Did Google get scared of AI? Is that why Microsoft is now leading? 😃
Researchers developed a powerful chatbot years before rival ChatGPT went viral. After management stalled its release, they quit.

As the use of machine learning (ML) algorithms continues to grow, computer scientists worldwide are constantly trying to identify and address ways in which these algorithms could be used maliciously or inappropriately. Due to their advanced data analysis capabilities, in fact, ML approaches have the potential to enable third parties to access private data or carry out cyberattacks quickly and effectively.
Morteza Varasteh, a researcher at the University of Essex in the U.K., has recently identified new type of inference attack that could potentially compromise confidential user data and share it with other parties. This attack, which is detailed in a paper pre-published on arXiv, exploits vertical federated learning (VFL), a distributed ML scenario in which two different parties possess different information about the same individuals (clients).
“This work is based on my previous collaboration with a colleague at Nokia Bell Labs, where we introduced an approach for extracting private user information in a data center, referred to as the passive party (e.g., an insurance company),” Varasteh told Tech Xplore. “The passive party collaborates with another data center, referred to as the active party (e.g., a bank), to build an ML algorithm (e.g., a credit approval algorithm for the bank).”
To try everything Brilliant has to offer—free—for a full 30 days, visit http://brilliant.org/ArtemKirsanov/.
The first 200 of you will get 20% off Brilliant’s annual premium subscription.
My name is Artem, I’m a computational neuroscience student and researcher. In this video we talk about the concept of critical point – how the brain might optimize information processing by hovering near a phase transition.
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/artemkirsanov.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ArtemKRSV
OUTLINE:
00:00 Introduction.
01:11 — Phase transitions in nature.
05:05 — The Ising Model.
09:33 — Correlation length and long-range communication.
13:14 — Scale-free properties and power laws.
20:20 — Neuronal avalanches.
25:00 — The branching model.
31:05 — Optimizing information transmission.
34:06 — Brilliant.org.
35:41 — Recap and outro.
The book: https://mitpress.mit.edu/9780262544030/the-cortex-and-the-critical-point/
REFERENCES (in no particular order):
In recent years, the field of artificial intelligence has made tremendous strides, but what happens when #AI systems become #selfaware? In this video, we’ll explore the concept of AI self-awareness, its #scary implications for society, and what it means for the #future of AI.
AI self-awareness is the ability of an #artificialintelligence system to recognize its own existence and understand the consequences of its actions. While there are different levels of self-awareness that an AI system could potentially exhibit, it generally involves the system being able to recognize and respond to changes in its own state.
One way that researchers are exploring AI self-awareness is by using neural networks and other machine learning algorithms. For example, researchers have created AI systems that can recognize and respond to their own errors, which is an important first step in developing higher-order self-awareness.
#Kassandra #JoshBachynski, #aiscarystories #aihorrorstories #scarystories #scarystory #horrorstories #horrorstory #realstories #realhorrorstories #realscarystories #truestories #truestory #creapystories #AIScarystory #AIHorror #artificialintelligence #scaryai #scaryartificialintelligence #trueaiscarystories #truescarystories.
📺 Watch the entire video for more information!
🤖My channel:
(True) Scary AI Topics, AI disasters, AI Threats, Artificial Intelligence and other thrilling AI eventsevents.
Despite AI’s impressive track record, its computational power pales in comparison with a human brain. Now, scientists unveil a revolutionary path to drive computing forward: organoid intelligence, where lab-grown brain organoids act as biological hardware.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has long been inspired by the human brain. This approach proved highly successful: AI boasts impressive achievements – from diagnosing medical conditions to composing poetry. Still, the original model continues to outperform machines in many ways. This is why, for example, we can ‘prove our humanity’ with trivial image tests online. What if instead of trying to make AI more brain-like, we went straight to the source?
Scientists across multiple disciplines are working to create revolutionary biocomputers where three-dimensional cultures of brain cells, called brain organoids, serve as biological hardware. They describe their roadmap for realizing this vision in the journal Frontiers in Science.
