leverage the tools available within the Generative AI Studio to fine-tune and deploy customized models. Google claims that enterprise-grade data governance, security, and safety features are also built into the Vertex AI platform. This provides confidence to customers in consuming the foundation models, customizing them with their own data, and building generative AI applications.
Customers can use the Model Garden to access and evaluate base models from Google and its partners. There are over 60 models, with pals for adding newer models in the future. Also, the Codey model for code completion, code generation, and chat, announced at the Google I/O conference in May, is now available for public preview.
The future of artificial intelligence and video games with their relation to simulation theory, and whether or not we may already be in a virtual world controlled by some other form of intelligence.
Deep Learning AI Specialization: https://imp.i384100.net/GET-STARTED
AI Marketplace: https://taimine.com/
AI news timestamps:
0:00 AI simulation theory intro.
0:59 The rise.
1:25 Controversies.
1:52 Full immersion.
2:22 The new era.
2:41 Bio activation.
5:54 Multi level simulation.
6:22 Beyond.
#ai #future #technology

Since I don’t work for any large companies involved in AI, nor do I anticipate ever doing so; and considering that I have completed my 40-year career (as an old man-now succesfully retired), I would like to share a video by someone I came across during my research into “True Open Source AI.”
I completely agree with the viewpoints expressed in this video (of which begins at ~ 4 mins into the video after technical matters). Additionally, I would like to add some of my own thoughts as well.
We need open source alternatives to large corporations so that people (that’s us humans) have options for freedom, and personal privacy when it comes to locally hosted AIs. The thought of a world completely controlled by Big Corp AI is even more frightening than George Orwell’s “Big Brother.” I believe there must be an alternative to this nightmarish scenario.
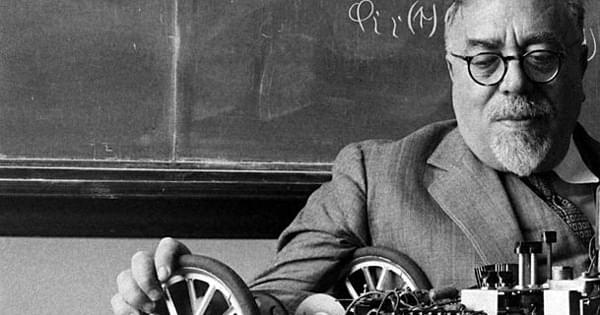
“Intelligence supposes goodwill,” Simone de Beauvoir wrote in the middle of the twentieth century. In the decades since, as we have entered a new era of technology risen from our minds yet not always consonant with our values, this question of goodwill has faded dangerously from the set of considerations around artificial intelligence and the alarming cult of increasingly advanced algorithms, shiny with technical triumph but dull with moral insensibility.
In De Beauvoir’s day, long before the birth of the Internet and the golden age of algorithms, the visionary mathematician, philosopher, and cybernetics pioneer Norbert Wiener (November 26, 1894–March 18, 1964) addressed these questions with astounding prescience in his 1954 book The Human Use of Human Beings, the ideas in which influenced the digital pioneers who shaped our present technological reality and have recently been rediscovered by a new generation of thinkers eager to reinstate the neglected moral dimension into the conversation about artificial intelligence and the future of technology.
A decade after The Human Use of Human Beings, Wiener expanded upon these ideas in a series of lectures at Yale and a philosophy seminar at Royaumont Abbey near Paris, which he reworked into the short, prophetic book God & Golem, Inc. (public library). Published by MIT Press in the final year of his life, it won him the posthumous National Book Award in the newly established category of Science, Philosophy, and Religion the following year.

