With the pace at which artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications are ramping up, we can expect to see industries and companies use these systems and tools in everyday processes. As these data-intensive applications continue to grow in complexity, the demand for high-speed transmission and efficient communication between computing units becomes paramount.
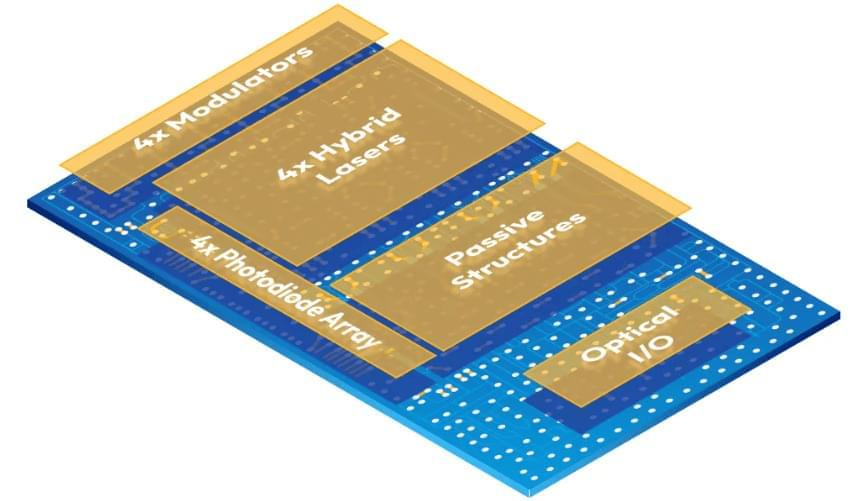
This need has sparked interest in optical interconnects, particularly in the context of short-reach connections between XPUs (CPUs, GPUs and memory). Silicon photonics is emerging as a promising technology that improves performance, cost-efficiency and thermal-management capabilities that ultimately improve the function of AI/ML applications compared with traditional approaches.
The key to getting the most out of artificial intelligence may lie in the use of silicon photonics, a powerful new tech.