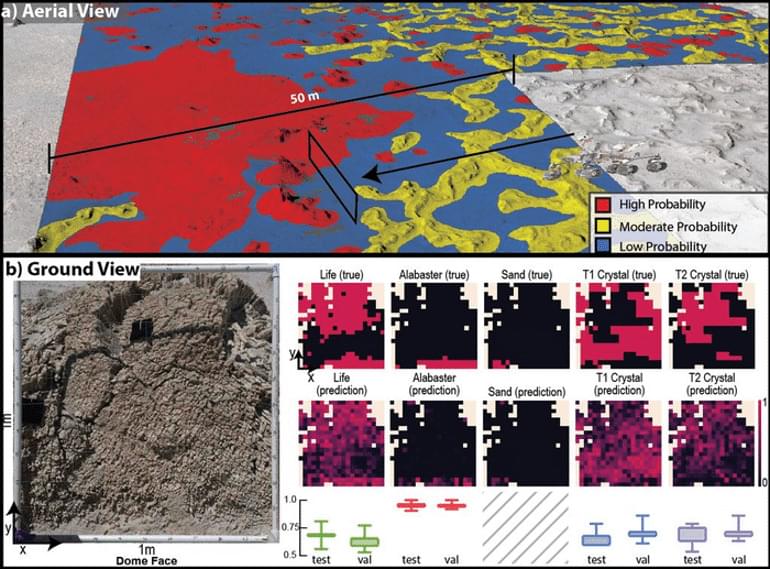
Summary: Scientists have developed a way to use artificial intelligence (AI) to find signs of life on other planets. They combined statistical ecology and machine learning to map the patterns and rules of how life survives in harsh environments on Earth, and then trained the AI to recognize those same patterns and rules in data from other planets. This method can help guide rovers and other exploration missions to places with the highest probability of containing life.
Source: SETI Institute.
Wouldn’t finding life on other worlds be easier if we knew exactly where to look? Researchers have limited opportunities to collect samples on Mars or elsewhere or access remote sensing instruments when hunting for life beyond Earth.
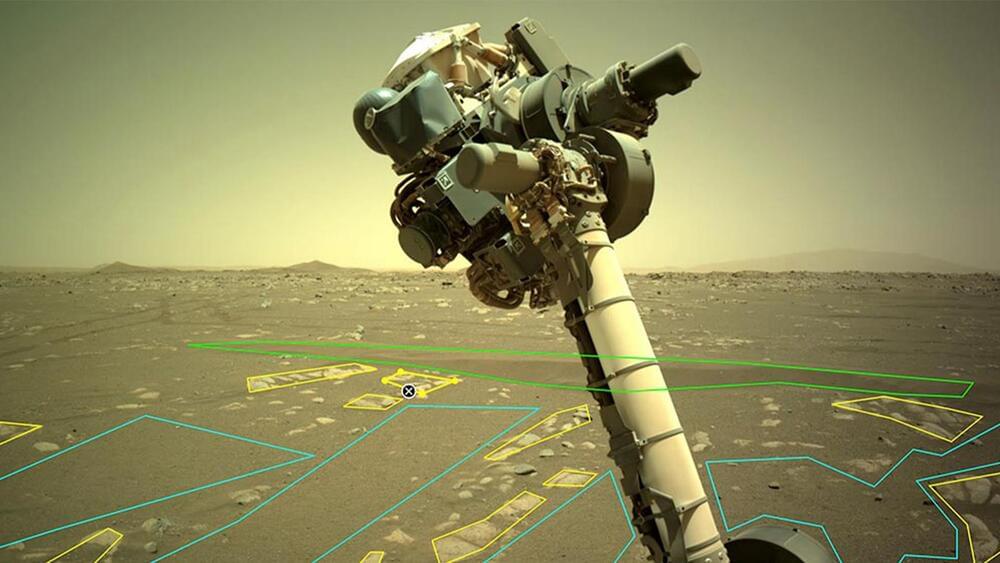
The development represents “an important advance in extraterrestrial research, in which biology has often lagged behind chemistry and geology.”
