As the use of machine learning (ML) algorithms continues to grow, computer scientists worldwide are constantly trying to identify and address ways in which these algorithms could be used maliciously or inappropriately. Due to their advanced data analysis capabilities, in fact, ML approaches have the potential to enable third parties to access private data or carry out cyberattacks quickly and effectively.
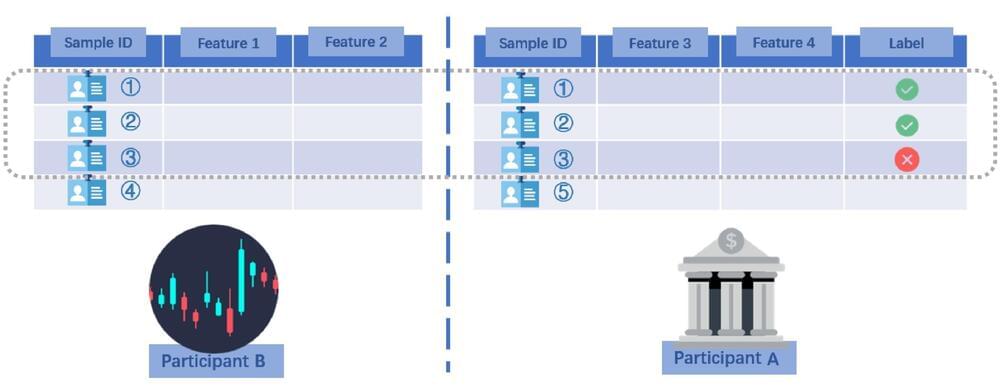
Morteza Varasteh, a researcher at the University of Essex in the U.K., has recently identified new type of inference attack that could potentially compromise confidential user data and share it with other parties. This attack, which is detailed in a paper pre-published on arXiv, exploits vertical federated learning (VFL), a distributed ML scenario in which two different parties possess different information about the same individuals (clients).
“This work is based on my previous collaboration with a colleague at Nokia Bell Labs, where we introduced an approach for extracting private user information in a data center, referred to as the passive party (e.g., an insurance company),” Varasteh told Tech Xplore. “The passive party collaborates with another data center, referred to as the active party (e.g., a bank), to build an ML algorithm (e.g., a credit approval algorithm for the bank).”