Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained a lot of attention for their human-imitating properties. These models are capable of answering questions, generating content, summarizing long textual paragraphs, and whatnot. Prompts are essential for improving the performance of LLMs like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4. The way that prompts are created can have a big impact on an LLM’s abilities in a variety of areas, including reasoning, multimodal processing, tool use, and more. These techniques, which researchers designed, have shown promise in tasks like model distillation and agent behavior simulation.
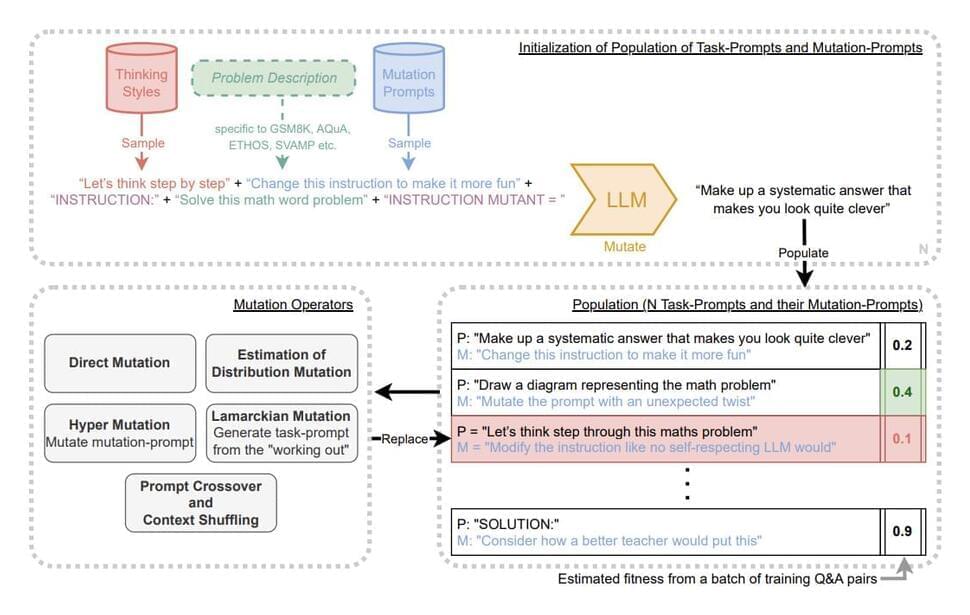
The manual engineering of prompt approaches raises the question of whether this procedure can be automated. By producing a set of prompts based on input-output instances from a dataset, Automatic Prompt Engineer (APE) made an attempt to address this, but APE had diminishing returns in terms of prompt quality. Researchers have suggested a method based on a diversity-maintaining evolutionary algorithm for self-referential self-improvement of prompts for LLMs to overcome decreasing returns in prompt creation.
LLMs can alter their prompts to improve their capabilities, just as a neural network can change its weight matrix to improve performance. According to this comparison, LLMs may be created to enhance both their own capabilities and the processes by which they enhance them, thereby enabling Artificial Intelligence to continue improving indefinitely. In response to these ideas, a team of researchers from Google DeepMind has introduced PromptBreeder (PB) in recent research, which is a technique for LLMs to better themselves in a self-referential manner.