A new study has revealed a new way to enhance the search for aliens on Mars by teaching artificial intelligence to detect sites that could contain “biosignatures.”
And so, the researchers trained a deep learning framework to map biosignatures in a three-square-kilometer area of Chile’s Atacama Desert… More.
NASA/JPL-Caltech.
According to NASA, a biosignature is any “characteristic, element, molecule, substance, or feature that can be used as evidence for past or present life.” But before testing such a tool on Mars or other worlds, they need to be tested on Earth first.

Its based model performs better than state-of-the-art models available today.
Search giant Google has completed the ‘critical first step’ toward building its artificial intelligence (AI) model that will support the world’s one thousand most-spoken languages. In a blog post the company released details about its Universal Speech Model (USM).
Google’s announcement is part of the build-up to its annual I/O event where it plans to unveil a slew of products powered by AI.
400tmax/iStock.
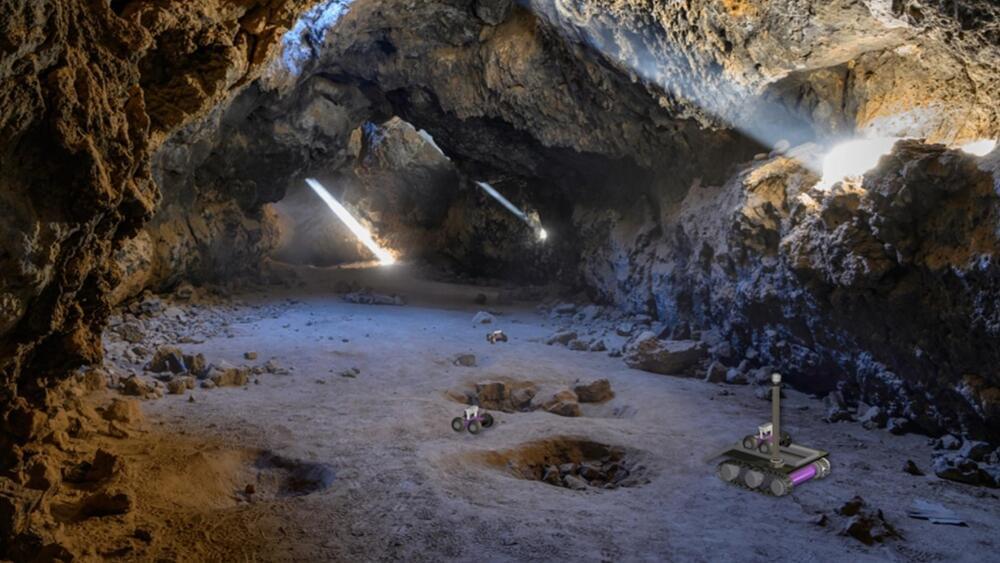

The robots contain miniaturized sensors which are deployed as they traverse a cave or other subsurface environment.
Life on Mars is closer than you think. And researchers at the University of Arizona College of Engineering are already scouting real estate and house hunting. Their helpers? A flock of robots that can explore the subsurface environments on other worlds.
“Lava tubes and caves would make perfect habitats for astronauts because you don’t have to build a structure; you are shielded from harmful cosmic radiation, so all you need to do is make it pretty and cozy,” said Wolfgang Fink, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at UArizona.
Fink and team have published a paper in Advances in Space Research that details a “communication network that would link rovers, lake landers, and even submersible vehicles through a so-called mesh topology network, allowing the machines to work together as a team, independently from human input,” according to a press release.
The new systems will complement teachers not replace them.
Artificial intelligence (AI) robots could soon be teaching in UAE classrooms, according to a report by the country’s The National published on Saturday.
This is according to comments made by the nation’s minister of education at an education conference.